Lab 1: Perform Vulnerability Research with Vulnerability Scoring Systems and Databases
Lab 1: Perform Vulnerability Research with Vulnerability Scoring Systems and Databases
Module 05: Vulnerability Analysis
Lab 1: Perform Vulnerability Research with Vulnerability Scoring Systems and Databases
Task 1: Perform Vulnerability Research in Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
firefox
https://cwe.mitre.org/
type SMB
search
You can click any link to view detailed information on the vulnerability.
click CWE-200) to view detailed information about the vulnerability.
navigate back to the CWE website, scroll down, and click the CWE List link present below the searched results.
Scroll down, and under the External Mappings section, click CWE Top 25 (2019).
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Module 05: Vulnerability Analysis
Lab 1: Perform Vulnerability Research with Vulnerability Scoring Systems and Databases
Task 2: Perform Vulnerability Research in Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is a publicly available and free-to-use list or dictionary of standardized
identifiers for common software vulnerabilities and exposures. It is used to discuss or share information about a unique
software or firmware vulnerability, provides a baseline for tool evaluation, and enables data exchange for cybersecurity
automation.
refrence blog for steps prob not on test
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Module 05: Vulnerability Analysis
Lab 1: Perform Vulnerability Research with Vulnerability Scoring Systems and Databases
Task 3: Perform Vulnerability Research in National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) is the U.S. government repository of standards-based vulnerability
management data represented using the Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP). These data enable the automation of
vulnerability management, security measurement, and compliance. The NVD includes databases of security checklist references,
security-related software flaws, misconfigurations, product names, and impact metrics.
refrence blog for steps prob not on test
Lab Scenario
As a professional ethical hacker or pen tester, your first step is to search for vulnerabilities in the target system or network using vulnerability scoring systems and databases. Vulnerability research provides awareness of advanced techniques to identify flaws or loopholes in the software that could be exploited. Using this information, you can use various tricks and techniques to launch attacks on the target system.
Lab Objectives
- Perform vulnerability research in Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
- Perform vulnerability research in Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
- Perform vulnerability research in National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
Overview of Vulnerabilities in Vulnerability Scoring Systems and Databases
Vulnerability databases collect and maintain information about various vulnerabilities present in the information systems.
The following are some of the vulnerability scoring systems and databases:
- Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
- Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
- Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
Task 1: Perform Vulnerability Research in Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) is a category system for software vulnerabilities and weaknesses. It has numerous categories of weaknesses that means that CWE can be effectively employed by the community as a baseline for weakness identification, mitigation, and prevention efforts. Further, CWE has an advanced search technique with which you can search and view the weaknesses based on research concepts, development concepts, and architectural concepts.
Here, we will use CWE to view the latest underlying system vulnerabilities.
By default, Windows 10 machine is selected, click Ctrl+Alt+Delete to activate the machine.
Alternatively, you can also click Ctrl+Alt+Delete button under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Ctrl+Alt+Delete button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
By default, Admin user profile is selected, click Pa$$w0rd to paste the password in the Password field and press Enter to login.
Alternatively, you can also click Pa$$w0rd under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Type Text | Type Password button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
If Welcome to Windows wizard appears, click Continue and in Sign in with Microsoft wizard, click Cancel.
Networks screen appears, click Yes to allow your PC to be discoverable by other PCs and devices on the network.
Launch any browser, here, we are using Mozilla Firefox. In the address bar of the browser place your mouse cursor and click https://cwe.mitre.org/ and press Enter
- If the Default Browser pop-up window appears, uncheck the Always perform this check when starting Firefox checkbox and click the Not now button.
- If a New in Firefox: Content Blocking pop-up window appears, follow the step and click Got it to finish viewing the information.
CWE website appears. In the Google Custom Search under Search CWE section, type SMB and click the search icon.
Here, we are searching for the vulnerabilities of the running services that were found in the target systems in previous module labs (Module 04 Enumeration).
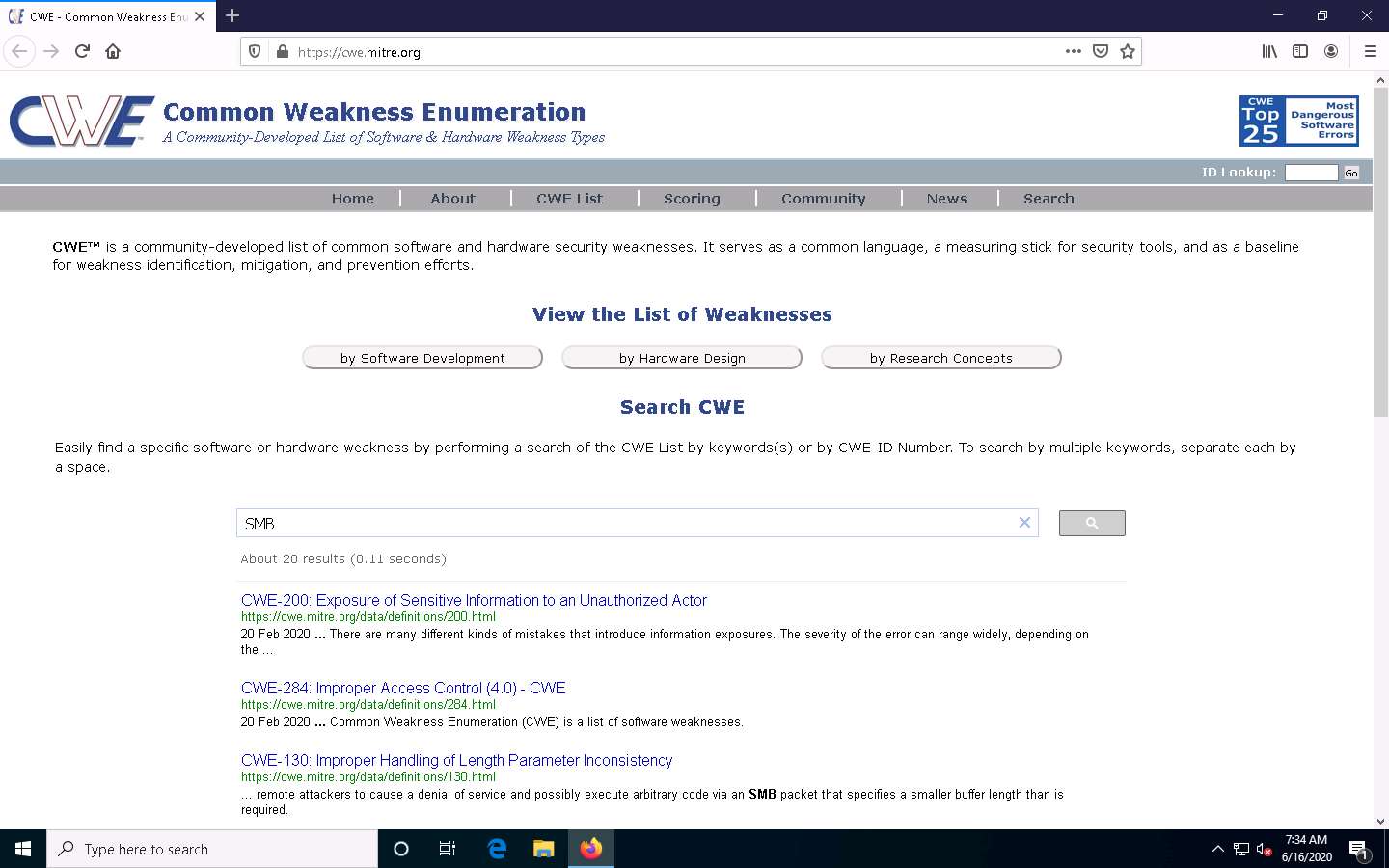
The search results appear, displaying the underlying vulnerabilities in the target service (here, SMB). You can click any link to view detailed information on the vulnerability.
The search results might differ in your lab environment.
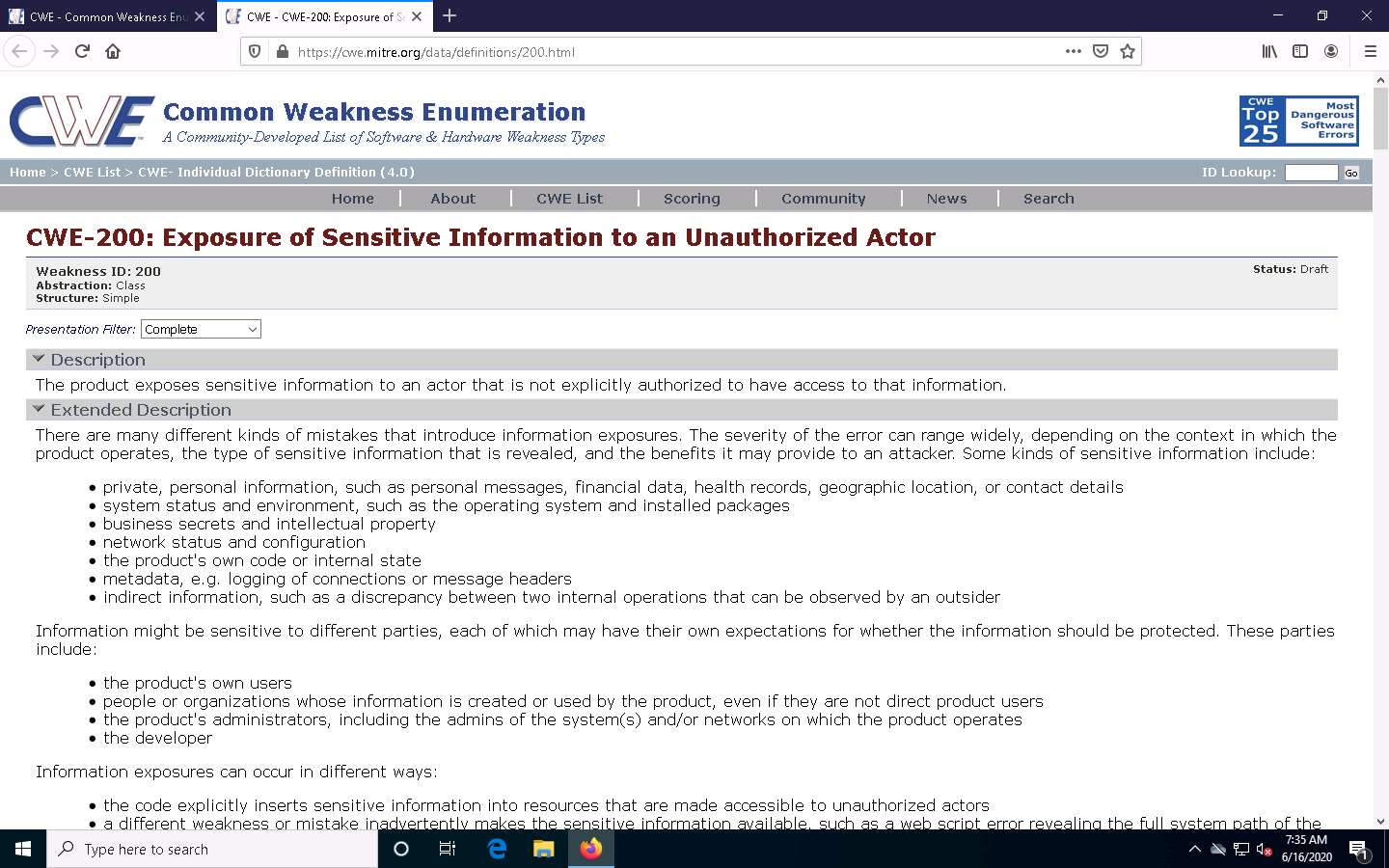
Now, click any link (here, CWE-200) to view detailed information about the vulnerability.
A new webpage appears in the new tab, displaying detailed information regarding the vulnerability. You can scroll-down further to view more information.
Similarly, you can click on other vulnerabilities and view detailed information.
Now, navigate back to the CWE website, scroll down, and click the CWE List link present below the searched results.
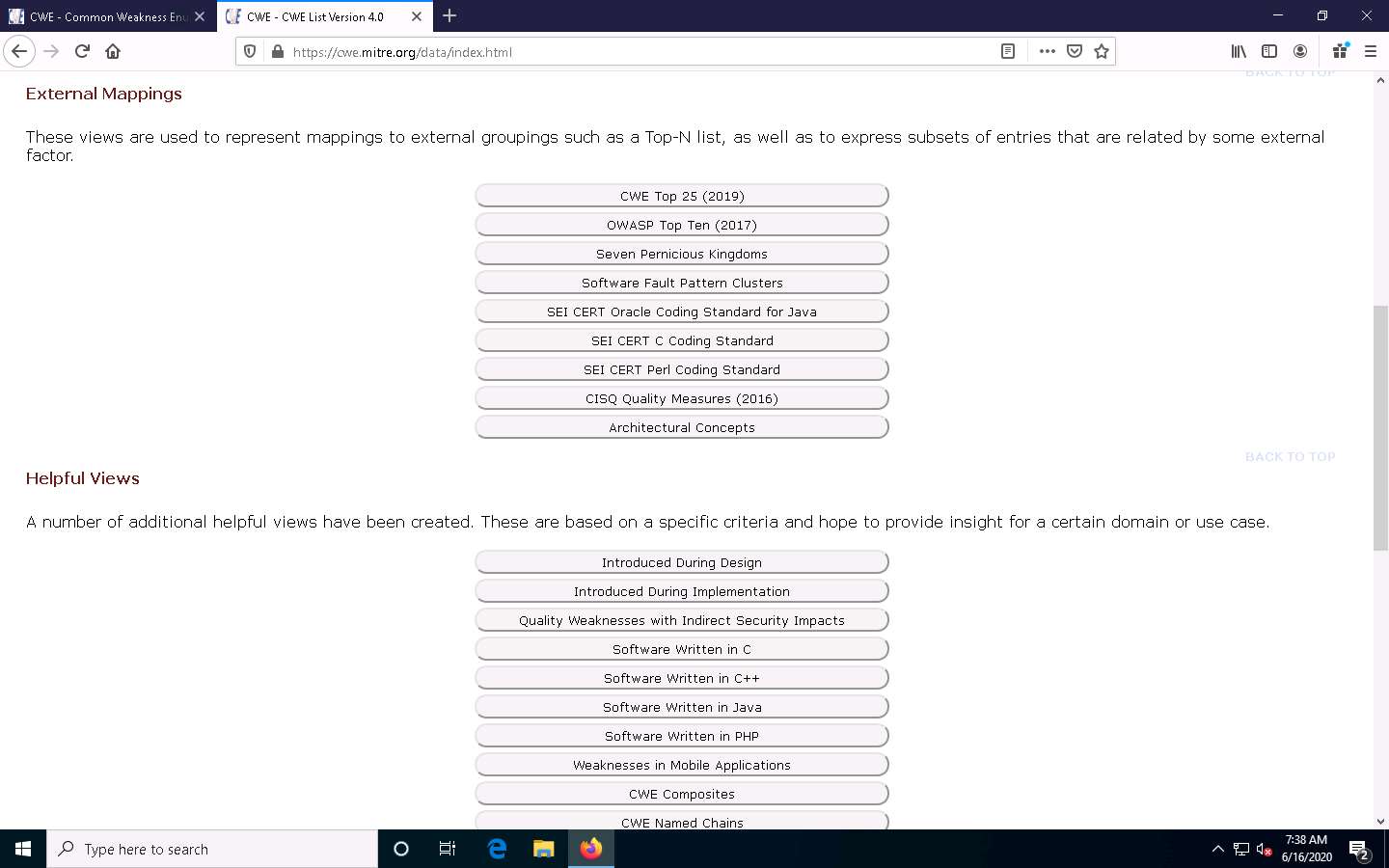
A new webpage appears, displaying CWE List Version. Scroll down, and under the External Mappings section, click CWE Top 25 (2019).
The result might differ in your lab environment.
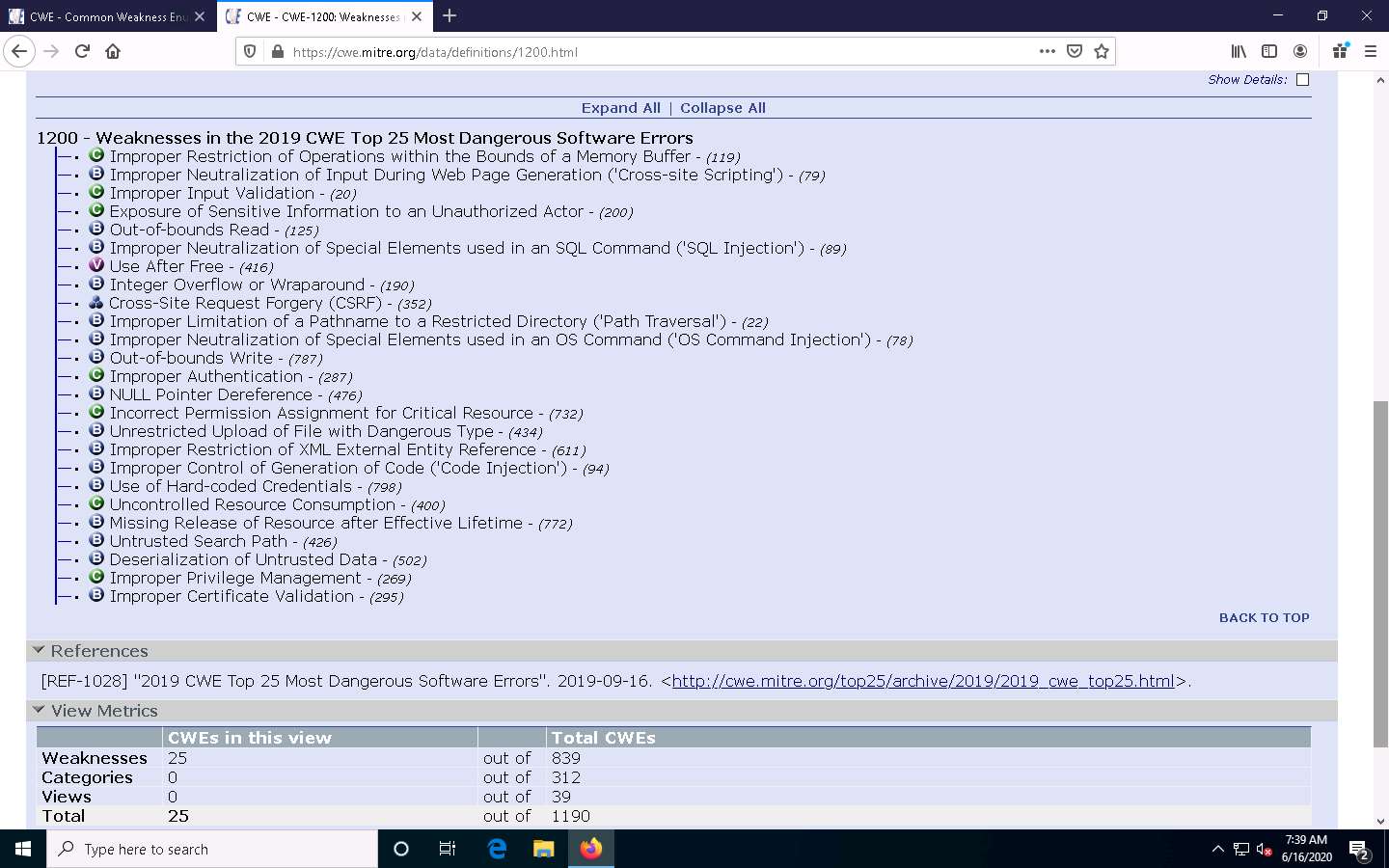
A webpage appears, displaying CWE VIEW: Weaknesses in the 2019 CWE Top 25 Most Dangerous Software Errors. Scroll down and view a list of Weaknesses in the 2019 CWE Top 25 Most Dangerous Software Errors under the Relationships section. You can click on each weakness to view detailed information on it.
This information can be used to exploit the vulnerabilities in the software and further launch attacks.
The result publishing year be might different in your lab environment.
Similarly, you can go back to the CWE website and explore other options, as well.
This concludes the demonstration of checking vulnerabilities in the Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE).
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Task 2: Perform Vulnerability Research in Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) is a publicly available and free-to-use list or dictionary of standardized identifiers for common software vulnerabilities and exposures. It is used to discuss or share information about a unique software or firmware vulnerability, provides a baseline for tool evaluation, and enables data exchange for cybersecurity automation.
Here, we will use CVE to view the latest underlying system and software vulnerabilities.
In Windows 10 machine, launch any browser (here, Mozilla Firefox). In the address bar of the browser place your mouse cursor and click https://cve.mitre.org/ and press Enter
CVE website appears. In the right pane, under the Newest CVE Entries section, recently discovered vulnerabilities are displayed.
The results might differ in your lab environment.
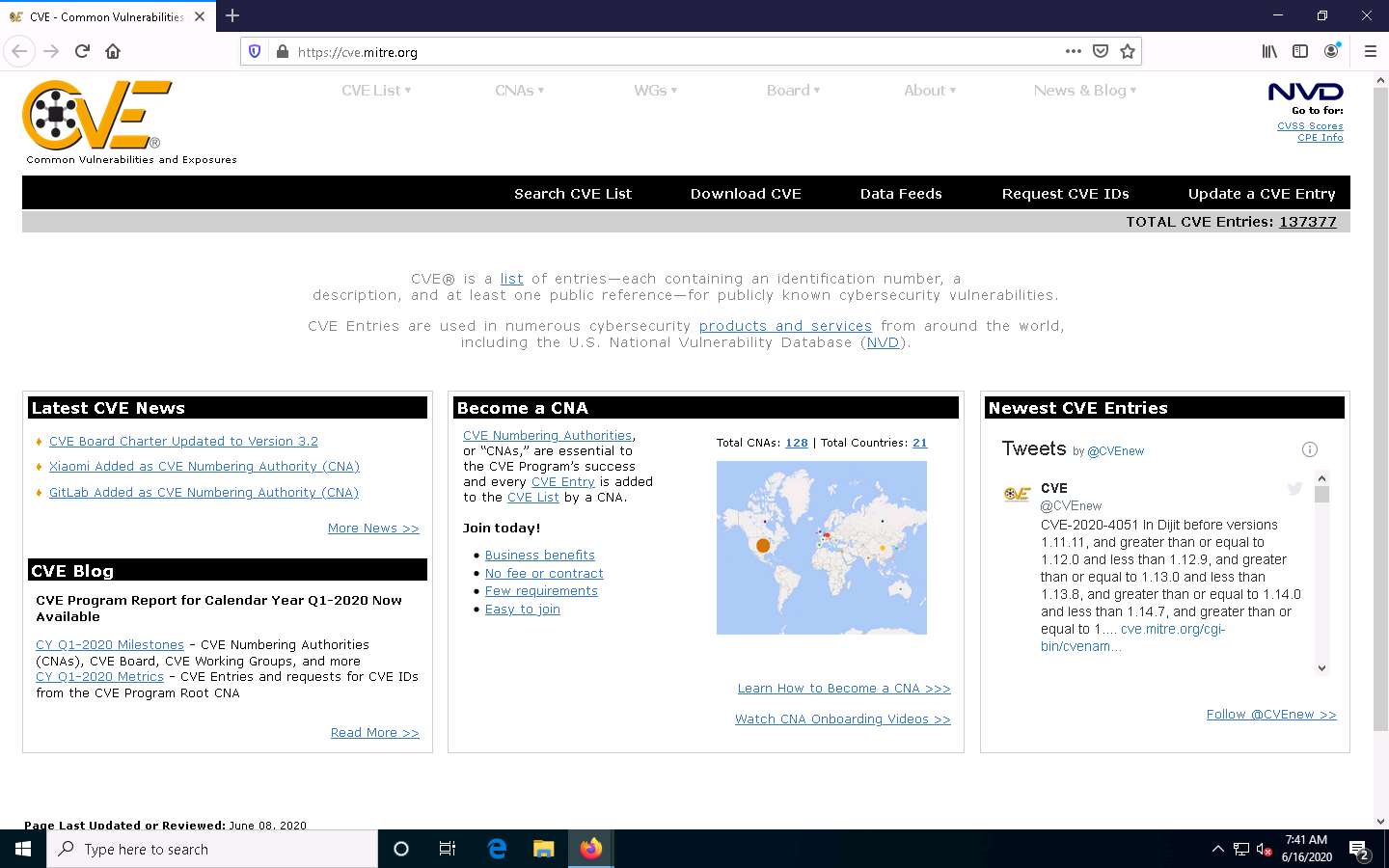
You can copy the name of any vulnerability under the Newest CVE Entries section and search on CVE to view detailed information on it. (here, we are selecting the vulnerability CVE-2020-13910)
Now, click on the Search CVE List tab. Under Search CVE List section, type the vulnerability name (here, CVE-2020-4051) in the search bar, and click Submit.
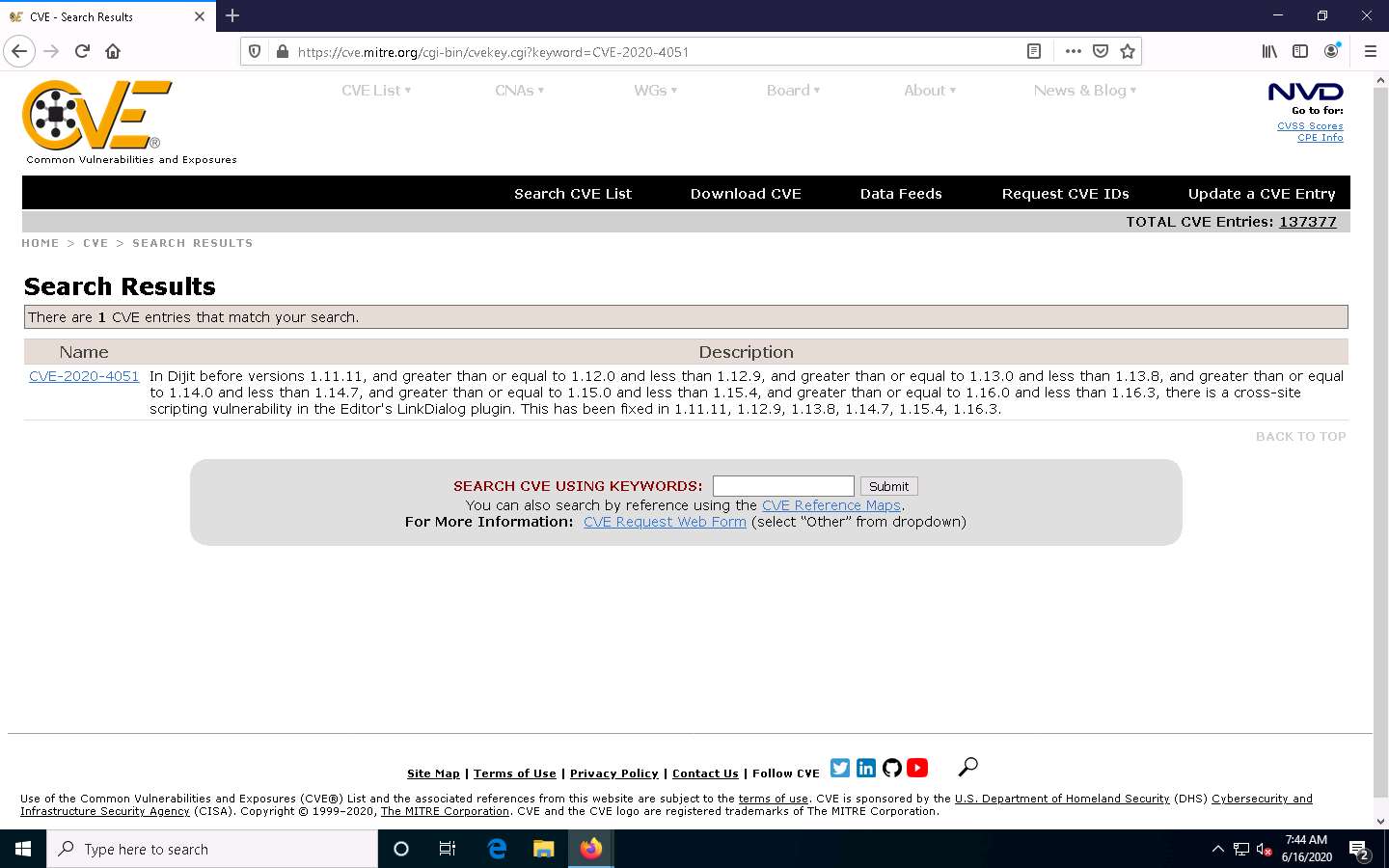
Search Results page appears, displaying the information regarding the searched vulnerability. You can click the vulnerability link to view further detailed information regarding the vulnerability.
Similarly, in the Search CVE List section, you can search for a service-related vulnerability by typing the service name (here, SMB) and click Submit.
You can search for the vulnerabilities of the running services that were found in the target systems in previous module labs (Module 04 Enumeration).
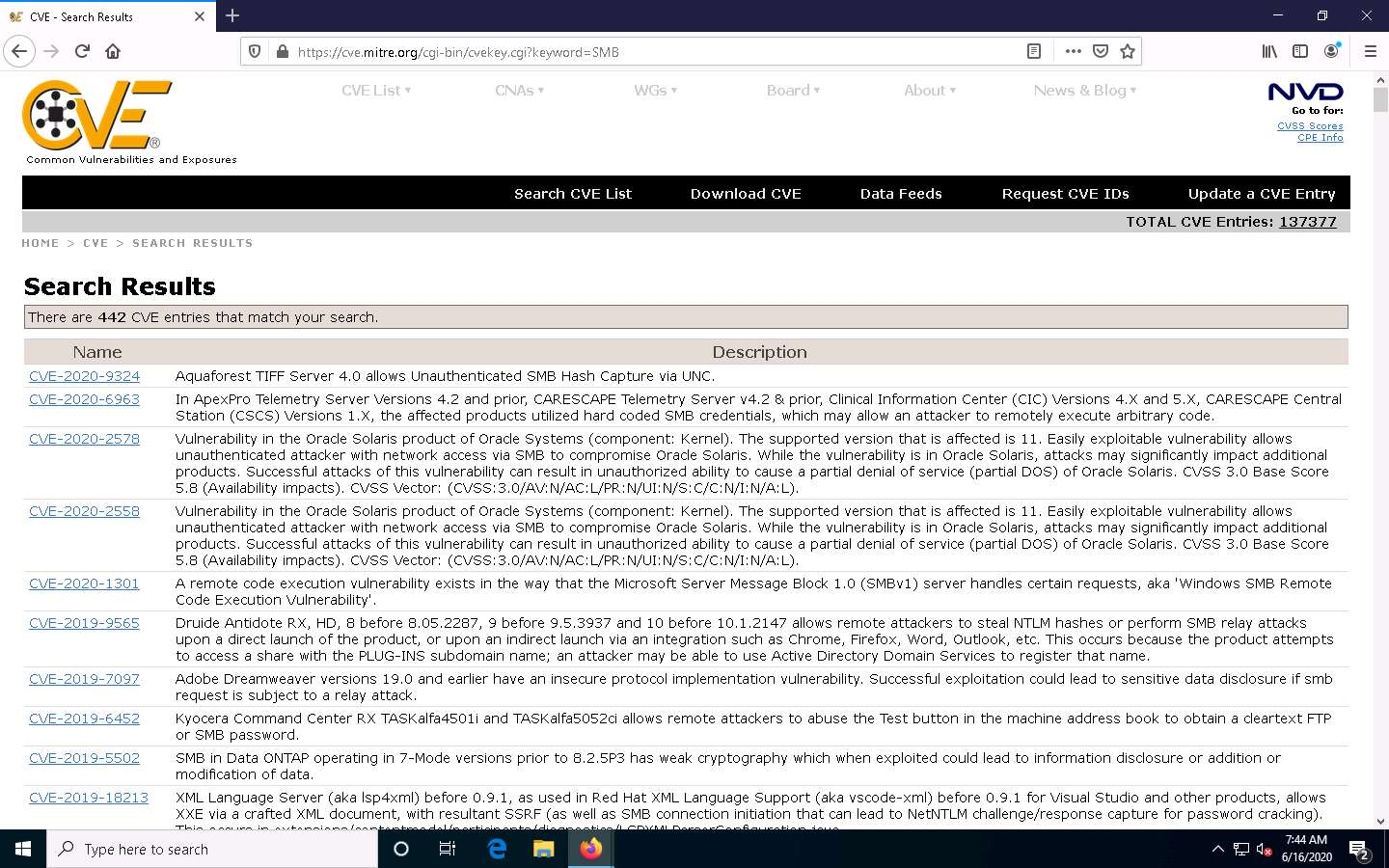
Search Results page appears, displaying a list of vulnerabilities in the target service (SMB) along with their description, as shown in the screenshot.
The results might vary in your lab environment.
Further, you can click on CVE-ID of any vulnerability to view its detailed information. Here, we will click on the first CVE-ID link.
Detailed information regarding the vulnerability is displayed such as its Description, References, and Date Entry Created. Further, you can click on links under the References section to view more information on the vulnerability.
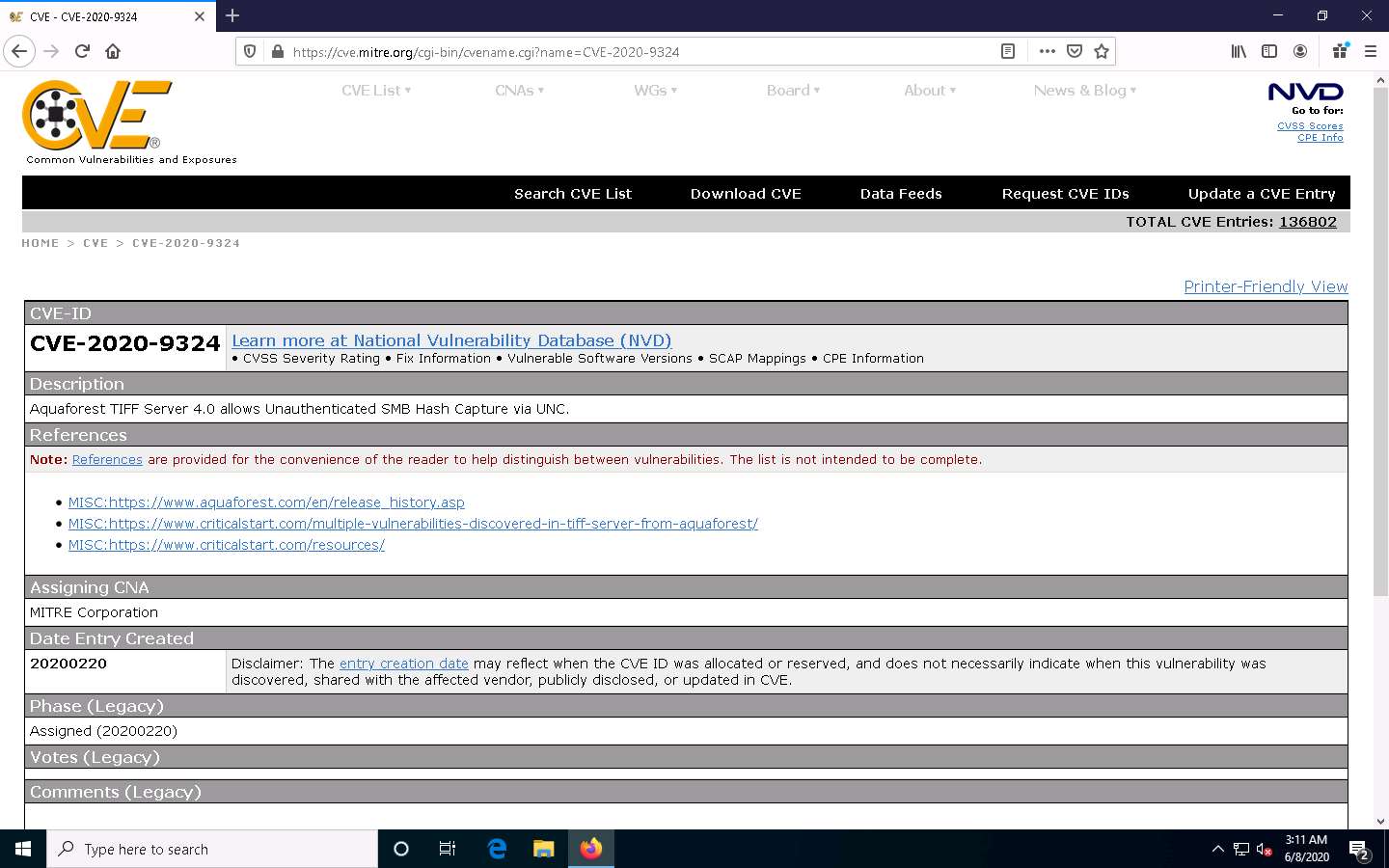
Likewise, you can search for other target services for the underlying vulnerabilities in the Search CVE List section.
This concludes the demonstration of checking vulnerabilities in the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE).
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Task 3: Perform Vulnerability Research in National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) is the U.S. government repository of standards-based vulnerability management data represented using the Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP). These data enable the automation of vulnerability management, security measurement, and compliance. The NVD includes databases of security checklist references, security-related software flaws, misconfigurations, product names, and impact metrics.
Here, we will use the NVD to view the latest underlying system and software vulnerabilities.
In Windows 10 machine, launch any browser (here, Mozilla Firefox). In the address bar of the browser place your mouse cursor and click https://nvd.nist.gov/ and press Enter
NATIONAL VULNERABILITY DATABASE website appears: the recently discovered vulnerabilities can be viewed.
You can click on the CVE-ID link (here, CVE-2020-6269) to view detailed information about the vulnerability.
The results might differ in your lab environment.
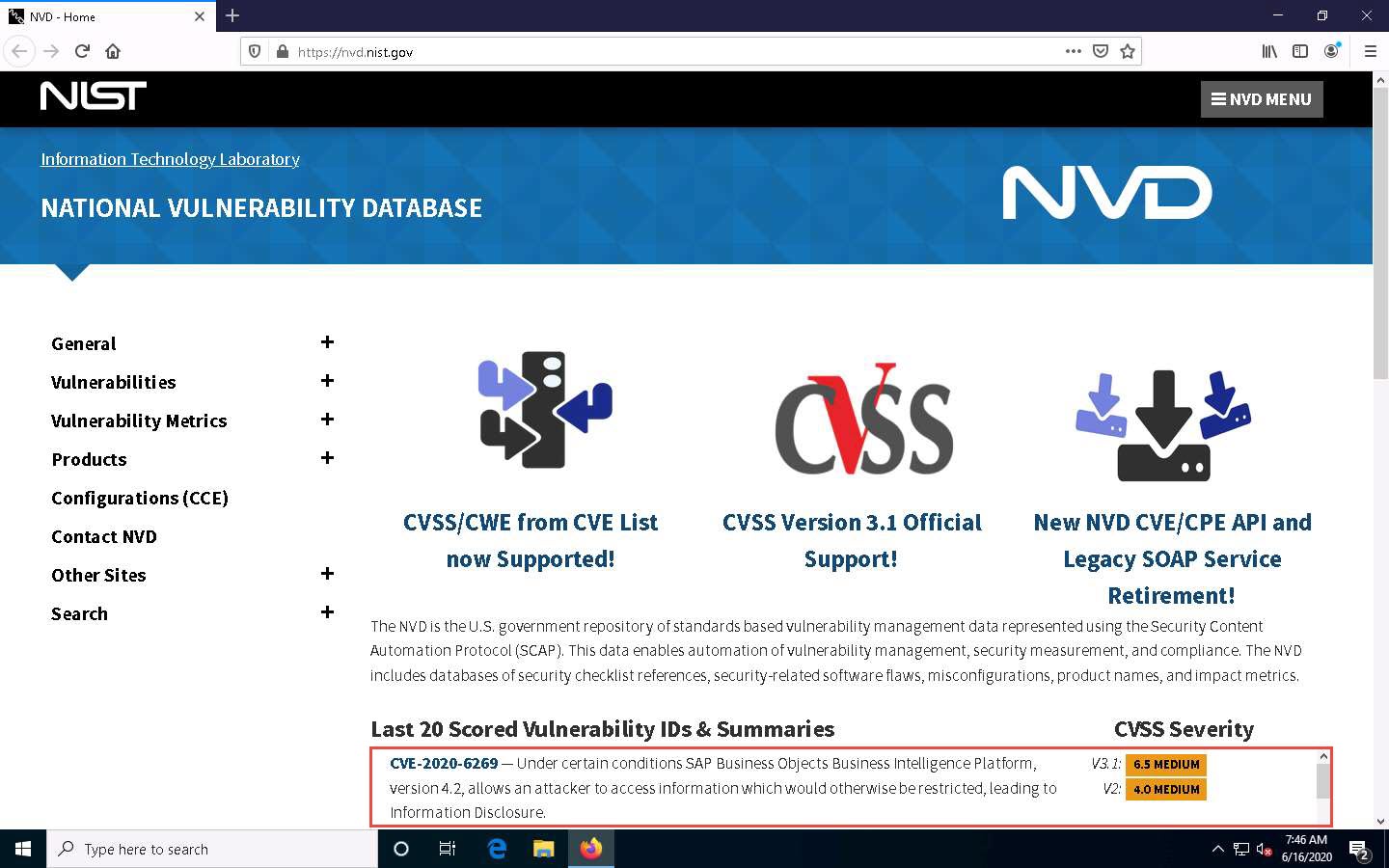
A new webpage appears, displaying CVE-2020-6269 Detail. You can view detailed information such as Current Description, Severity, References, and Weakness Enumeration.
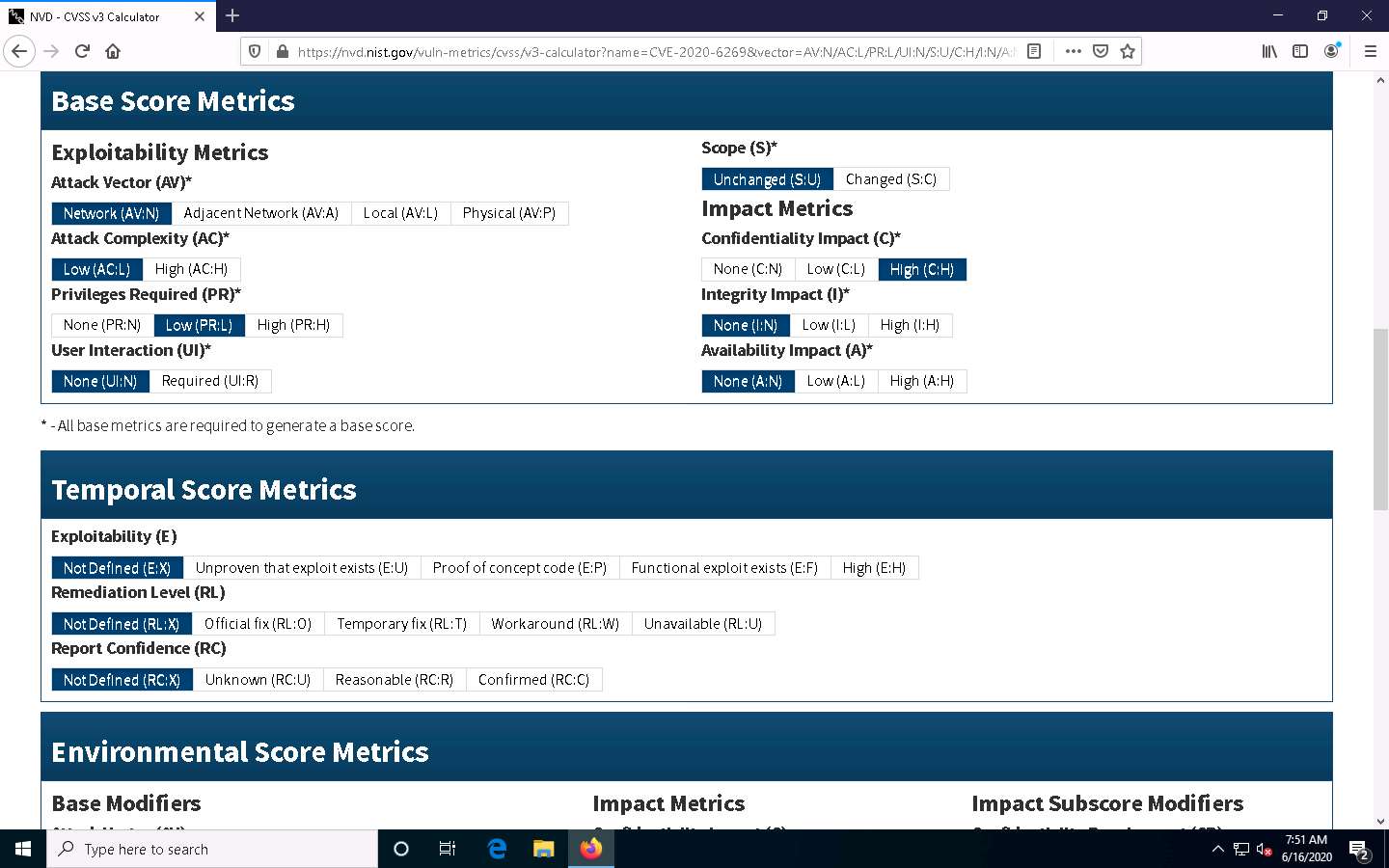
Under the Severity section, click the Base Score link to view the CVSS details regarding the vulnerability.
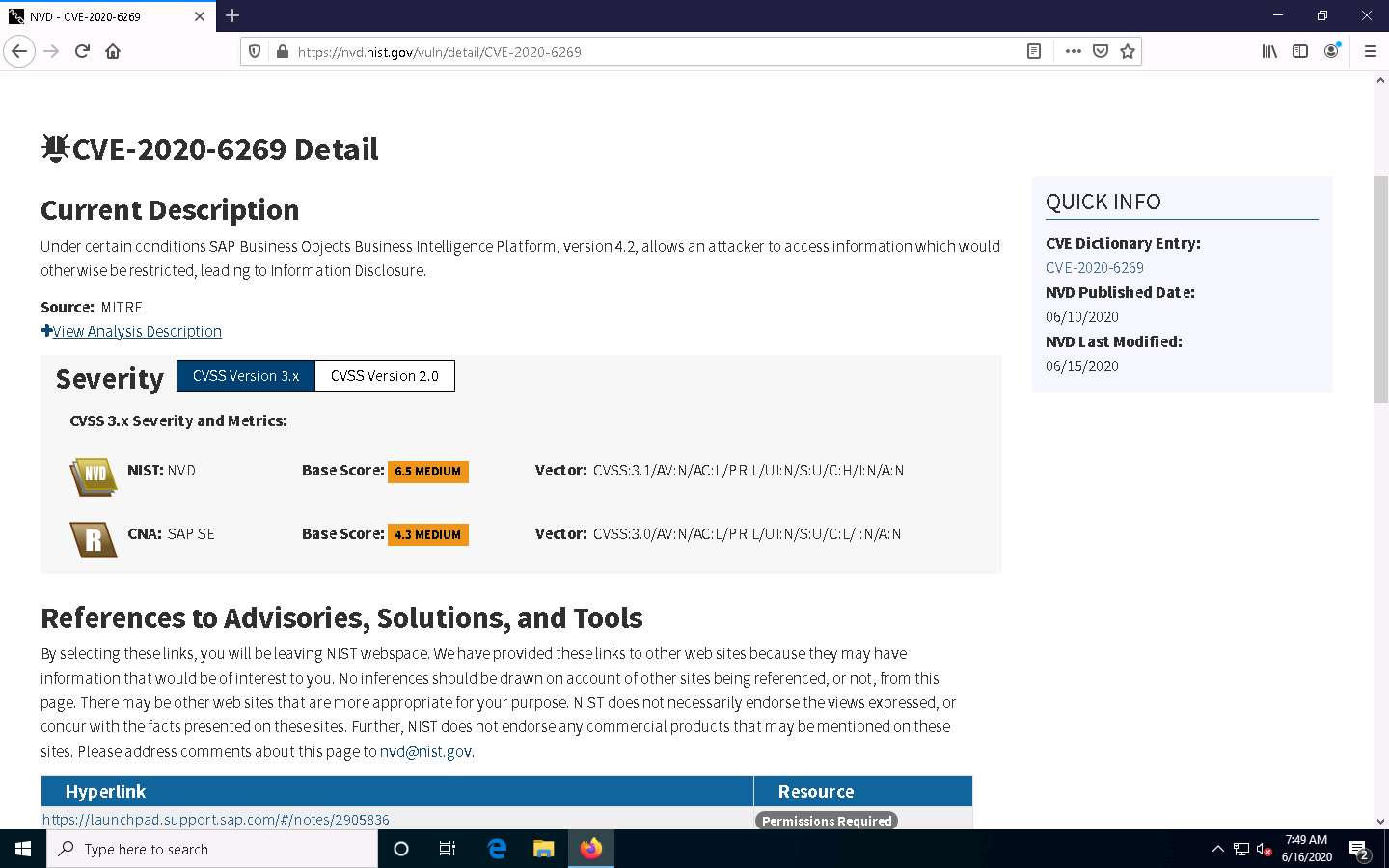
A new webpage appears, displaying information such as Base Scores, Temporal Score, and Environmental Score Overall Score related to a vulnerability in graphical form, under Common Vulnerability Scoring System Calculator CVE-2020-6269.
- Base Score: The metric most relied upon by enterprises and deals with the inherent qualities of a vulnerability. The table below describes the severity of a vulnerability depending upon the Base Score range:
- Temporal Score: Represents the qualities of the vulnerability that change over time, and the Environmental score represents the qualities of the vulnerability that are specific to the affected user's environment.
- Overall Score: Sum total of both the scores (CVSS Base Score, CVSS Temporal Score).
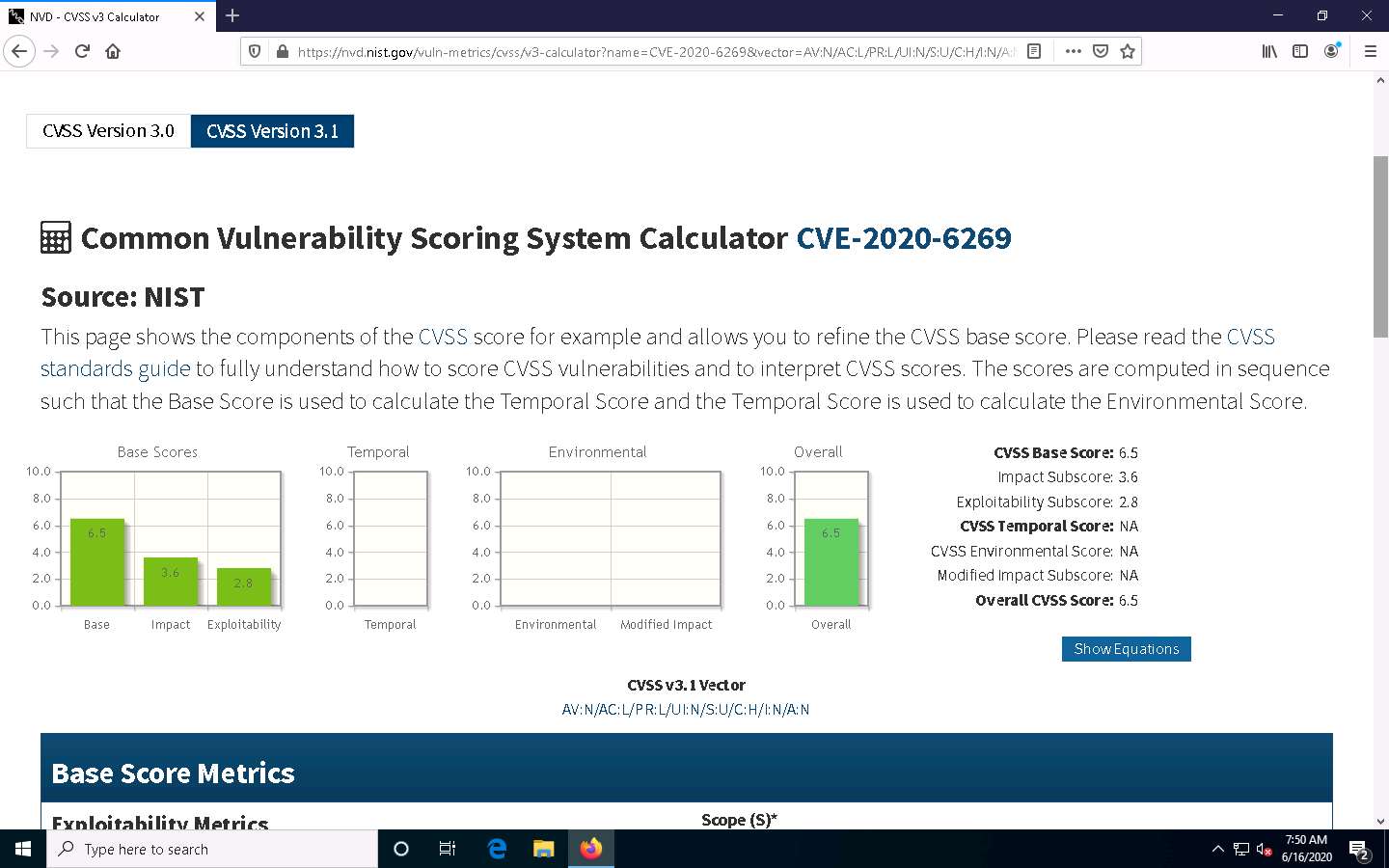
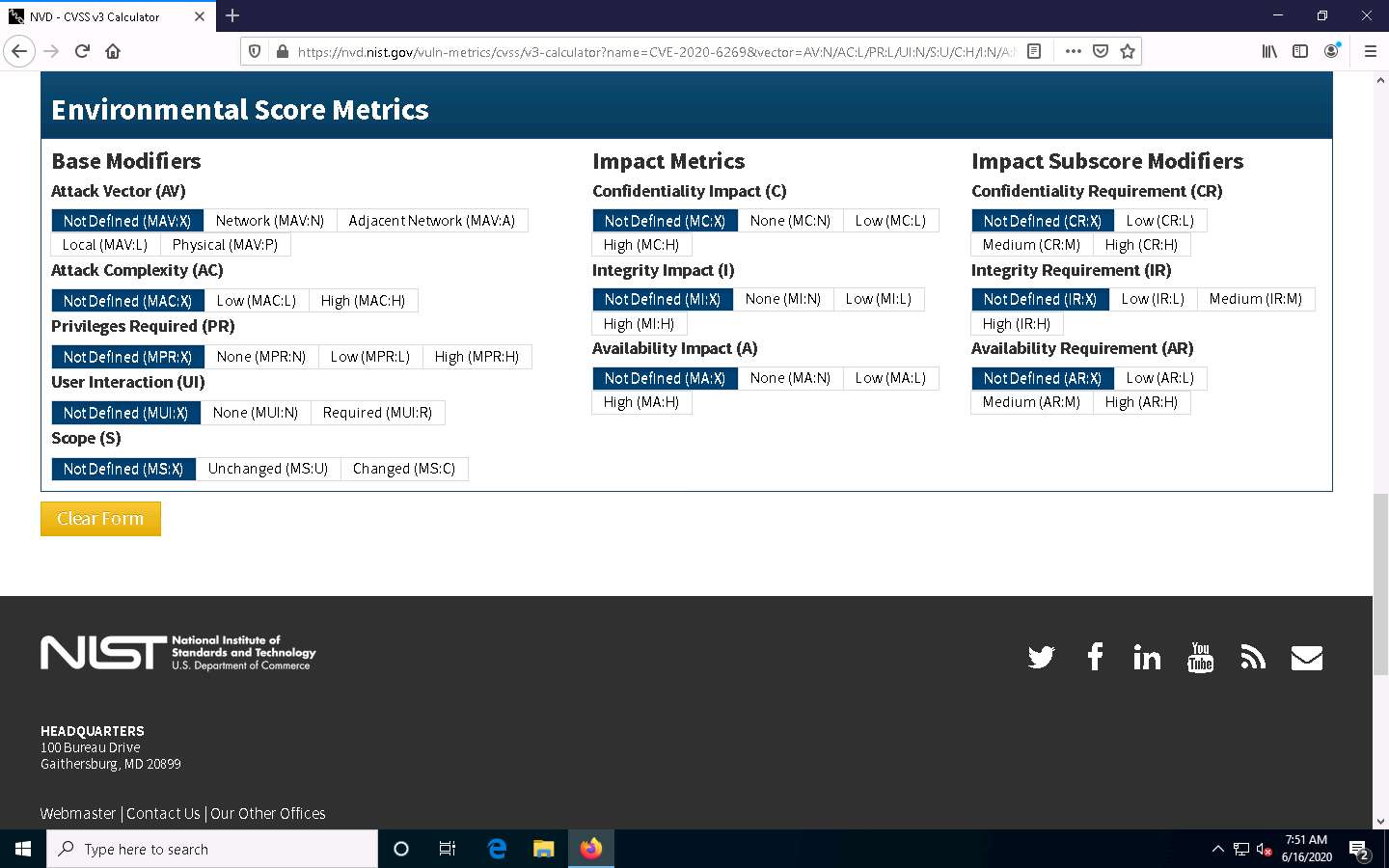
Scroll down to view more detailed information on different score metrics such as Base Score Metrics, Temporal Score Metrics, and Environmental Score Metrics.
The results might differ depending upon the selected vulnerability
Now, navigate back to the main page of the NATIONAL VULNERABILITY DATABASE website. Expand Vulnerabilities and click Search & Statistics option, as shown in the screenshot.
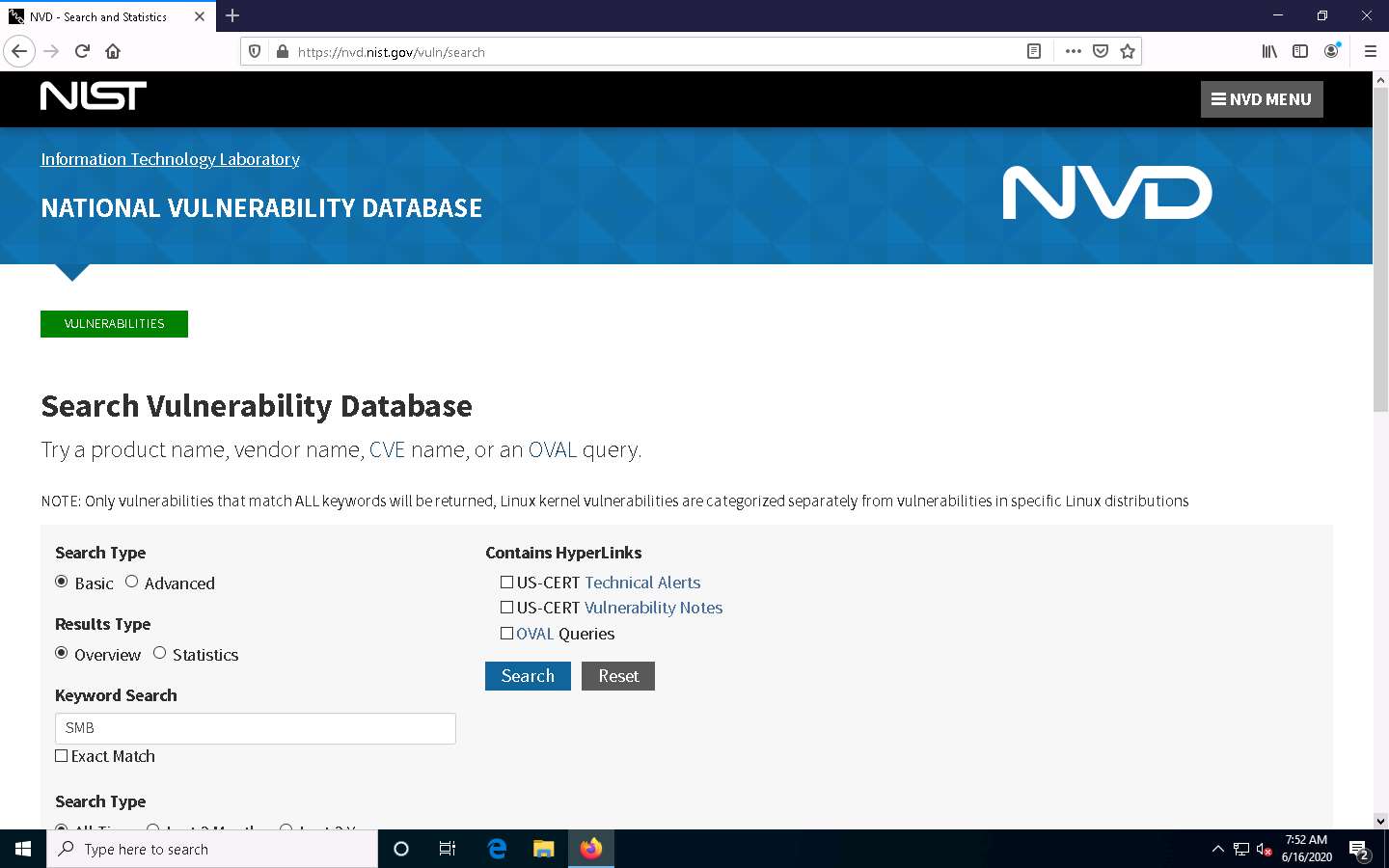
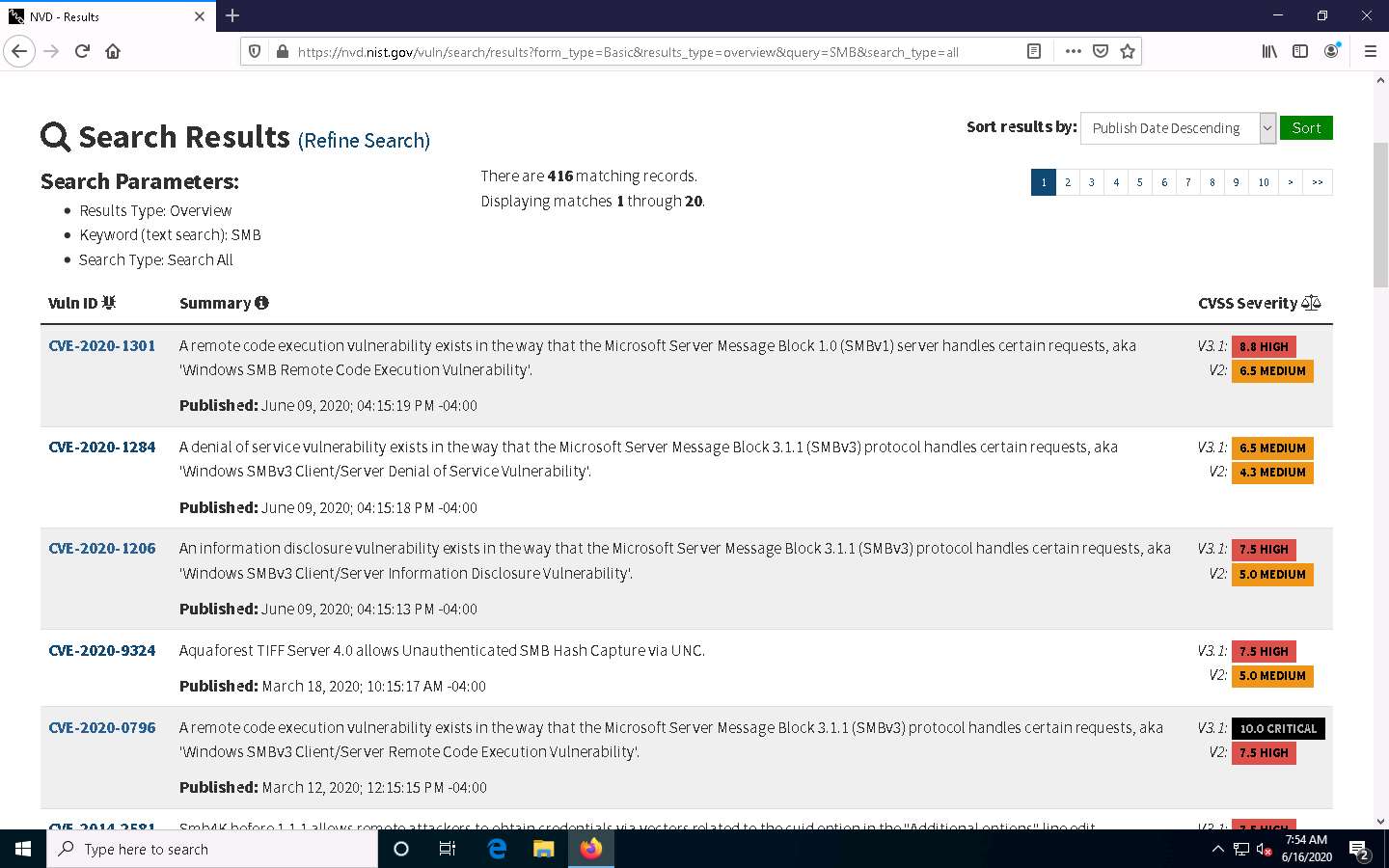
Search Vulnerability Database page appears. In the Keyword Search field, type a target service (here, SMB) to find vulnerabilities associated with it and click Search.
You can search for the vulnerabilities of the running services that were found in the target systems in previous module labs (Module 04 Enumeration).
The Search Results page appears, displaying detailed information on the underlying vulnerabilities in the target service.
You can further view detailed information on each vulnerability by clicking on the Vuln ID link.
Likewise, you can search for other target services for the underlying vulnerability in the Search Vulnerability Database section.
This concludes the demonstration of checking vulnerabilities in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD).
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Comments
Post a Comment