Lab 4: Scan beyond IDS and Firewall
Lab 4: Scan beyond IDS and Firewall
Module 03: Scanning Networks
Lab 4: Scan beyond IDS and Firewall
https://ciphertm.blogspot.com/2021/03/lab-4-scan-beyond-ids-and-firewall.html
sudo su
cd
nmap -f [Target IP Address]
-f switch is used to split the IP packet into tiny fragment packets.
nmap -g 80 [Target IP Address]
-g or --source-port option to perform source port manipulation.
nmap -mtu 8 [Target IP Address]
-mtu: specifies the number of Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) (here, 8 bytes of packets).
nmap -D RND:10 [Target IP Address]
-D: performs a decoy scan and RND: generates a random and non-reserved IP addresses.
Lab Scenario
As a professional ethical hacker or a pen tester, the next step after discovering the OS of the target IP address(es) is to perform network scanning without being detected by the network security perimeters such as the firewall and IDS. IDSs and firewalls are efficient security mechanisms; however, they still have some security limitations. You may be required to launch attacks to exploit these limitations using various IDS/firewall evasion techniques such as packet fragmentation, source routing, IP address spoofing, etc. Scanning beyond the IDS and firewall allows you to evaluate the target network’s IDS and firewall security.
Lab Objectives
- Scan beyond IDS/firewall using various evasion techniques
- Create custom packets using Colasoft Packet Builder to scan beyond the IDS/firewall
- Create custom UDP and TCP packets using Hping3 to scan beyond the IDS/firewall
- Create custom packets using Nmap to scan beyond the IDS/firewall
Overview of Scanning beyond IDS and Firewall
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and firewall are the security mechanisms intended to prevent an unauthorized person from accessing a network. However, even IDSs and firewalls have some security limitations. Firewalls and IDSs intend to avoid malicious traffic (packets) from entering into a network, but certain techniques can be used to send intended packets to the target and evade IDSs/firewalls.
Techniques to evade IDS/firewall:
- Packet Fragmentation: Send fragmented probe packets to the intended target, which re-assembles it after receiving all the fragments
- Source Routing: Specifies the routing path for the malformed packet to reach the intended target
- Source Port Manipulation: Manipulate the actual source port with the common source port to evade IDS/firewall
- IP Address Decoy: Generate or manually specify IP addresses of the decoys so that the IDS/firewall cannot determine the actual IP address
- IP Address Spoofing: Change source IP addresses so that the attack appears to be coming in as someone else
- Creating Custom Packets: Send custom packets to scan the intended target beyond the firewalls
- Randomizing Host Order: Scan the number of hosts in the target network in a random order to scan the intended target that is lying beyond the firewall
- Sending Bad Checksums: Send the packets with bad or bogus TCP/UPD checksums to the intended target
- Proxy Servers: Use a chain of proxy servers to hide the actual source of a scan and evade certain IDS/firewall restrictions
- Anonymizers: Use anonymizers that allow them to bypass Internet censors and evade certain IDS and firewall rules
Task 1: Scan beyond IDS/Firewall using various Evasion Techniques
Nmap offers many features to help understand complex networks with enabled security mechanisms and supports mechanisms for bypassing poorly implemented defenses. Using Nmap, various techniques can be implemented, which can bypass the IDS/firewall security mechanisms.
Here, we will use Nmap to evade IDS/firewall using various techniques such as packet fragmentation, source port manipulation, MTU, and IP address decoy.
Click Windows 10 to switch to the Windows 10 machine.
Navigate to Control Panel --> System and Security --> Windows Defender Firewall --> Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off, enable Windows Defender Firewall and click OK, as shown in the screenshot.
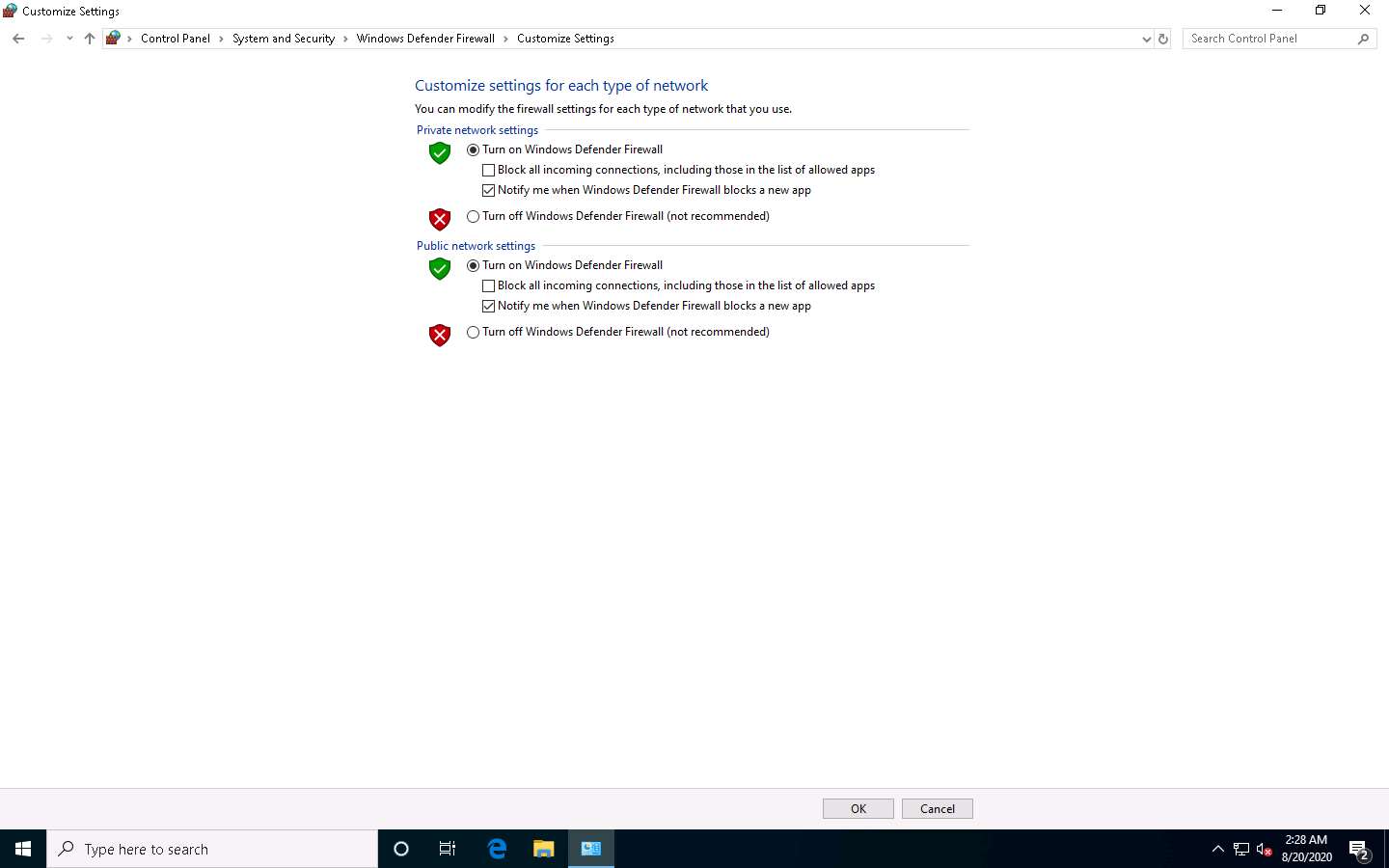
Minimize the Control Panel window, navigate to the Desktop and double-click Wireshark shortcut.
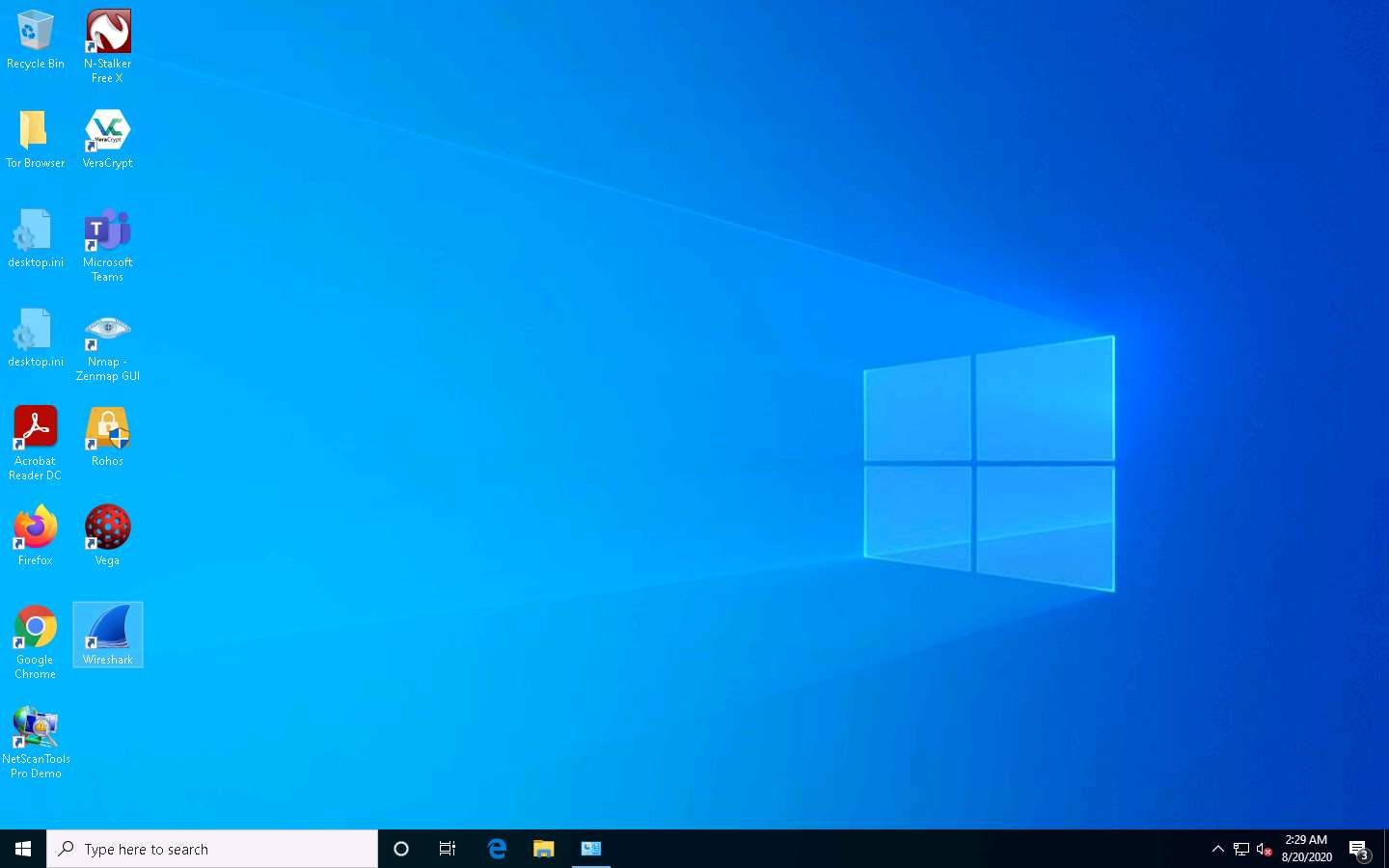
The Wireshark Network Analyzer window appears, Start capturing packets by double-clicking the available ethernet or interface (here, Ethernet2).
If Software Update window appears, click Remind me later.
Click Parrot Security to switch to the Parrot Security machine.
Click the MATE Terminal icon in the top-left corner of the Desktop window to open a Terminal window.
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type sudo su and press Enter to run the programs as a root user.
In the [sudo] password for attacker field, type toor as a password and press Enter.
The password that you type will not be visible.
Now, type cd and press Enter to jump to the root directory.
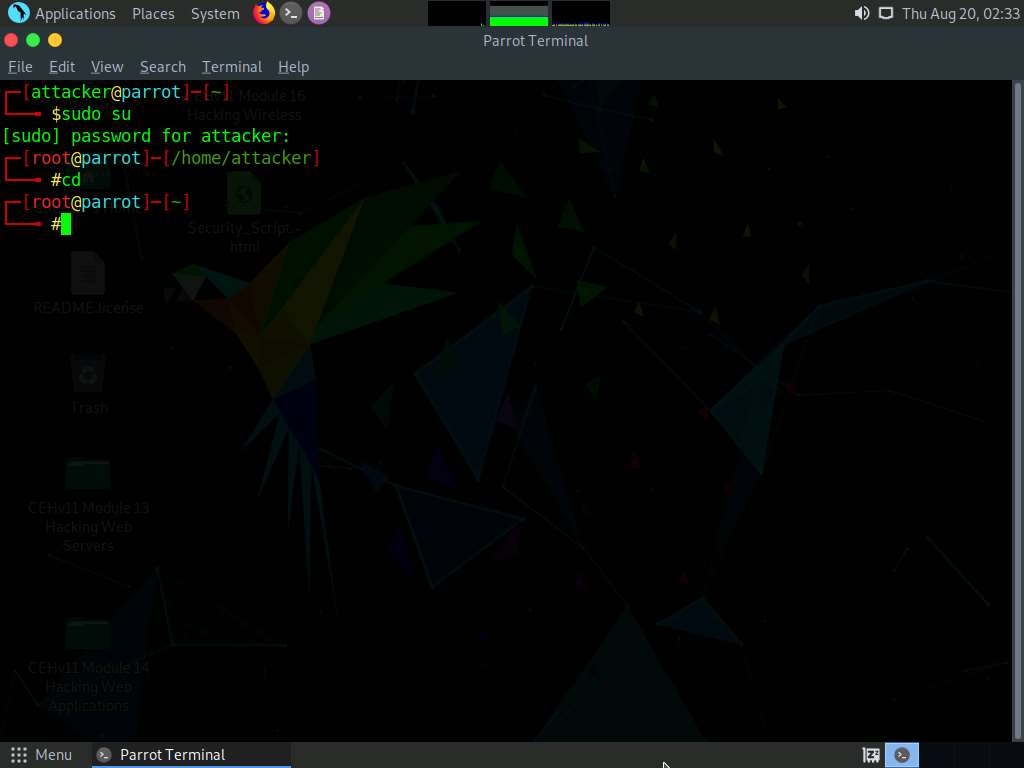
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type nmap -f [Target IP Address], (here, the target machine is Windows 10 [10.10.10.10]) and press Enter.
-f switch is used to split the IP packet into tiny fragment packets.
Packet fragmentation refers to the splitting of a probe packet into several smaller packets (fragments) while sending it to a network. When these packets reach a host, IDSs and firewalls behind the host generally queue all of them and process them one by one. However, since this method of processing involves greater CPU consumption as well as network resources, the configuration of most of IDSs makes it skip fragmented packets during port scans.
Although Windows Defender Firewall is turned on in the target system (here, Windows 10), you can still obtain the results displaying all open TCP ports along with the name of services running on the ports, as shown in the screenshot.
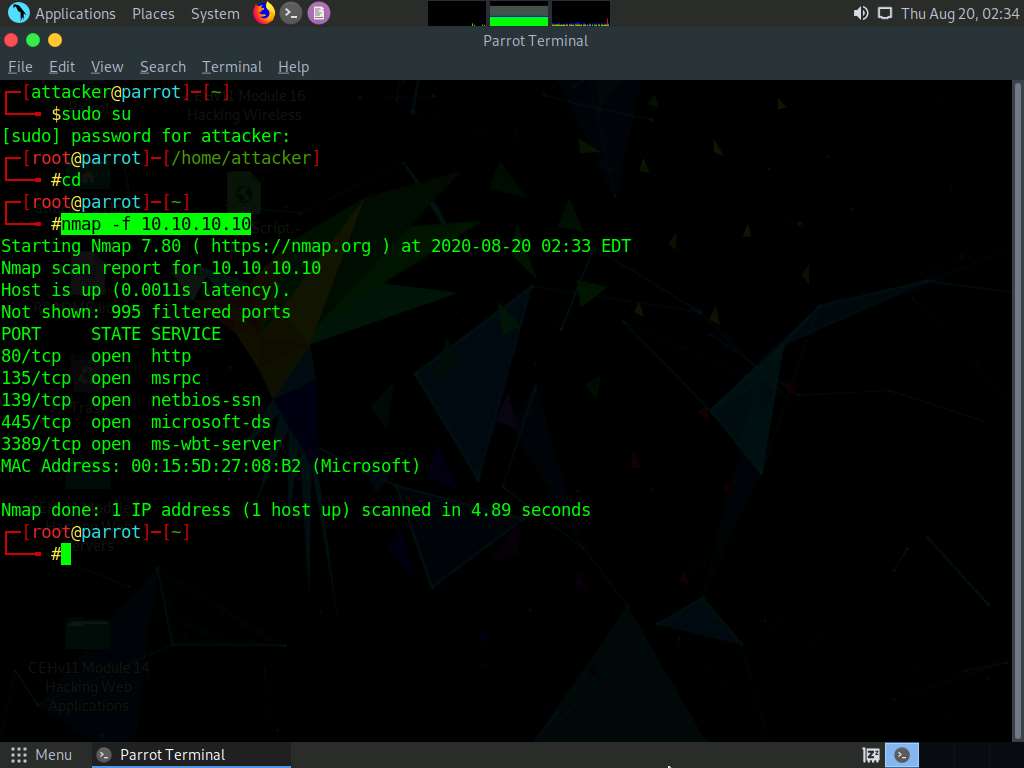
In the Parrot Terminal window, type nmap -g 80 [Target IP Address], (here, target IP address is 10.10.10.10) and press Enter.
In this command, you can use the -g or --source-port option to perform source port manipulation.
Source port manipulation refers to manipulating actual port numbers with common port numbers to evade IDS/firewall: this is useful when the firewall is configured to allow packets from well-known ports like HTTP, DNS, FTP, etc.
The results appear, displaying all open TCP ports along with the name of services running on the ports, as shown in the screenshot.
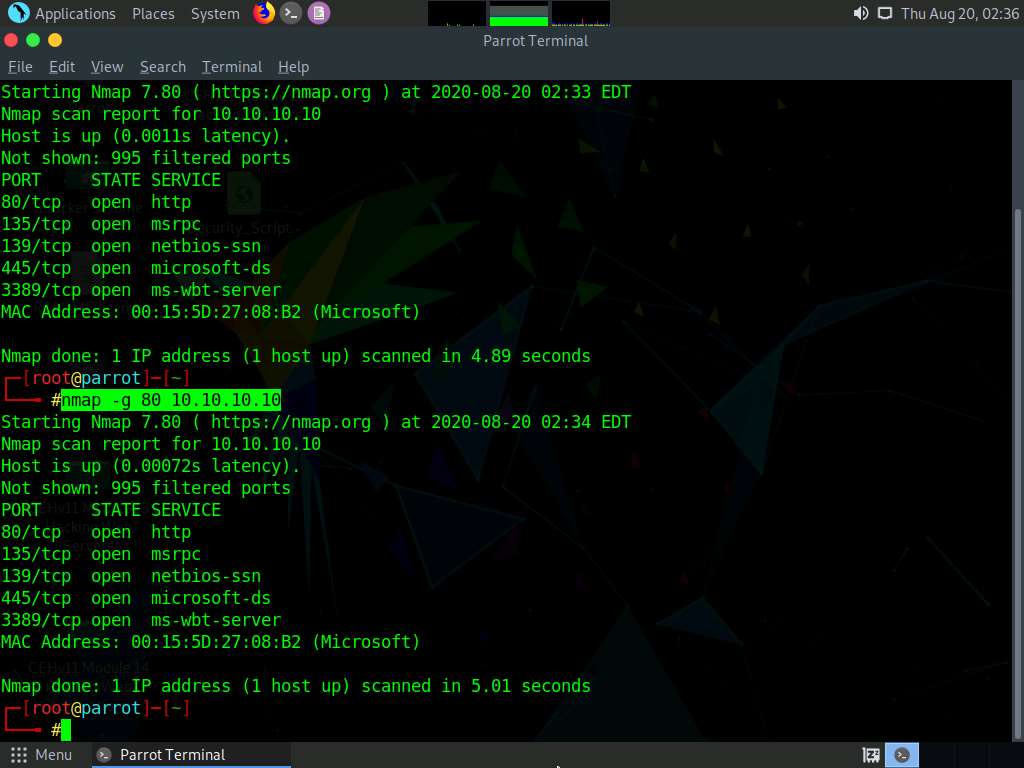
Now, type nmap -mtu 8 [Target IP Address] (here, target IP address is 10.10.10.10) and press Enter.
In this command, -mtu: specifies the number of Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) (here, 8 bytes of packets).
Using MTU, smaller packets are transmitted instead of sending one complete packet at a time. This technique evades the filtering and detection mechanism enabled in the target machine.
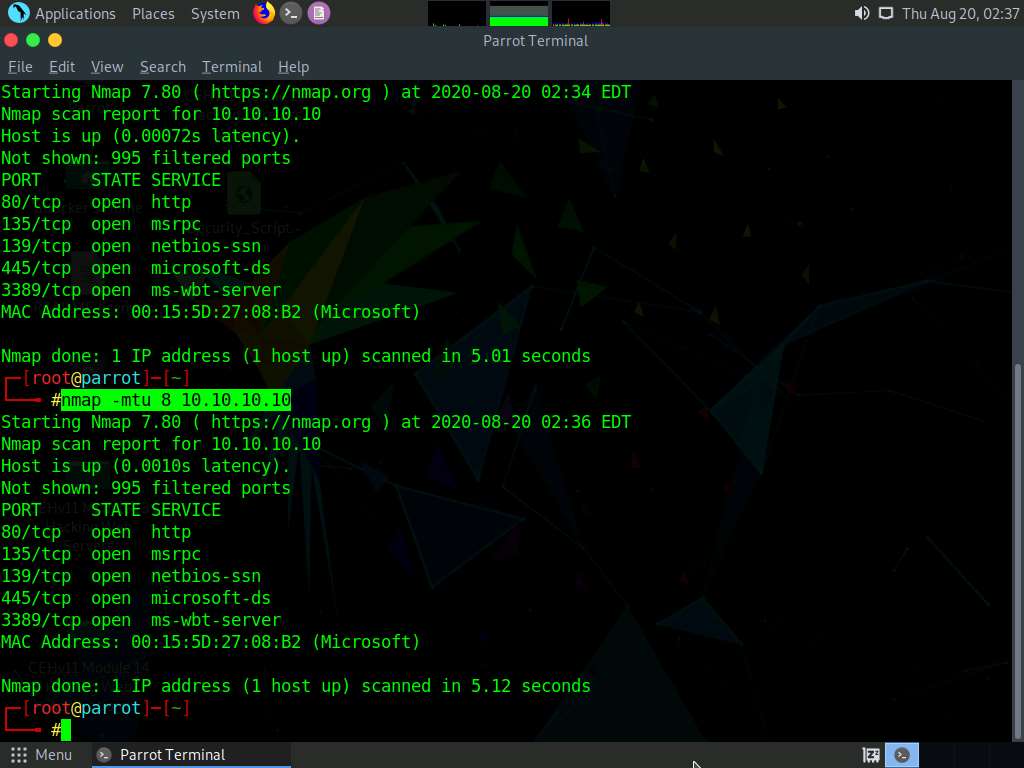
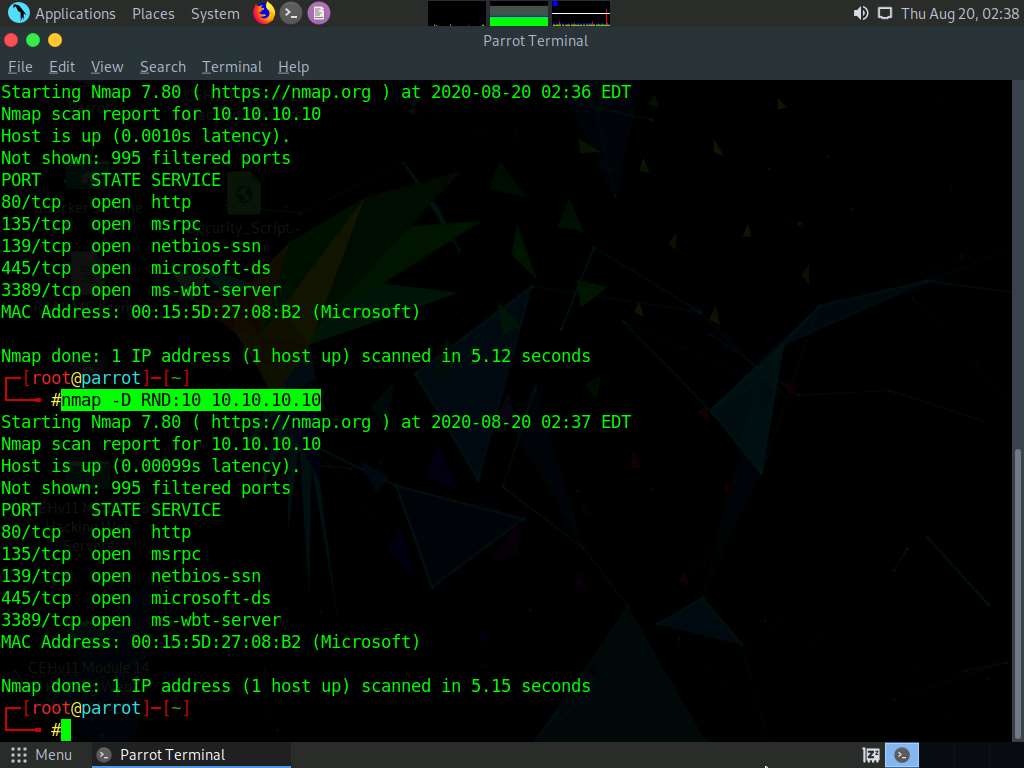
Now, type nmap -D RND:10 [Target IP Address] (here, target IP address is 10.10.10.10) and press Enter.
In this command, -D: performs a decoy scan and RND: generates a random and non-reserved IP addresses.
The IP address decoy technique refers to generating or manually specifying IP addresses of the decoys to evade IDS/firewall. This technique makes it difficult for the IDS/firewall to determine which IP address was actually scanning the network and which IP addresses were decoys. By using this command, Nmap automatically generates a random number of decoys for the scan and randomly positions the real IP address between the decoy IP addresses.
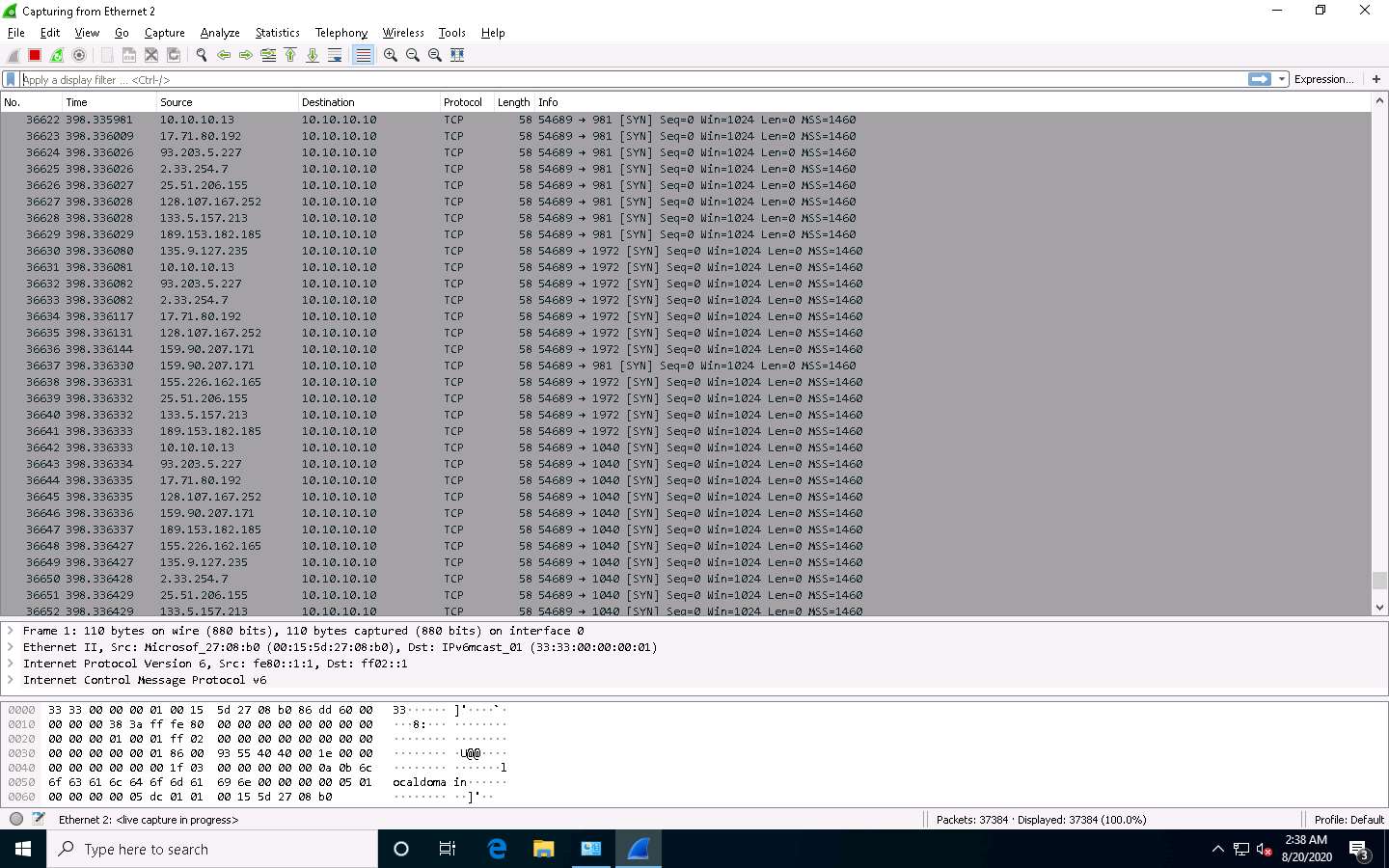
Now, click Windows 10 to switch to the Windows 10 machine (target machine) and observe packets captured by Wireshark, which displays the multiple IP addresses in the source section, as shown in the screenshot.
This concludes the demonstration of evading IDS and firewall using various evasion techniques in Nmap.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Comments
Post a Comment