Lab 1: Perform Wireless Traffic Analysis
Lab 1: Perform Wireless Traffic Analysis
Task 1: Wi-Fi Packet Analysis using Wireshark
pretty useless guide its just opening the file...... know wireshark commands to complete what your looking for.
open wireshark
click file open the capture file for the lab in this case D:\CEH-Tools\CEHv11 moduel 16 hacking wirelss sample captures WEPcrack01.cap
802.11 protocol indicates wireless
use wireshark commands from here to find what your looking for
Lab Scenario
As a professional ethical hacker or pen tester, your next step in hacking wireless networks is to capture and analyze the traffic of the target wireless network.
This wireless traffic analysis will help you to determine the weaknesses and vulnerable devices in the target network. In the process, you will determine the network’s broadcasted SSID, the presence of multiple access points, the possibility of recovering SSIDs, the authentication method used, WLAN encryption algorithms, etc.
The labs in this exercise demonstrate how to use various tools and techniques to capture and analyze the traffic of the target wireless network.
Lab Objectives
- Wi-Fi Packet Analysis using Wireshark
Overview of Wireless Traffic Analysis
Wireless traffic analysis helps in determining the appropriate strategy for a successful attack. Wi-Fi protocols are unique at Layer 2, and traffic over the air is not serialized, which makes it easy to sniff and analyze wireless packets. You can use various Wi-Fi packet-sniffing tools to capture and analyze the traffic of a target wireless network.
Task 1: Wi-Fi Packet Analysis using Wireshark
Wireshark is a network protocol sniffer and analyzer. It lets you capture and interactively browse the traffic running on a target network. Wireshark can read live data from Ethernet, Token-Ring, FDDI, serial (PPP and SLIP), and 802.11 wireless LAN. Npcap is a library that is integrated with Wireshark for complete WLAN traffic analysis, visualization, drill-down, and reporting. Wireshark can be used in monitor mode to capture wireless traffic. It is able to capture a vast number of management, control, data frames, etc. and further analyze the Radiotap header fields to gather critical information such as protocols and encryption techniques used, length of the frames, MAC addresses, etc.
Here, we will use Wireshark to analyze captured Wi-Fi packets.
In order to capture wireless traffic, a wireless adapter is required and using an adapter in the iLabs environment is not possible, therefore, in this lab, we are using a sample capture file (WEPcrack-01.cap) to analyze wireless packets.
By default, Windows 10 machine selected, click Ctrl+Alt+Delete.
Alternatively, you can also click Ctrl+Alt+Delete button under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Ctrl+Alt+Delete button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
By default, Admin user profile is selected, click Pa$$w0rd to paste the password in the Password field and press Enter to login.
Alternatively, you can also click Pa$$w0rd under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Type Text | Type Password button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
If Welcome to Windows wizard appears, click Continue and in Sign in with Microsoft wizard, click Cancel.
Networks screen appears, click Yes to allow your PC to be discoverable by other PCs and devices on the network.
In the Desktop, double-click Wireshark shortcut.

The Wireshark Network Analyzer window appears.
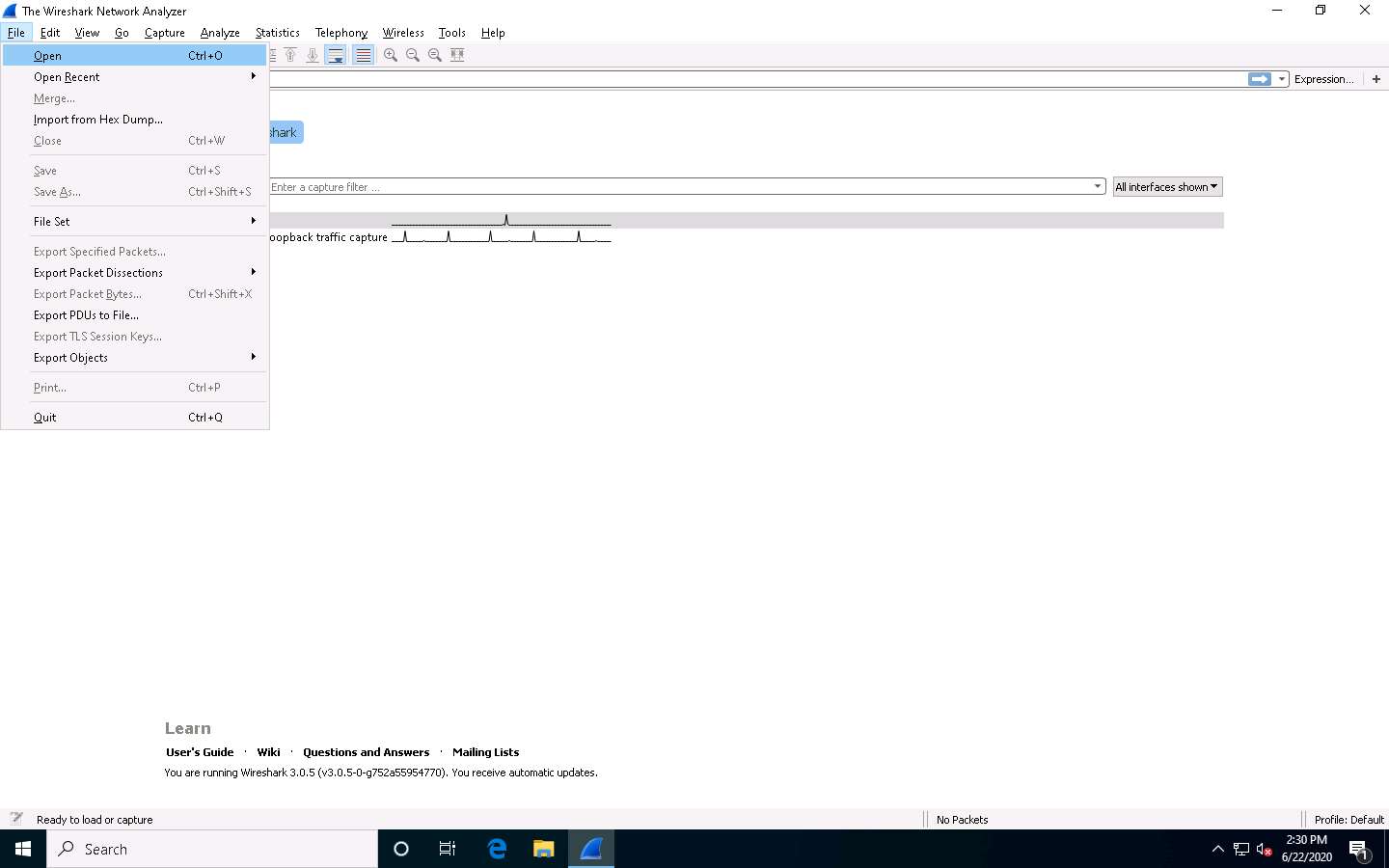
In the menu bar, click File and click Open option from the drop-down list.
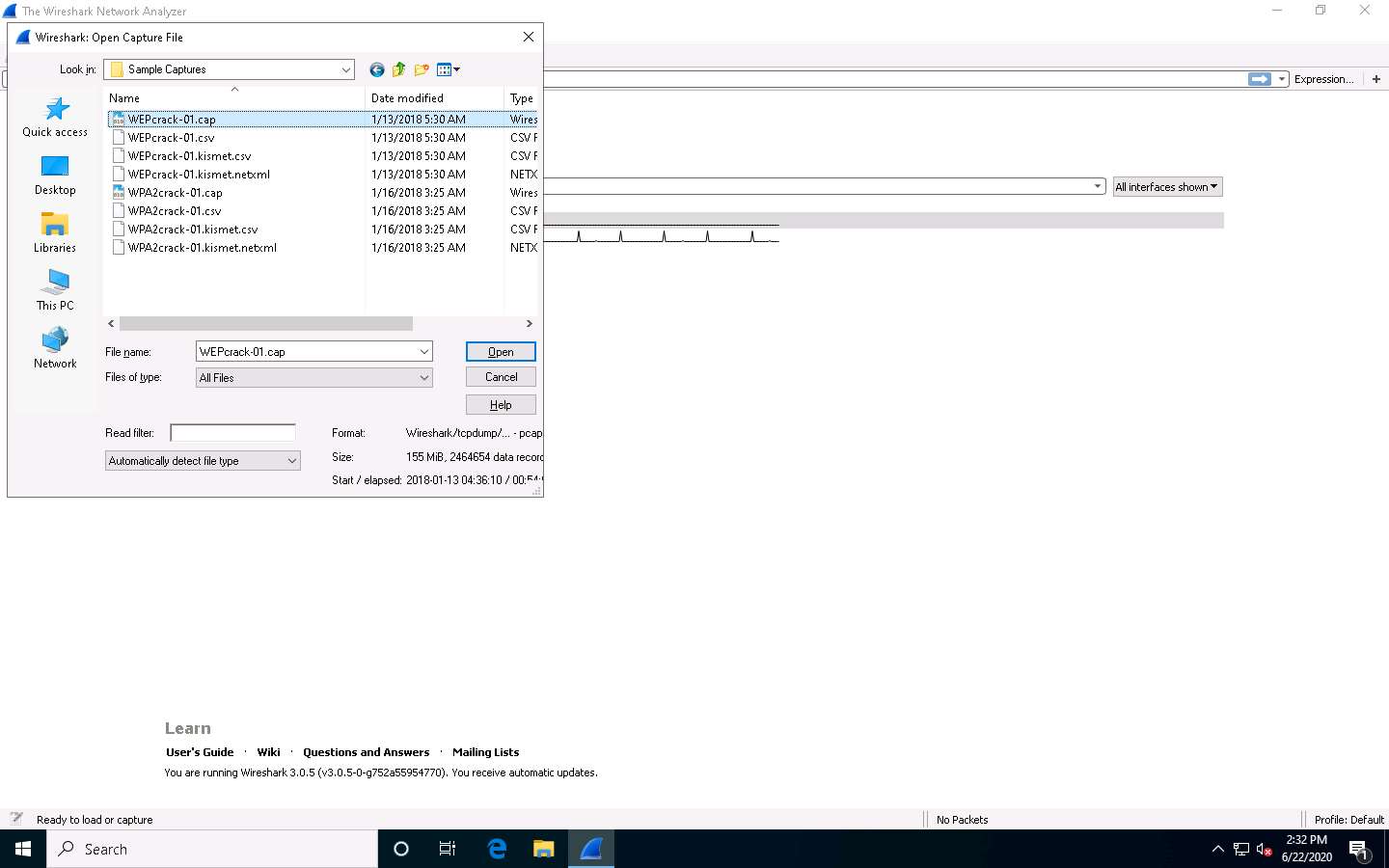
Wireshark: Open Capture File window appears, navigate to D:\CEH-Tools\CEHv11 Module 16 Hacking Wireless Networks\Sample Captures, select WEPcrack-01.cap and click Open.
Here, we are an
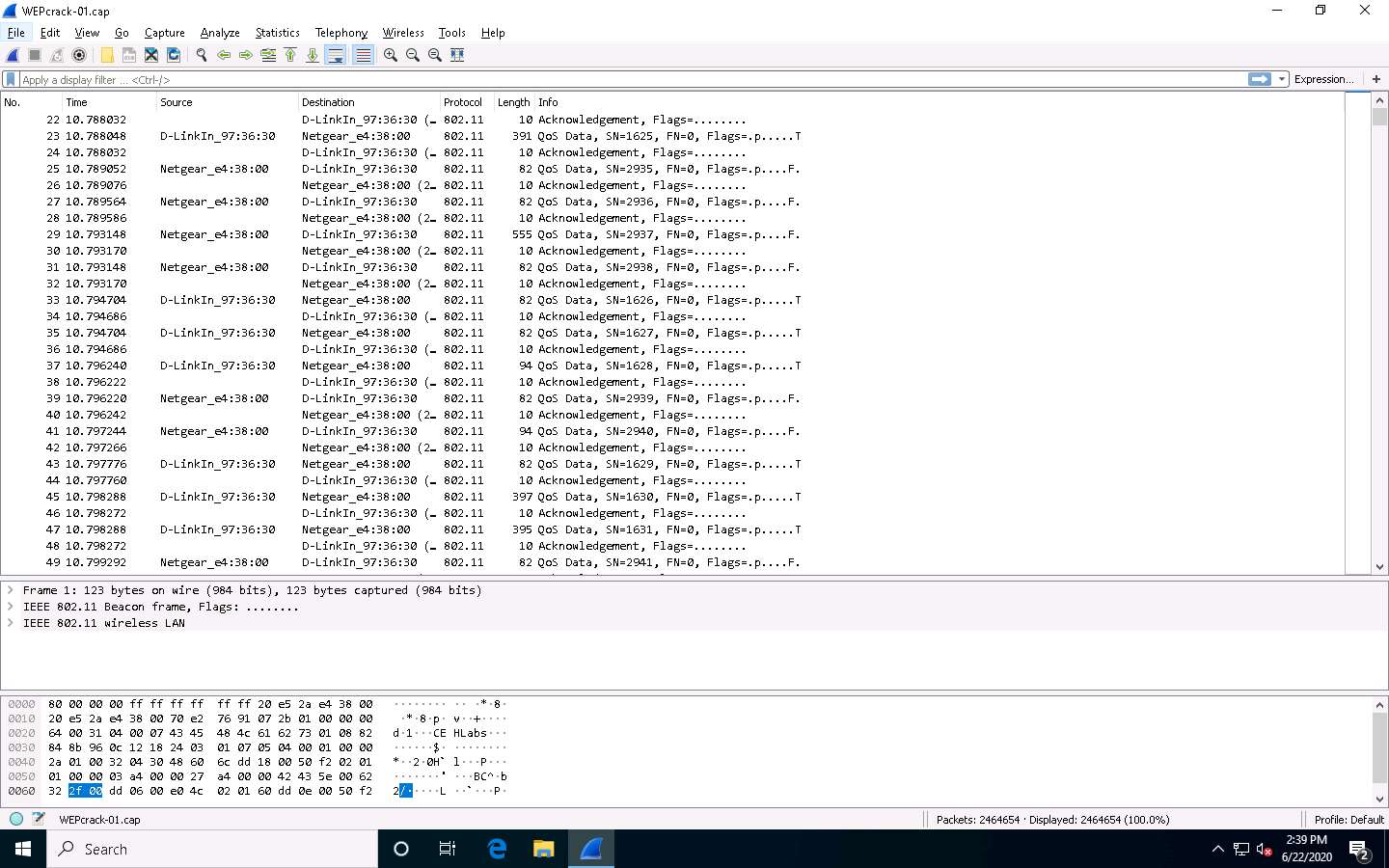
The WEPcrack-01.cap file opens in Wireshark window showing you the details of the packet for analysis. Here you can see the wireless packets captured which were otherwise masked to look like ethernet traffic.
Here 802.11 protocol indicates wireless packets.
You can access the saved packet capture file anytime, and by issuing packet filtering commands in the Filter field, you can narrow down the packet search in an attempt to find packets containing sensible information.
In real time, attackers enforce packet capture and packet filtering techniques to capture packets containing passwords (only for websites implemented on HTTP channel), perform attacks such as session hijacking, and so on.
Similarly you can also analyze the WPA2crack-01.cap file for WPA packets.
This concludes the demonstration of how to analyze Wi-Fi packets using Wireshark.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
You can also use other wireless traffic analyzers such as AirMagnet WiFi Analyzer PRO (https://www.netally.com), SteelCentral Packet Analyzer (https://www.riverbed.com), Omnipeek Network Protocol Analyzer (https://www.liveaction.com), CommView for Wi-Fi (https://www.tamos.com), and Capsa Portable Network Analyzer (https://www.colasoft.com) to analyze Wi-Fi traffic.
Comments
Post a Comment