Task 3: Perform OS Discovery using Unicornscan
Task 3: Perform OS Discovery using Unicornscan
Unicornscan is a Linux-based command line-oriented network information-gathering and reconnaissance tool. It is an asynchronous TCP and UDP port scanner and banner grabber that enables you to discover open ports, services, TTL values, etc. running on the target machine. In Unicornscan, the OS of the target machine can be identified by observing the TTL values in the acquired scan result.
Here, we will use the Unicornscan tool to perform OS discovery on the target system.
Click Parrot Security to switch to the Parrot Security machine.
Click the MATE Terminal icon at the top of the Desktop window to open a Terminal window.
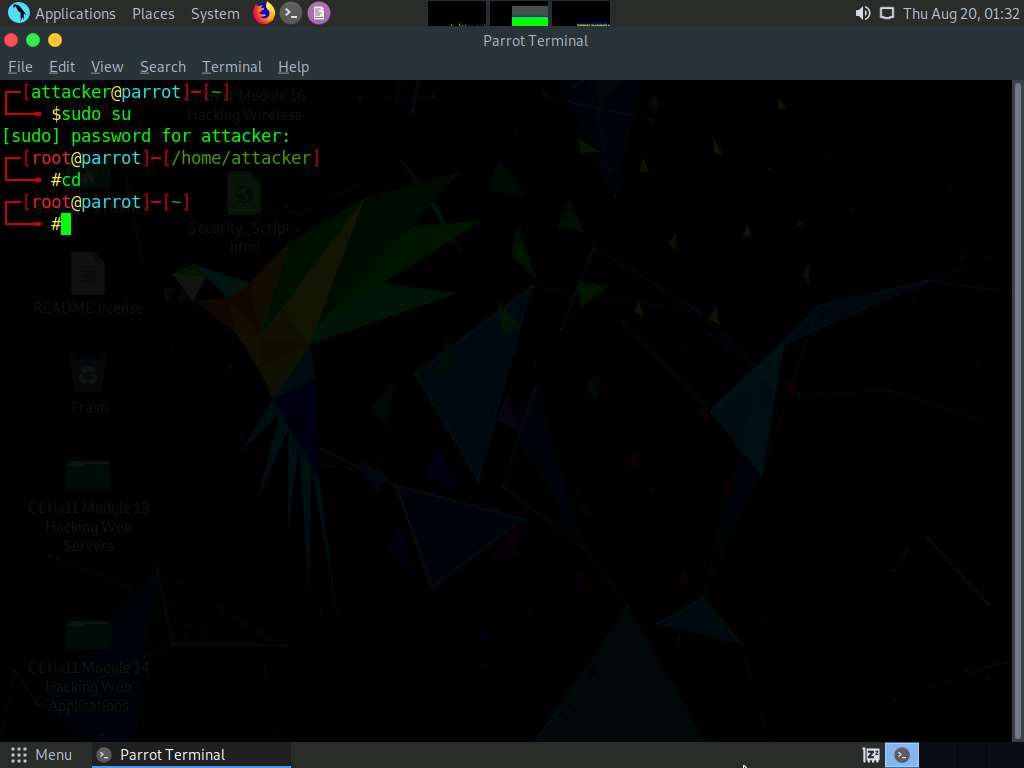
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type sudo su and press Enter to run the programs as a root user.
In the [sudo] password for attacker field, type toor as a password and press Enter.
The password that you type will not be visible.
Now, type cd and press Enter to jump to the root directory.
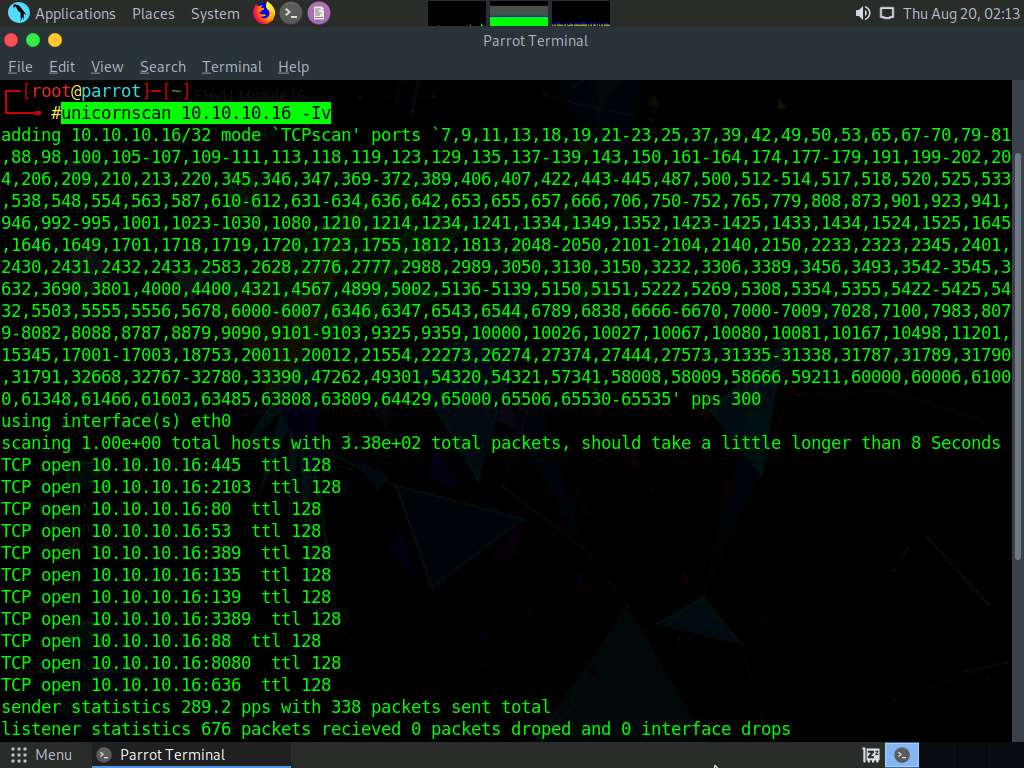
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type unicornscan [Target IP Address] -Iv (here, the target machine is Windows Server 2016 [10.10.10.16]) and press Enter.
In this command, -I specifies an immediate mode and v specifies a verbose mode.
The scan results appear, displaying the open TCP ports along with the obtained TTL value of 128. As shown in the screenshot, the ttl values acquired after the scan are 128; hence, the OS is possibly Microsoft Windows (Windows 7/8/8.1/10 or Windows Server 2008/12/16).
Here, the target machine is Windows Server 2016 (10.10.10.16).
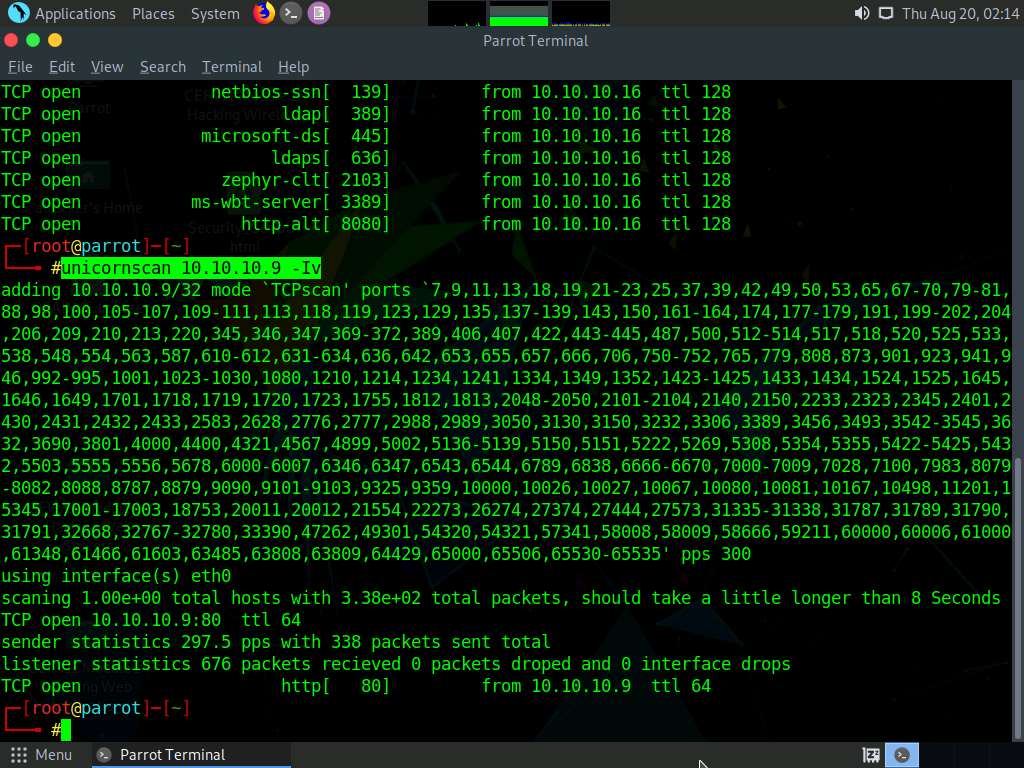
In the Parrot Terminal window, type unicornscan [Target IP Address] -Iv (here, the target machine is Ubuntu [10.10.10.9]) and press Enter.
The scan results appear, displaying the open TCP ports along with a TTL value of 64. As shown in the screenshot, the ttl value acquired after the scan is 64; hence, the OS is possibly a Linux-based machine (Google Linux, Ubuntu, Parrot, or Kali).
This concludes the demonstration of discovering the OS of the target machine using Unicornscan.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Comments
Post a Comment