Lab 2: Perform Wireless Attacks
Lab 2: Perform Wireless Attacks
Lab 2: Perform Wireless Attacks
Task 1: Crack a WEP network using Aircrack-ng
on desktop for this lab there is a file on the desktop
CEHv11 Module 16 Hacking Wireless Networks folder and copy Sample Captures and Wordlist folders.
paste the files sample captures and wordlist to desktop
terminal
sudo su
cd
aircrack-ng '/home/attacker/Desktop/Sample Captures/WEPcrack-01.cap
Task 2: Crack a WPA2 Network using Aircrack-ng this is if you have the BSSID of the device
follow task 1 if needed to put files on desktop
type in terminal:
aircrack-ng -a2 -b [Target BSSID] -w /home/attacker/Desktop/Wordlist/password.txt '/home/attacker/Desktop/Sample Captures/WPA2crack-01.cap'
the BSSID in this case is 20:E5:2A:E4:38:00
make sure command is exact or it wont work had lots of troubles
aircrack-ng -a2 -b [Target BSSID] -w /home/attacker/Desktop/Wordlist/password.txt '/home/attacker/Desktop/Sample Captures/WPA2crack-01.cap'
results appear showing key found with the password
Lab Scenario
As an expert ethical hacker or pen tester, you must have the required knowledge to perform wireless attacks in order to test the target network’s security infrastructure.
After performing the discovery, mapping, and analysis of the target wireless network, you have gathered enough information to launch an attack. You should now carry out various types of attacks on the target network, including Wi-Fi encryption cracking (WEP, WPA, and WPA2), fragmentation, MAC spoofing, DoS, and ARP poisoning attacks.
WEP encryption is used for wireless networks, but it has several exploitable vulnerabilities. When seeking to protect a wireless network, the first step is always to change your SSID from the default before you actually connect the wireless router to the access point. Moreover, if an SSID broadcast is not disabled on an access point, ensure that you do not use a DHCP server, which would automatically assign IP addresses to wireless clients. This is because war-driving tools can easily detect your internal IP address.
As an ethical hacker and pen tester of an organization, you must test its wireless security, exploit WEP flaws, and crack the network’s access point keys.
The labs in this exercise demonstrate how to perform wireless attacks using various hacking tools and techniques.
Lab Objectives
- Crack a WEP network using Aircrack-ng
- Crack a WPA2 network using Aircrack-ng
Overview of Wireless Attacks
There are several different types of Wi-Fi attacks that attackers use to eavesdrop on wireless network connections in order to obtain sensitive information such as passwords, banking credentials, and medical records, as well as to spread malware.
These include:
Fragmentation attack: When successful, such attacks can obtain 1,500 bytes of PRGA (pseudo random generation algorithm)
MAC spoofing attack: The attacker changes their MAC address to that of an authenticated user in order to bypass the access point’s MAC-filtering configuration
Disassociation attack: The attacker makes the victim unavailable to other wireless devices by destroying the connectivity between the access point and client
Deauthentication attack: The attacker floods station(s) with forged deauthentication packets to disconnect users from an access point
Man-in-the-middle attack: An active Internet attack in which the attacker attempts to intercept, read, or alter information between two computers
Wireless ARP poisoning attack: An attack technique that exploits the lack of a verification mechanism in the ARP protocol by corrupting the ARP cache maintained by the OS in order to associate the attacker’s MAC address with the target host
Rogue access points: Wireless access points that an attacker installs on a network without authorization and that are not under the management of the network administrator
Evil twin: A fraudulent wireless access point that pretends to be a legitimate access point by imitating another network name
Wi-Jacking attack: A method used by attackers to gain access to an enormous number of wireless networks
Task 1: Crack a WEP network using Aircrack-ng
Aircrack-ng is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP, and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless networks. The program runs on both Linux and Windows.
In this task, we will use the Aircrack-ng suite to crack the WEP encryption of a network.
In order to capture wireless traffic, a wireless adapter is required and using an adapter in the iLabs environment is not possible, therefore, in this lab, we are using a sample capture file (WEPcrack-01.cap) to crack WEP key.
Click Parrot Security to switch to the Parrot Security machine.
In the login page, the attacker username will be selected by default. Enter password as toor in the Password field and press Enter to log in to the machine.
Navigate to the Places in the top-section of the window nd click Desktop from the drop-down list.
If a Question pop-up window appears asking you to update the machine, click No to close the window.
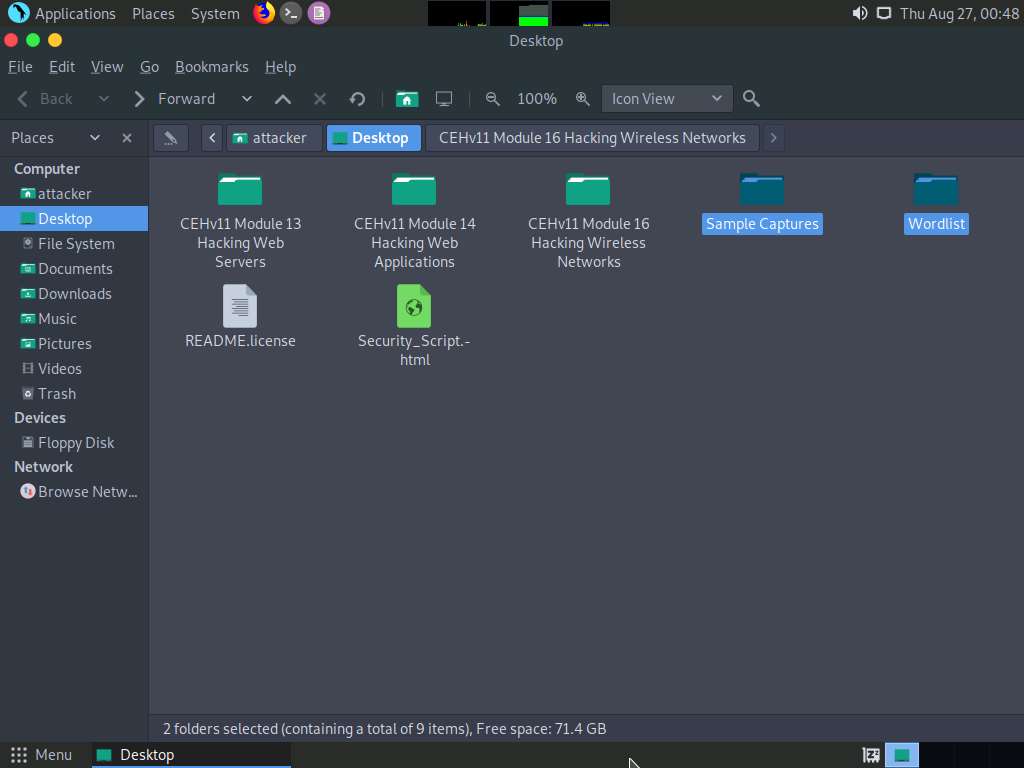
The Desktop window appears, navigate to the CEHv11 Module 16 Hacking Wireless Networks folder and copy Sample Captures and Wordlist folders.
To copy the folders, firstly select both the folders and then press Ctrl+C.
Now, navigate to the Desktop and press Ctrl+V to paste the copied folders (Sample Captures and Wordlist). Close the Desktop window.
Click the MATE Terminal icon at the top of the Desktop window to open a Terminal window.
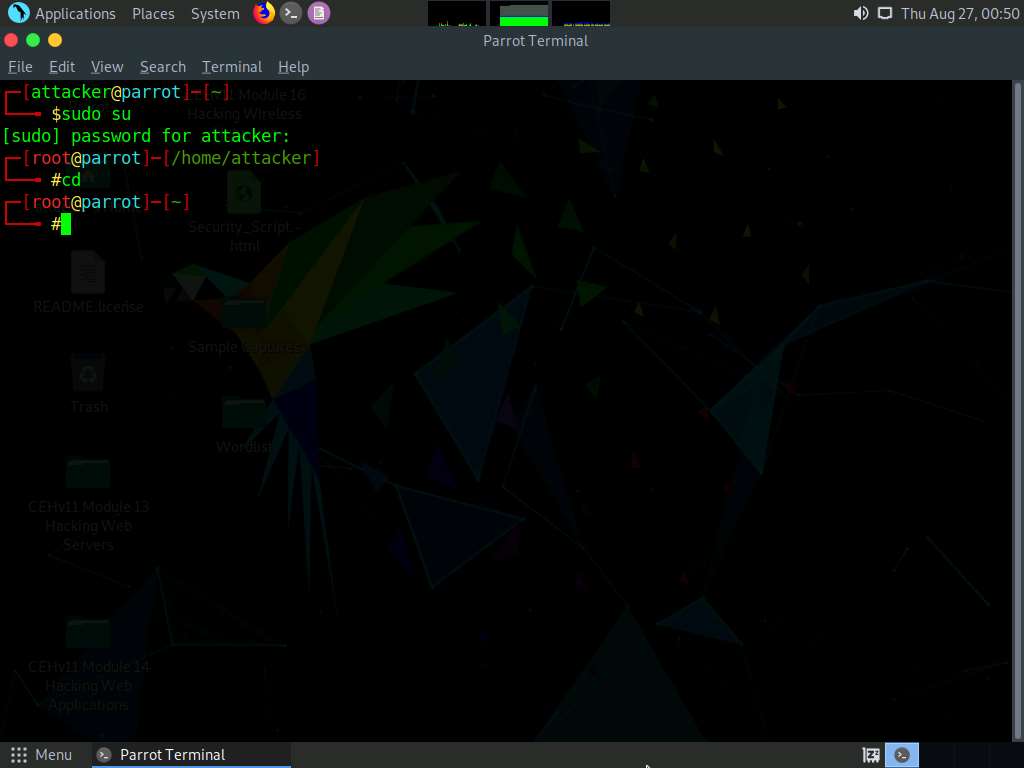
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type sudo su and press Enter to run the programs as a root user.
In the [sudo] password for attacker field, type toor as a password and press Enter.
The password that you type will not be visible.
Now, type cd and press Enter to jump to the root directory.
In the Parrot Terminal window, type aircrack-ng '/home/attacker/Desktop/Sample Captures/WEPcrack-01.cap' and press Enter.
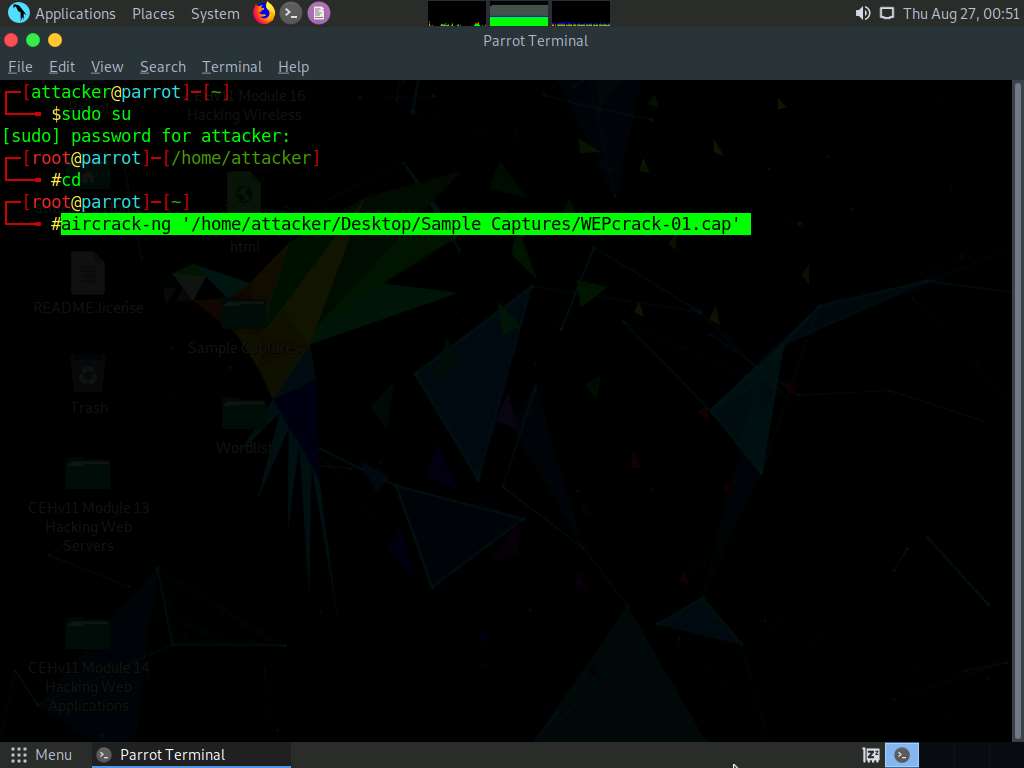
By issuing the above command aircrack-ng will crack the WEP key of the CEHLabs as shown in the screenshot.
In real-life attacks, attackers will use this key to connect to the access point and joint the target network. Once they enter the target network, they can use scanning tools to scan for open devices, perform a vulnerability analysis, and then start exploiting any vulnerabilities they find.
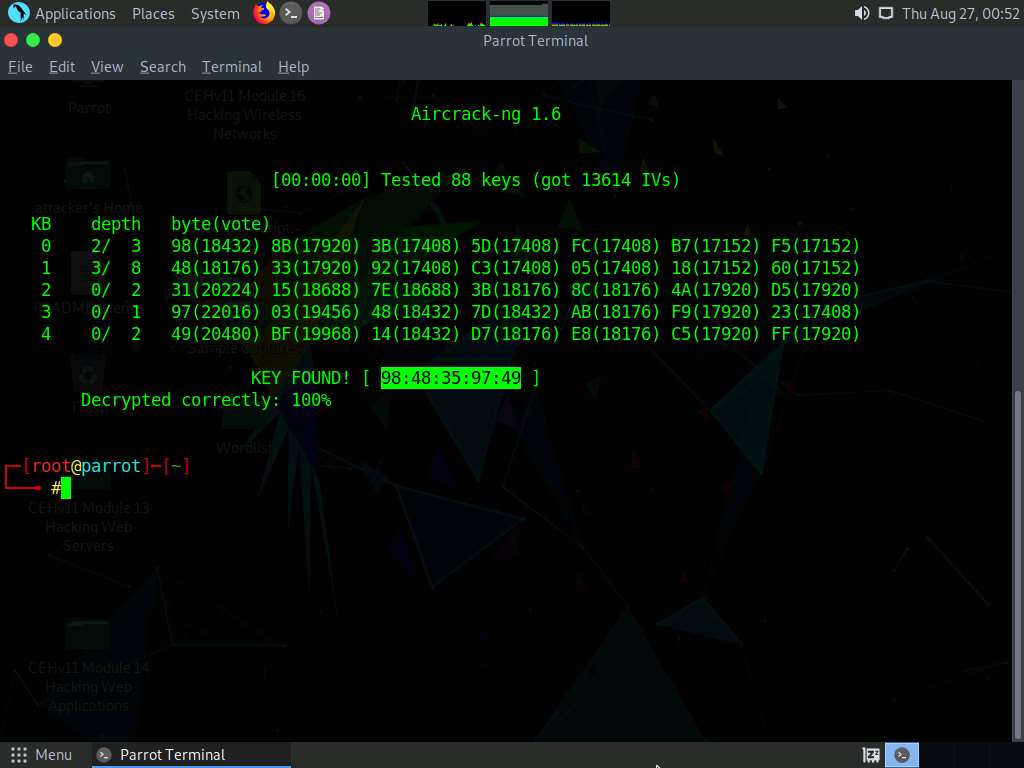
This concludes the demonstration of how to crack a WEP network using Aircrack-ng.
Task 2: Crack a WPA2 Network using Aircrack-ng
WPA2 is an upgrade to WPA; it includes mandatory support for Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP), an AES-based encryption protocol with strong security. WPA2 has two modes of operation: WPA2-Personal and WPA2-Enterprise. Despite being stronger than both WEP and WPA, the WPA2 encryption method can also be cracked using various techniques and tools.
In this task, we will use the Aircrack-ng suite to crack a WPA2 network.
Before starting this task, you need to configure your access point router (CEHLabs) to work in WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) encryption mode. To do so, navigate to the router’s default IP address and change the authentication mode from WPA to WPA2-PSK, with the password as password1.
In order to capture wireless traffic, a wireless adapter is required and using an adapter in the iLabs environment is not possible, therefore, in this lab, we are using a sample capture file (WPA2crack-01.cap) to crack WPA key.
Ensure that Sample Captures and Wordlist folders are present at the location home/attacker/Desktop which we copied in the previous task. If not, then navigate to the CEHv11 Module 16 Hacking Wireless Networks folder on the Desktop, copy the Sample Captures and Wordlist folders and paste them at the location home/attacker/Desktop.
Click the MATE Terminal icon at the top of the Desktop window to open a Terminal window.
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type sudo su and press Enter to run the programs as a root user.
In the [sudo] password for attacker field, type toor as a password and press Enter.
The password that you type will not be visible.
Now, type cd and press Enter to jump to the root directory.
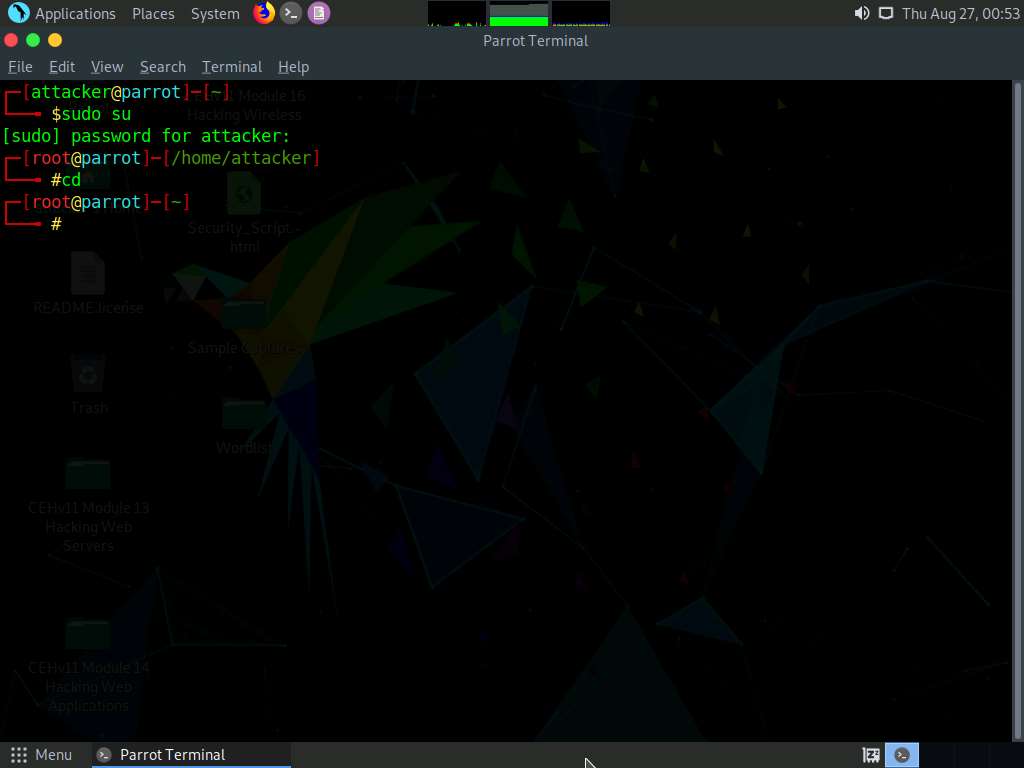
In the Parrot Terminal window, type aircrack-ng -a2 -b [Target BSSID] -w /home/attacker/Desktop/Wordlist/password.txt '/home/attacker/Desktop/Sample Captures/WPA2crack-01.cap' and press Enter. Here, the BSSID of the target is 20:E5:2A:E4:38:00.
- -a is the technique used to crack the handshake, 2=WPA technique.
- -b refers to bssid; replace with the BSSID of the target router.
- -w stands for wordlist; provide the path to a wordlist.
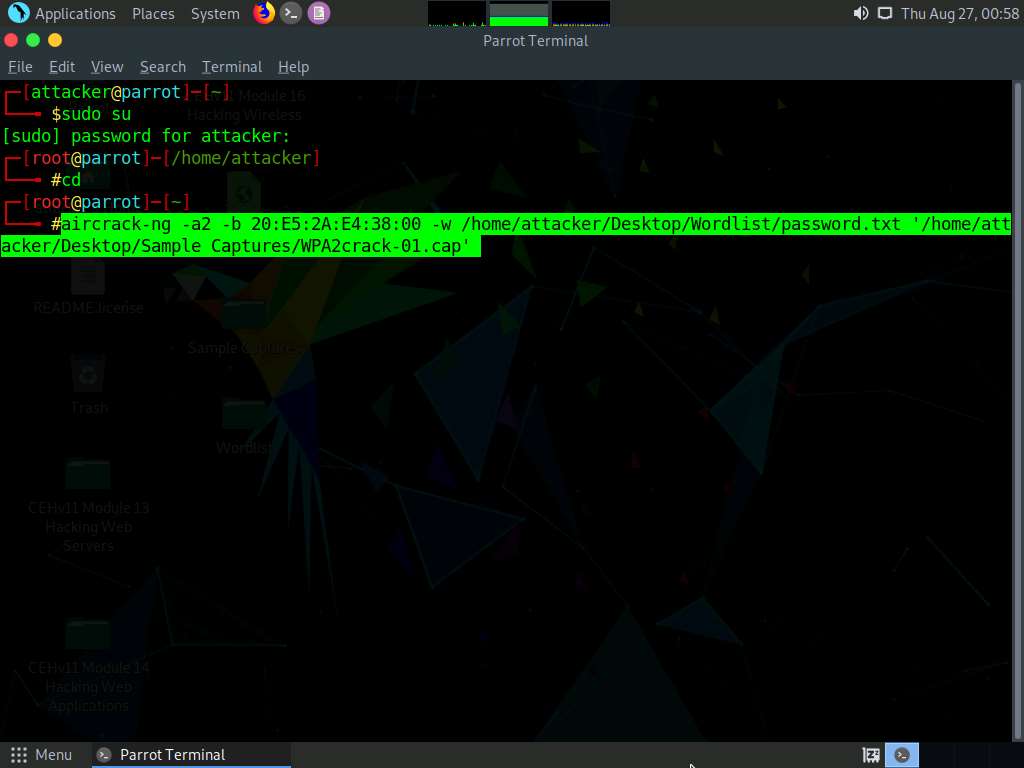
The result appears, showing the WPA handshake packet captured with airodump-ng. The target access point’s password is cracked and displayed in plain text next to the message KEY FOUND!, as shown in the screenshot.
If the password is complex, aircrack-ng will take a long time to crack it.
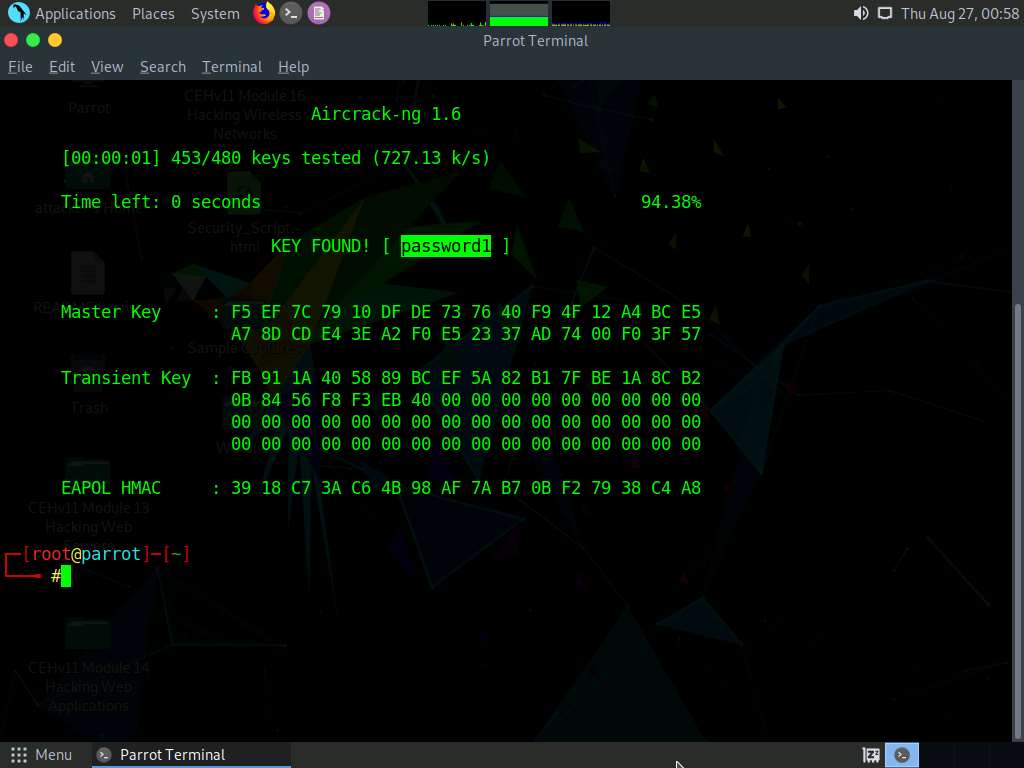
This concludes the demonstration of how to crack a WPA2 network using Aircrack-ng.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
You can also use other tools such as Elcomsoft Wireless Security Auditor (https://www.elcomsoft.com), Portable Penetrator (https://www.secpoint.com), WepCrackGui (https://sourceforge.net), Pyrit (https://github.com), and WepAttack (http://wepattack.sourceforge.net) to crack WEP/WPA/WPA2 encryption.
Comments
Post a Comment