Lab 2: Perform SNMP Enumeration
Lab 2: Perform SNMP Enumeration
Module 04: Enumeration
Lab 2: Perform SNMP Enumeration
Task 1: Perform SNMP Enumeration using snmp-check
this will show the snmp port being used by public community string
it will show ip routing information tcp connections listening ports
it will show storage information file system and device info
terminal
sudo su
cd
nmap -sU -p 161 10.10.10.16
port 161 is open/filtered and being used by SNMP,
snmp-check 10.10.10.16
It reveals that the extracted SNMP port 161 is being used by the default “public” community string.
might have to scroll up to see this it will be the line starting with [+]
scroll down to see Network information, Network interfaces, Network IP and Routing information, and TCP connections and listening ports.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Module 04: Enumeration
Lab 2: Perform SNMP Enumeration
Task 2: Perform SNMP Enumeration using SoftPerfect Network Scanner
Navigate to Z:\CEHv11 Module 04 Enumeration\SNMP Enumeration Tools\SoftPerfect Network Scanner and double-click netscan_setup.exe.'
In the Options menu, click Remote SNMP…
Mark All/None
10.10.10.5-10.10.10.20), and click the Start Scanning button.
right click select and select Properties to view individual results
or select open device
Lab Scenario
As a professional ethical hacker or penetration tester, your next step is to carry out SNMP enumeration to extract information about network resources (such as hosts, routers, devices, and shares) and network information (such as ARP tables, routing tables, device-specific information, and traffic statistics).
Using this information, you can further scan the target for underlying vulnerabilities, build a hacking strategy, and launch attacks.
Lab Objectives
Perform SNMP enumeration using snmp-check
Perform SNMP enumeration using SoftPerfect Network Scanner
Overview of SNMP Enumeration
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is an application layer protocol that runs on UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and maintains and manages routers, hubs, and switches on an IP network. SNMP agents run on networking devices on Windows and UNIX networks.
SNMP enumeration uses SNMP to create a list of the user accounts and devices on a target computer. SNMP employs two types of software components for communication: the SNMP agent and SNMP management station. The SNMP agent is located on the networking device, and the SNMP management station communicates with the agent.
Task 1: Perform SNMP Enumeration using snmp-check
snmp-check is a tool that enumerates SNMP devices, displaying the output in a simple and reader-friendly format. The default community used is “public.” As an ethical hacker or penetration tester, it is imperative that you find the default community strings for the target device and patch them up.
Here, we will use the snmp-check tool to perform SNMP enumeration on the target IP address
We will use a Parrot Security (10.10.10.13) machine to target a Windows Server 2016 (10.10.10.16) machine.
Click Parrot Security to switch to the Parrot Security machine.
In the login page, the attacker username will be selected by default. Enter password as toor in the Password field and press Enter to log in to the machine.
If a Parrot Updater pop-up appears at the top-right corner of Desktop, ignore and close it.
If a Question pop-up window appears asking you to update the machine, click No to close the window.
Click the MATE Terminal icon at the top of the Desktop window to open a Terminal window.
Before starting SNMP enumeration, we must first discover whether the SNMP port is open. SNMP uses port 161 by default; to check whether this port is opened, we will first run Nmap port scan.
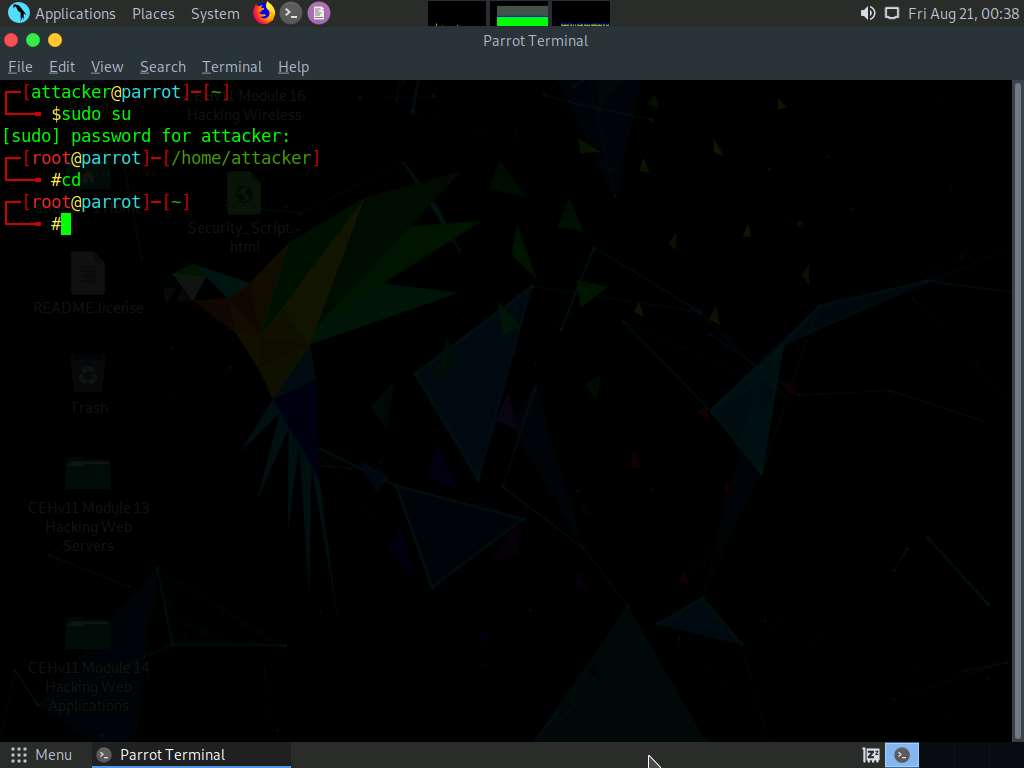
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type sudo su and press Enter to run the programs as a root user.
In the [sudo] password for attacker field, type toor as a password and press Enter.
The password that you type will not be visible.
Now, type cd and press Enter to jump to the root directory.
In the Parrot Terminal window, type nmap -sU -p 161 [Target IP address] (in this example, the target IP address is 10.10.10.16) and press Enter.
-sU performs a UDP scan and -p specifies the port to be scanned.
The results appear, displaying that port 161 is open/filtered and being used by SNMP, as shown in the screenshot.
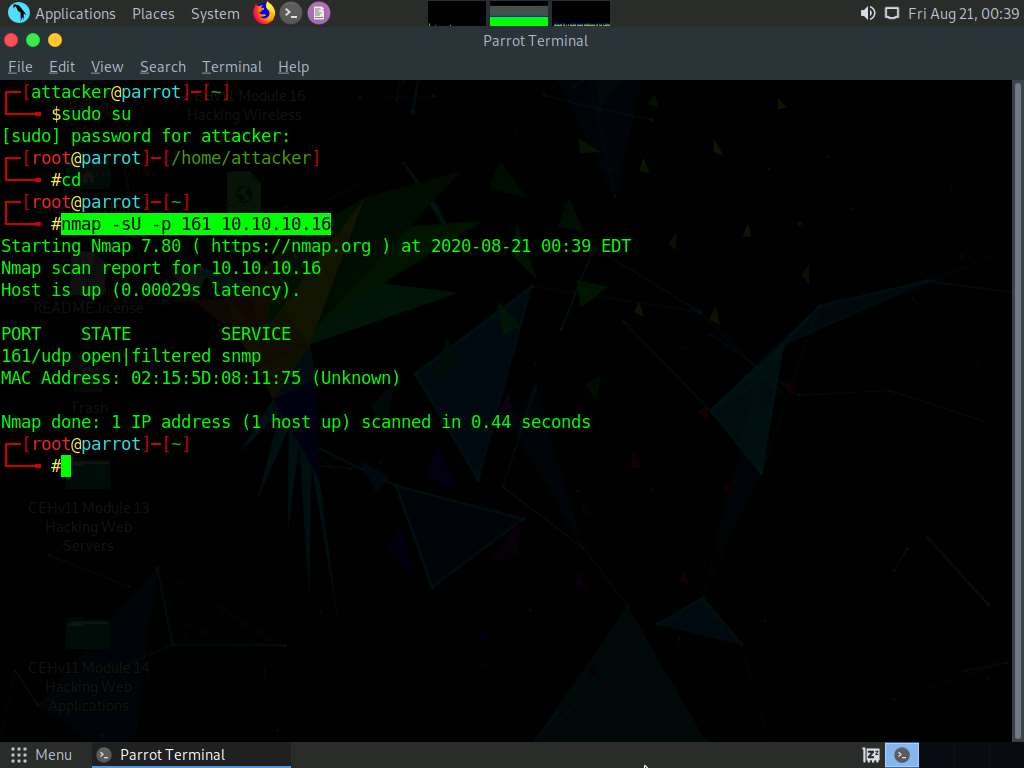
We have established that the SNMP service is running on the target machine. Now, we shall exploit it to obtain information about the target system.
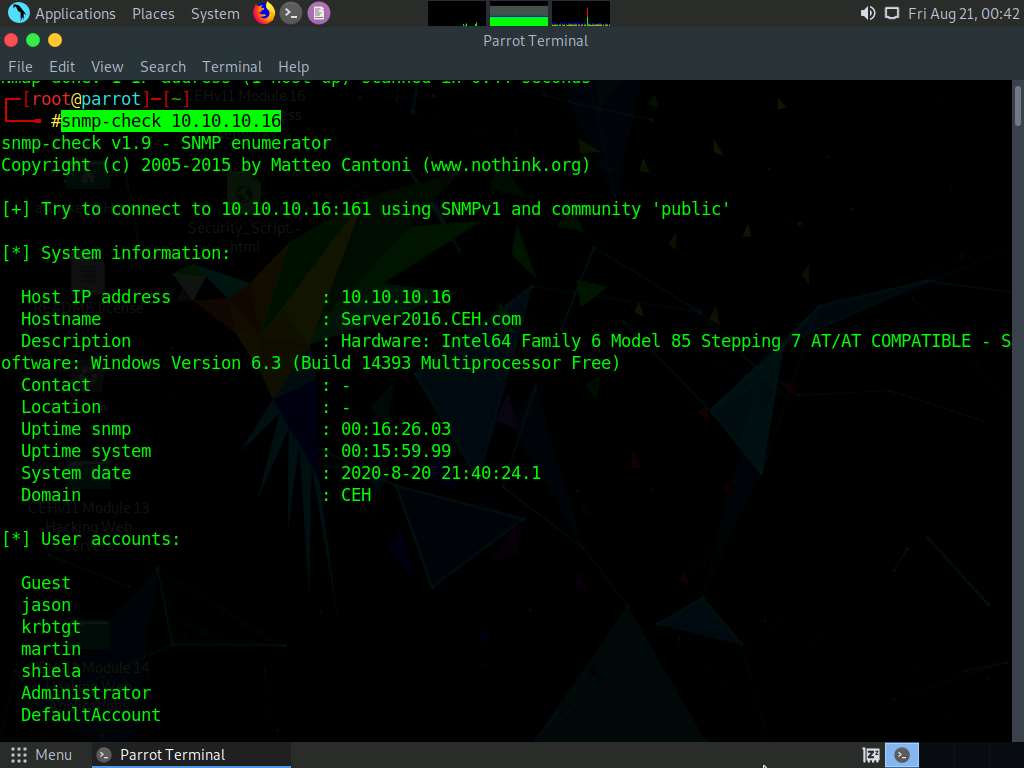
In the Parrot Terminal window, type snmp-check [Target IP Address] (in this example, the target IP address is 10.10.10.16) and press Enter.
The result appears as shown in the screenshot. It reveals that the extracted SNMP port 161 is being used by the default “public” community string.
If the target machine does not have a valid account, no output will be displayed.
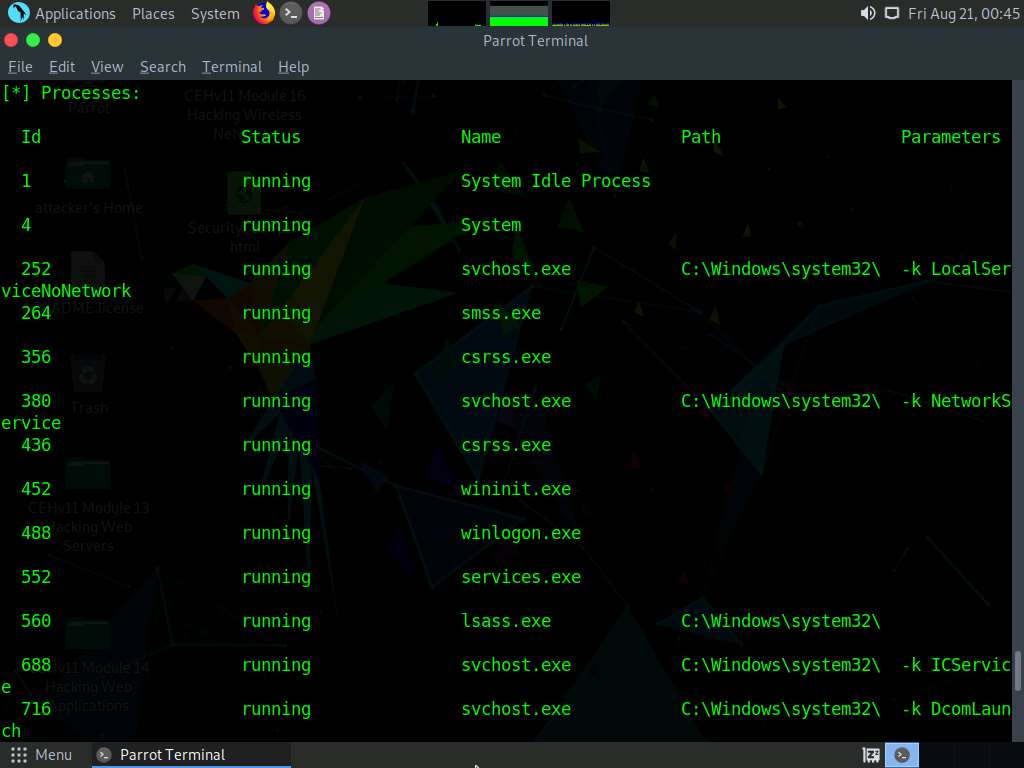
The snmp-check command enumerates the target machine, listing sensitive information such as System information and User accounts.
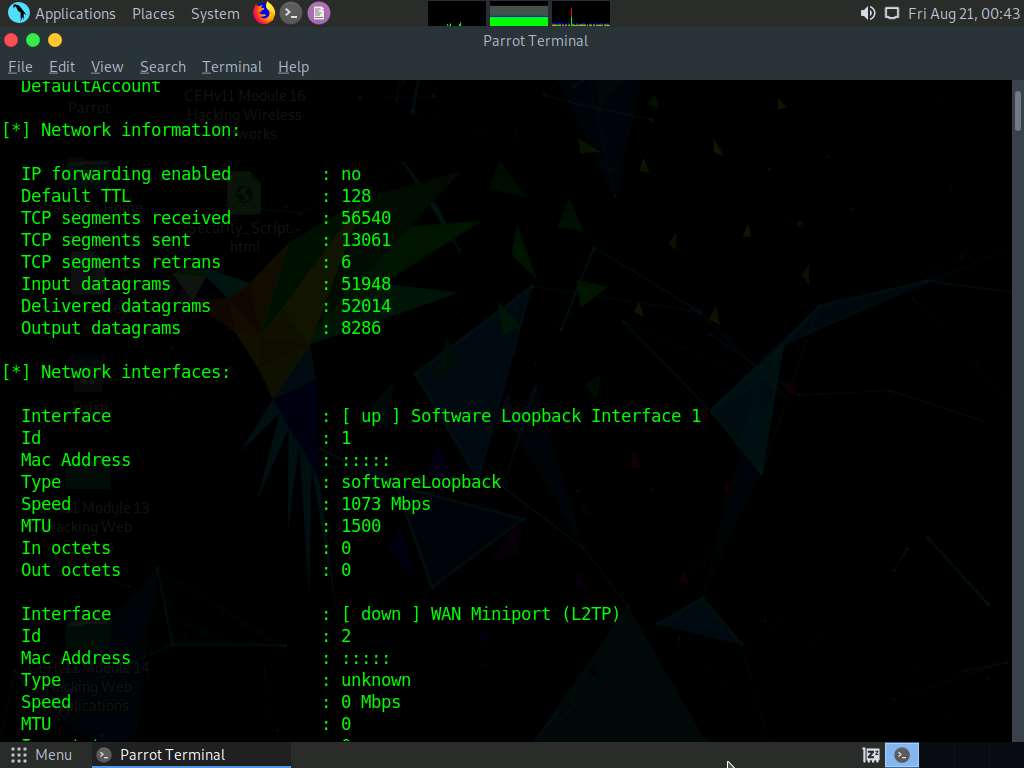
Scroll down to view detailed information regarding the target network under the following sections: Network information, Network interfaces, Network IP and Routing information, and TCP connections and listening ports.
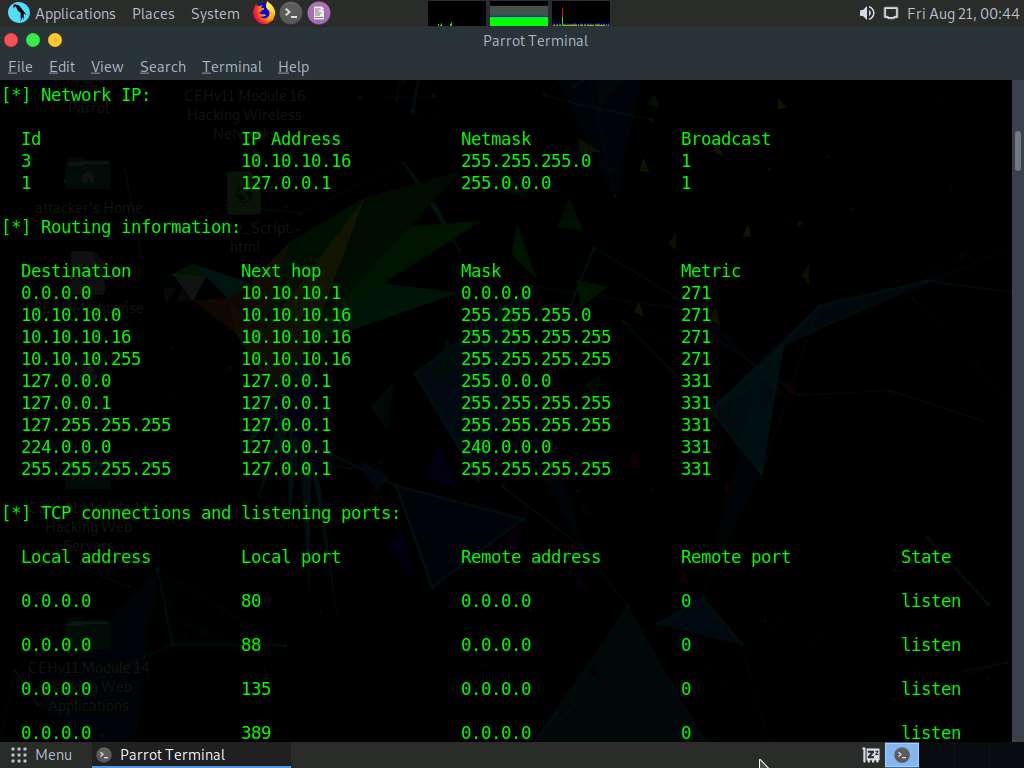
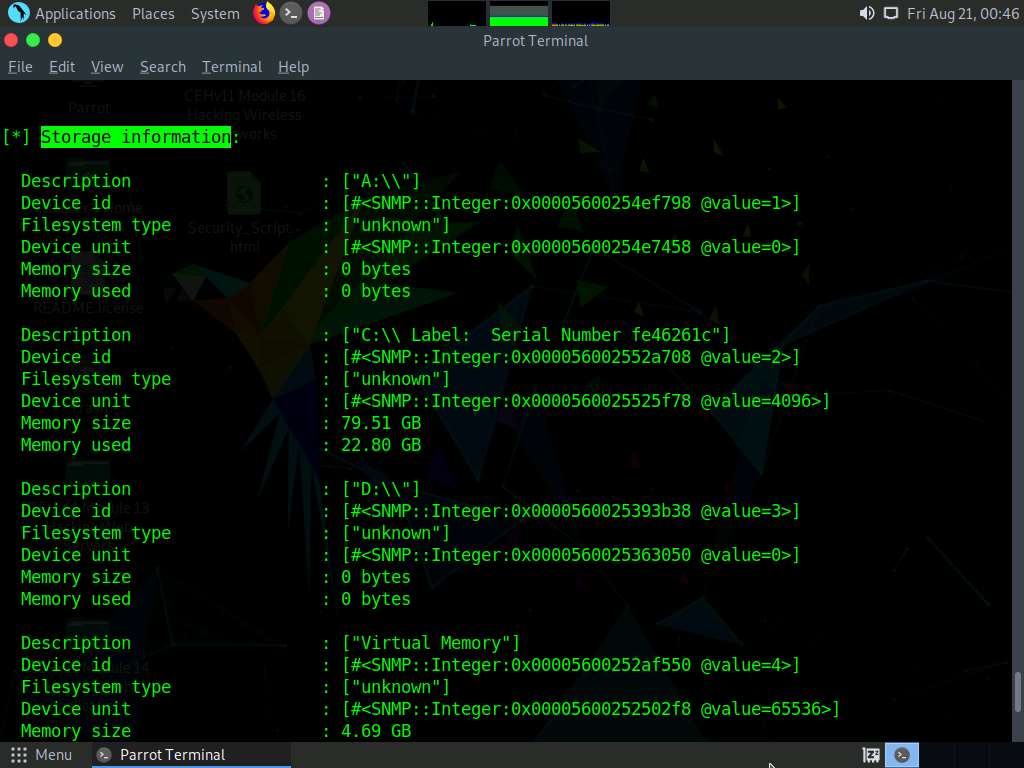
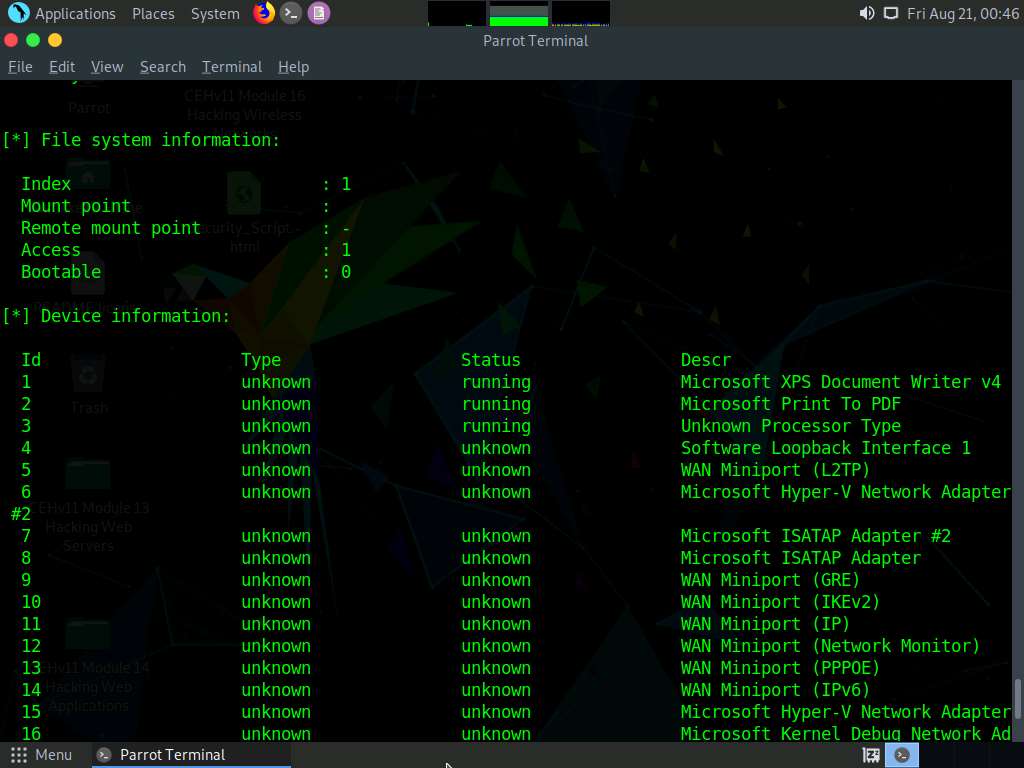
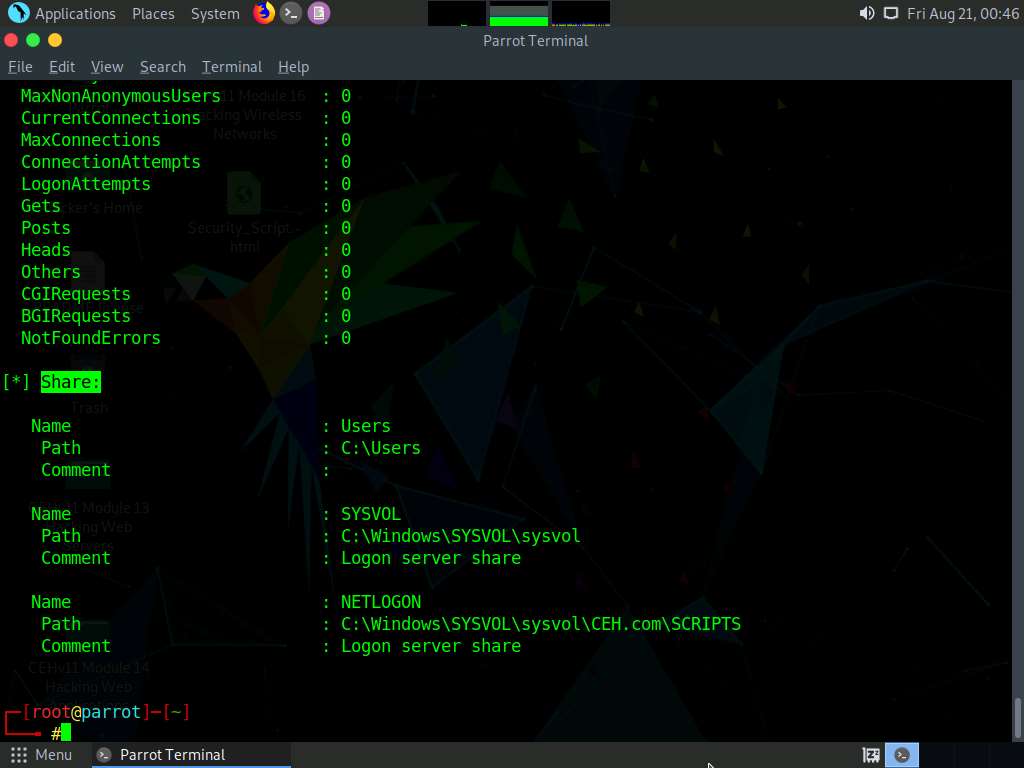
Similarly, scrolling down reveals further sensitive information on Processes, Storage information, File system information, Device information, Share, etc.
This concludes the demonstration of performing SNMP enumeration using the snmp-check.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Task 2: Perform SNMP Enumeration using SoftPerfect Network Scanner
SoftPerfect Network Scanner can ping computers, scan ports, discover shared folders, and retrieve practically any information about network devices via WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation), SNMP, HTTP, SSH, and PowerShell.
The program also scans for remote services, registries, files, and performance counters. It can check for a user-defined port and report if one is open, and is able to resolve hostnames as well as auto-detect your local and external IP range. SoftPerfect Network Scanner offers flexible filtering and display options, and can export the NetScan results to a variety of formats, from XML to JSON. In addition, it supports remote shutdown and Wake-On-LAN.
Here, we will use the SoftPerfect Network Scanner to perform SNMP enumeration on a target system.
Click Windows Server 2019 to switch to the Windows Server 2019 machine.
Navigate to Z:\CEHv11 Module 04 Enumeration\SNMP Enumeration Tools\SoftPerfect Network Scanner and double-click netscan_setup.exe.
If a User Account Control pop-up appears, click Yes.
When the Setup - SoftPerfect Network Scanner window appears, click Next and follow the installation steps to install SoftPerfect Network Scanner, using all default settings.
On completion of the installation, click Finish.
Ensure that the Launch SoftPerfect Network Scanner option is selected.
When the Welcome to the Network Scanner wizard appears, click Continue.
The SoftPerfect Network Scanner GUI window will appear, as shown in the screenshot.
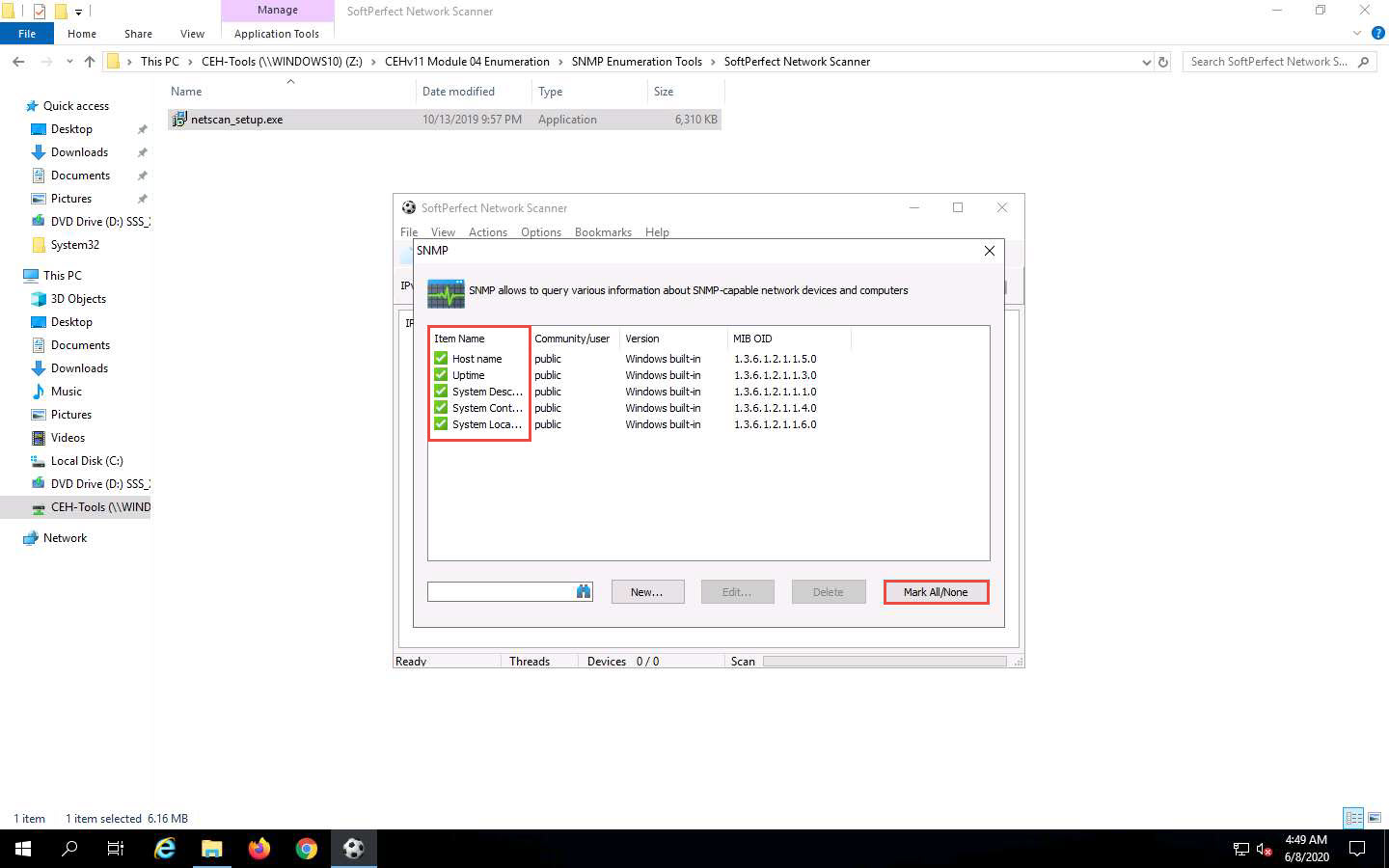
In the Options menu, click Remote SNMP…. The SNMP pop-up window will appear.
Click the Mark All/None button to select all the items available for SNMP scanning and close the window.
To scan your network, enter an IP range in the IPv4 From and To fields (in this example, the target IP address range is 10.10.10.5-10.10.10.20), and click the Start Scanning button.
The status bar at the lower-right corner of the GUI displays the status of the scan.
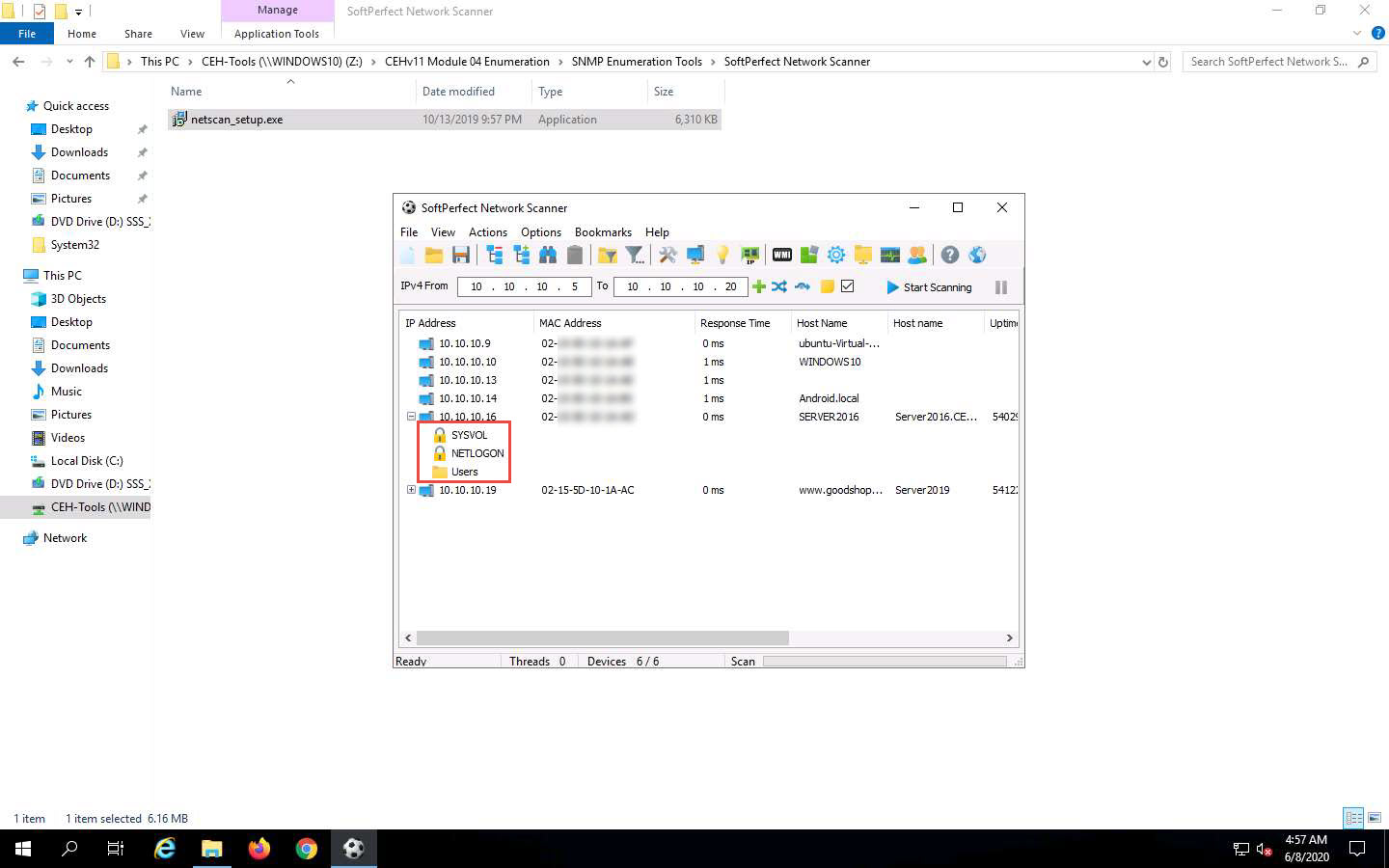
The scan results appear, displaying the active hosts in the target IP address range, as shown in the screenshot.
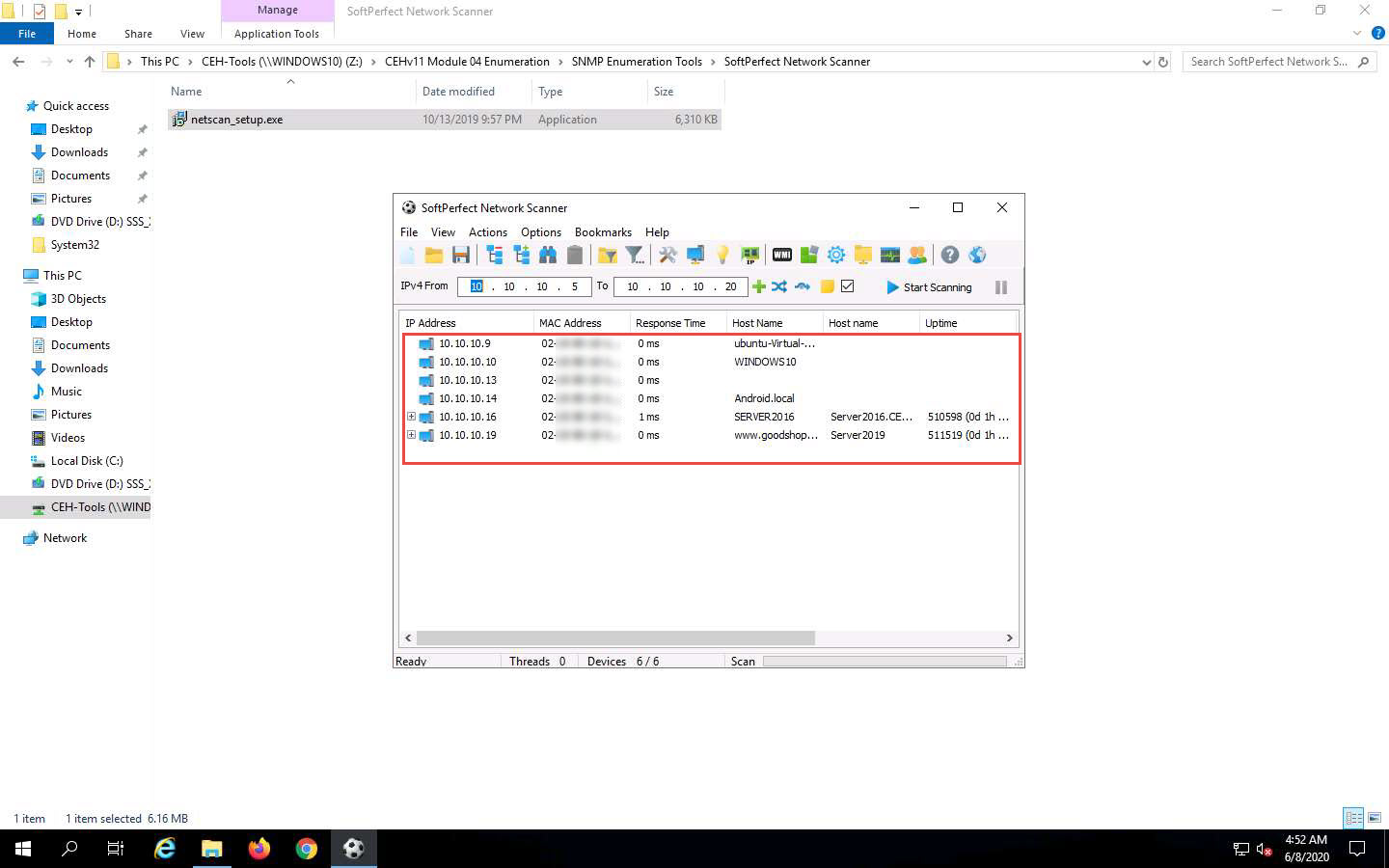
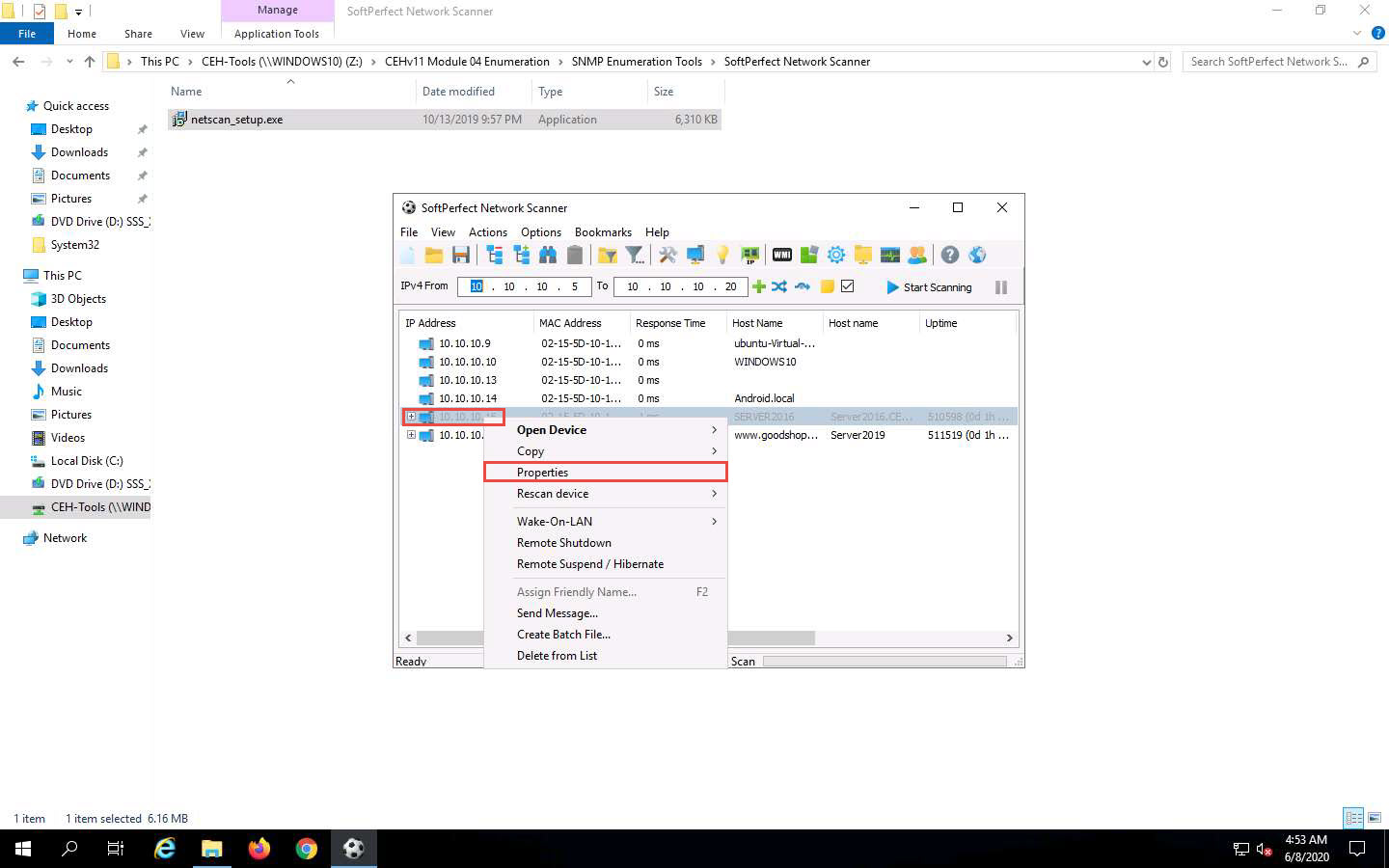
To view the properties of an individual IP address, right-click a particular IP address (in this example, 10.10.10.16) and select Properties, as shown in the screenshot.
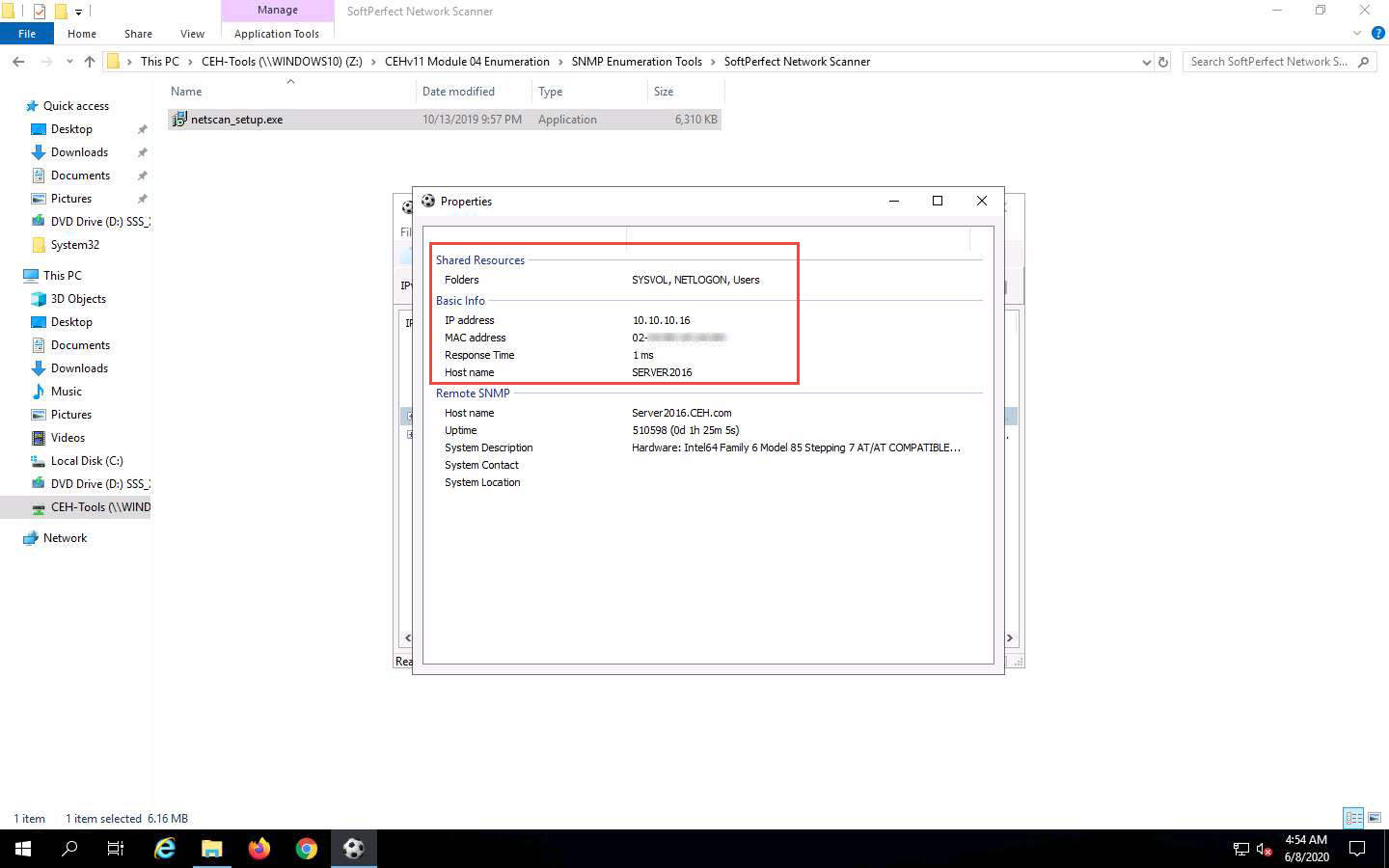
The Properties window appears, displaying the Shared Resources and Basic Info of the machine corresponding to the selected IP address.
Close the Properties window.
To view the shared folders, note the scanned hosts that have a + node before them. Expand the node to view all the shared folders.
In this example, we are targeting the Windows Server 2016 machine (10.10.10.16).
Right-click the selected host, and click Open Device. A drop-down list appears, containing options that allow you to connect to the remote machine over HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and Telnet.
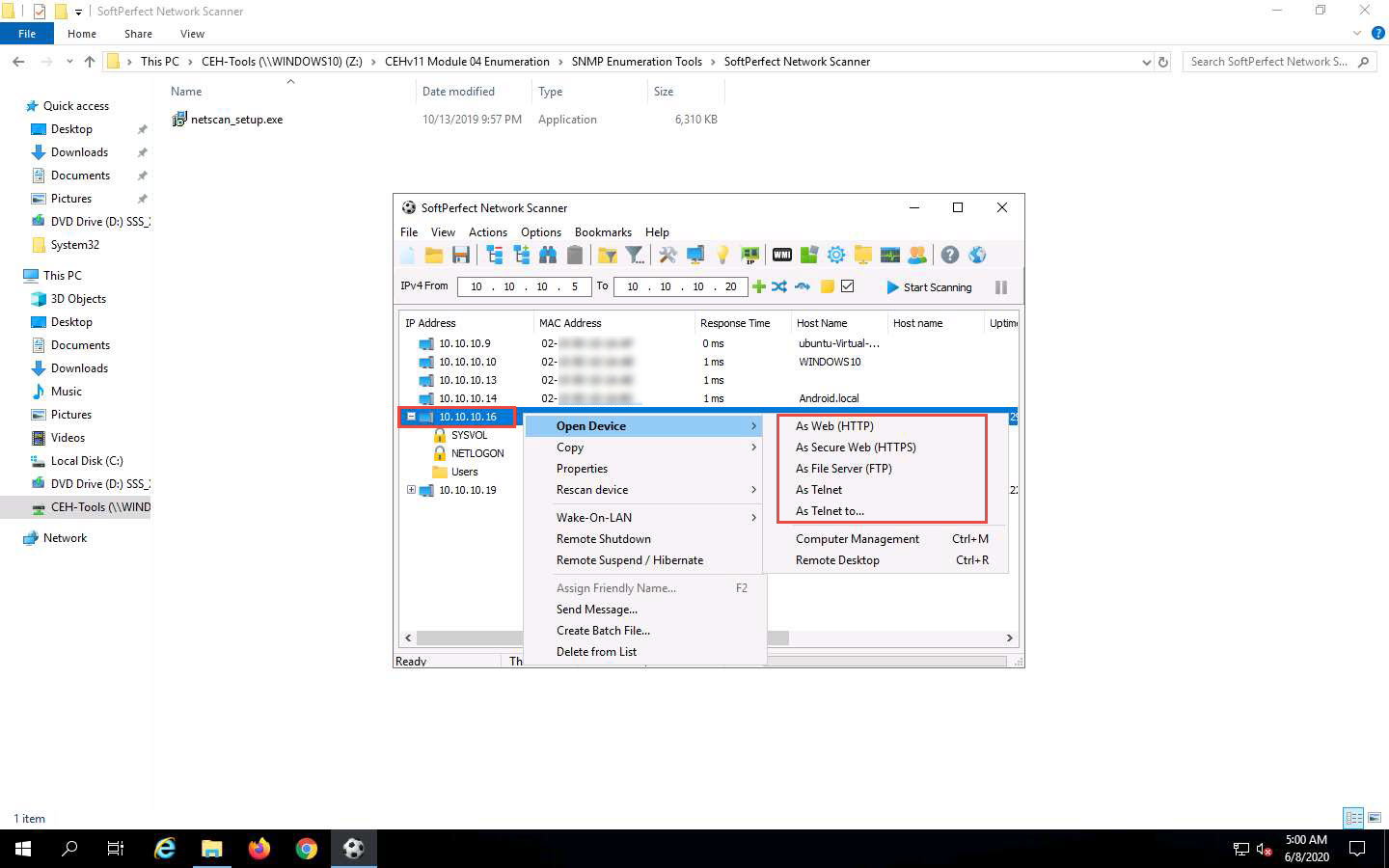
If the selected host is not secure enough, you may use these options to connect to the remote machines. You may also be able to perform activities such as sending a message and shutting down a computer remotely. These features are applicable only if the selected machine has a poor security configuration.
This concludes the demonstration of performing SNMP enumeration using the SoftPerfect Network Scanner.
You can also use other SNMP enumeration tools such as Network Performance Monitor (https://www.solarwinds.com), OpUtils (https://www.manageengine.com), PRTG Network Monitor (https://www.paessler.com), Engineer’s Toolset (https://www.solarwinds.com), and WhatsUp® Gold (https://www.ipswitch.com) to perform SNMP enumeration on the target network.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Comments
Post a Comment