Lab 1: Perform Social Engineering using Various Techniques
Lab 1: Perform Social Engineering using Various Techniques
Module 09: Social Engineering
Lab 1: Perform Social Engineering using Various Techniques
Task 1: Sniff Credentials using the Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET)
The Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET) is an open-source Python-driven tool aimed at penetration
testing via social engineering. SET is particularly useful to attackers, because it is freely
available and can be used to carry out a range of attacks. For example, it allows attackers to
draft email messages, attach malicious files, and send them to a large number of people using spear
phishing. Moreover, SET’s multi-attack method allows Java applets, the Metasploit browser, and Credential
Harvester/Tabnabbing to be used simultaneously. SET categorizes attacks according to the attack vector used
such as email, web, and USB.
Although many kinds of attacks can be carried out using SET, it is also a must-have tool for penetration
testers to check for vulnerabilities. For this reason, SET is the standard for social engineering penetration
tests, and is strongly supported within the security community.
As an ethical hacker, penetration tester, or security administrator, you should be familiar with SET and be
able to use it to perform various tests for network vulnerabilities.
refer to blog
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Module 09: Social Engineering
Lab 1: Perform Social Engineering using Various Techniques
Task 2: Perform Phishing using ShellPhish
In a phishing attack, an attacker poses as a legitimate website or company by registering a fake domain name,
building a lookalike website, and then mailing a link to the fake website to several users. When users click on
the link, they are redirected to the fake webpage, where they are lured into sharing sensitive details such as
contact details, account numbers, or credit card information, without realizing that they are on a phishing site.
In phishing attacks, phishers (attackers) can target individuals who avail bank and online payment services. They
send messages to bank customers that claim to be from a bank and appear legitimate, because attackers use
manipulated URLs and website forgery to deceive victims. Not realizing that they are on a fake website, users
provide their personal information and bank details. However, it is not only bank customers who are targeted,
hackers are also increasingly engaging in spear-phishing campaigns against bank employees.
Various phishing techniques include:
Spear Phishing: A targeted attack aimed at specific individuals within an organization
Whaling: An attack that targets high profile executives like CEOs, CFOs, politicians, and celebrities, who have
extensive access to confidential and highly valuable information
Pharming: An attack in which web traffic is redirected to a fraudulent website by installing a malicious
program on a personal computer or server
Spimming: A variant of spam that exploits Instant Messaging platforms to flood spam across the network
ShellPhish is a phishing tool used to obtain user credentials for various social networking platforms such as
Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. It can also provide the victim system’s public IP address, browser
information, hostname, and geolocation
refer to blog
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Lab Scenario
As a professional ethical hacker or penetration tester, you should use various social engineering techniques to examine the security of an organization and the awareness of employees.
In a social engineering test, you should try to trick the user into disclosing personal information such as credit card numbers, bank account details, telephone numbers, or confidential information about their organization or computer system. In the real world, attackers would use these details either to commit fraud or to launch further attacks on the target system
Lab Objectives
- Sniff Credentials using the Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET)
- Perform phishing using ShellPhish
Overview of Social Engineering Techniques
There are three types of social engineering attacks: human-, computer-, and mobile-based.
- Human-based social engineering uses interaction to gather sensitive information, employing techniques such as impersonation, vishing, and eavesdropping
- Computer-based social engineering uses computers to extract sensitive information, employing techniques such as phishing, spamming, and instant messaging
- Mobile-based social engineering uses mobile applications to obtain information, employing techniques such as publishing malicious apps, repackaging legitimate apps, using fake security applications, and SMiShing (SMS Phishing)
Task 1: Sniff Credentials using the Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET)
The Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET) is an open-source Python-driven tool aimed at penetration testing via social engineering. SET is particularly useful to attackers, because it is freely available and can be used to carry out a range of attacks. For example, it allows attackers to draft email messages, attach malicious files, and send them to a large number of people using spear phishing. Moreover, SET’s multi-attack method allows Java applets, the Metasploit browser, and Credential Harvester/Tabnabbing to be used simultaneously. SET categorizes attacks according to the attack vector used such as email, web, and USB.
Although many kinds of attacks can be carried out using SET, it is also a must-have tool for penetration testers to check for vulnerabilities. For this reason, SET is the standard for social engineering penetration tests, and is strongly supported within the security community.
As an ethical hacker, penetration tester, or security administrator, you should be familiar with SET and be able to use it to perform various tests for network vulnerabilities.
Here, we will sniff Facebook credentials using the SET.
Click on Parrot Security to switch to the Parrot Security machine.
In the login page, the attacker username will be selected by default. Enter password as toor in the Password field and press Enter to log in to the machine.
If a Question pop-up window appears asking you to update the machine, click No to close the window.
Click the MATE Terminal icon at the top of the Desktop window to open a Terminal window.
A Parrot Terminal window appears. In the terminal window, type sudo su and press Enter to run the programs as a root user.
In the [sudo] password for attacker field, type toor as a password and press Enter.
The password that you type will not be visible.
Now, type cd and press Enter to jump to the root directory.
Type cd setoolkit and press Enter to navigate to the setoolkit folder.
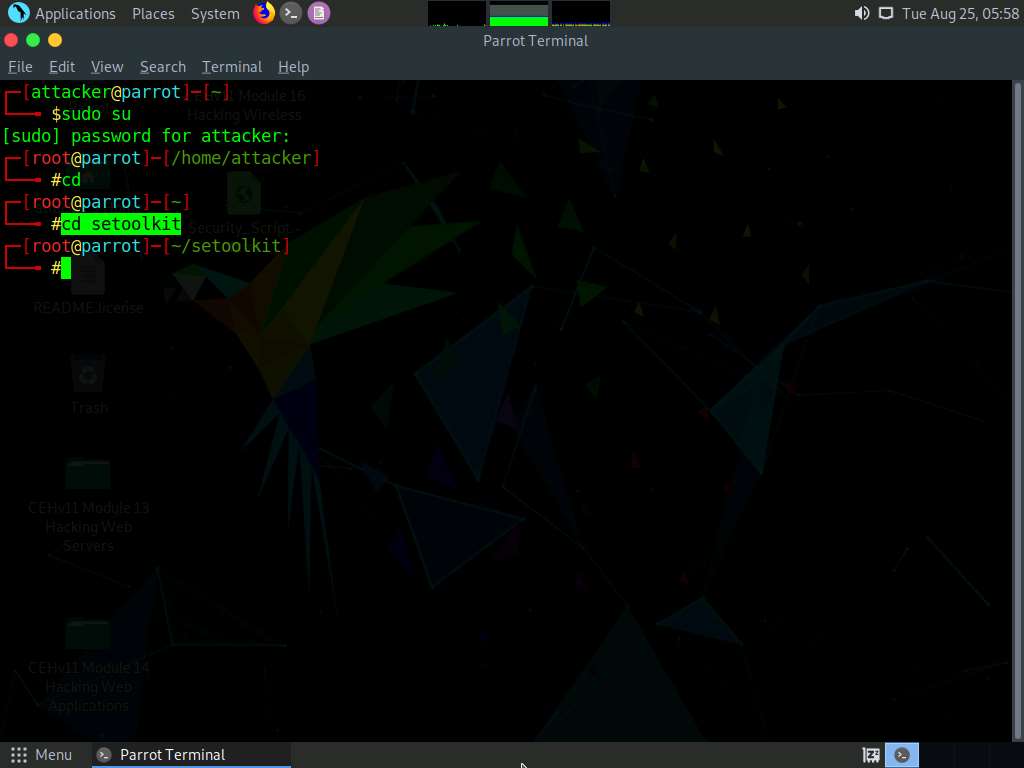
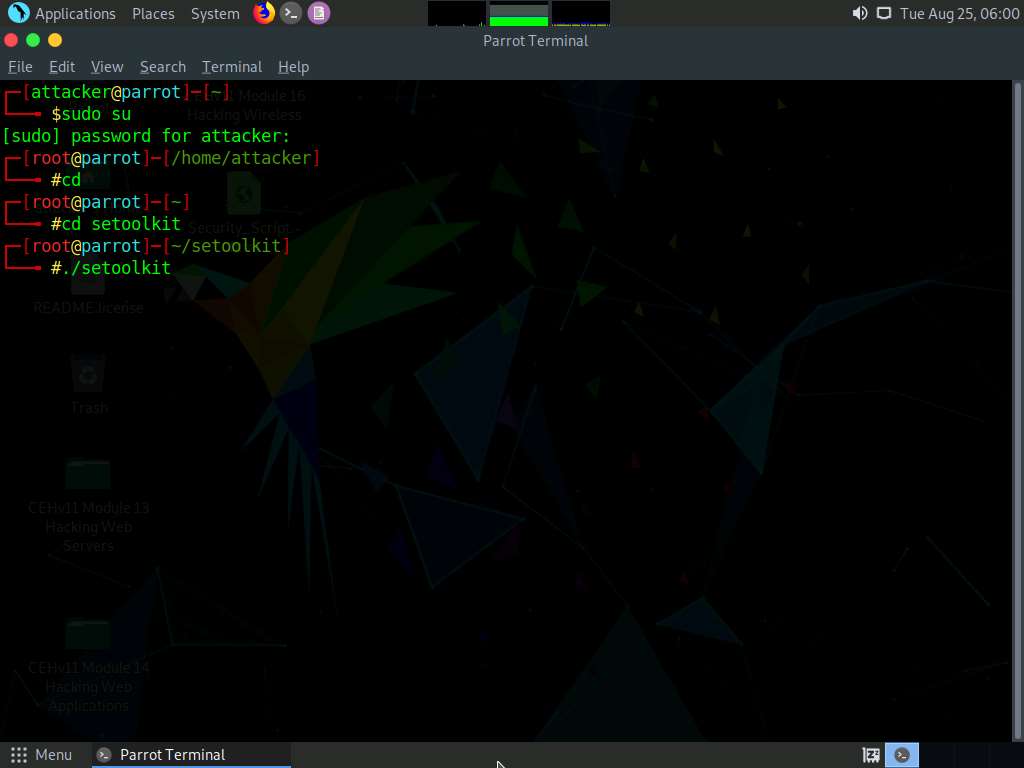
Now, type ./setoolkit and press Enter to launch Social-Engineer Toolkit.
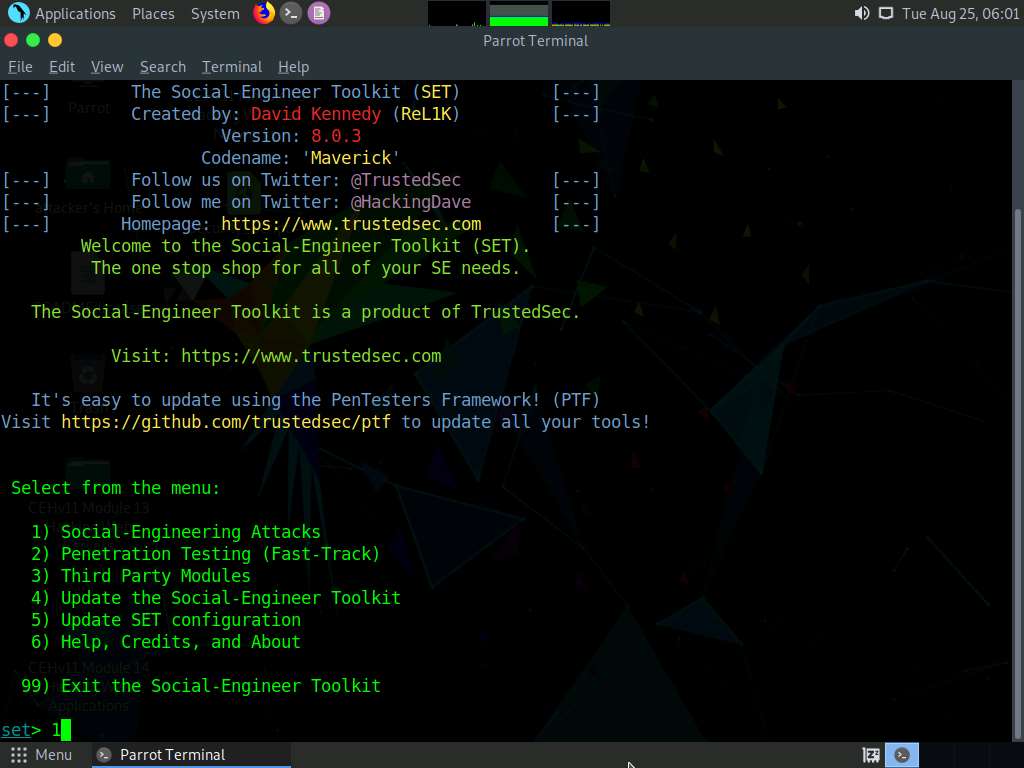
The SET menu appears, as shown in the screenshot. Type 1 and press Enter to choose Social-Engineering Attacks
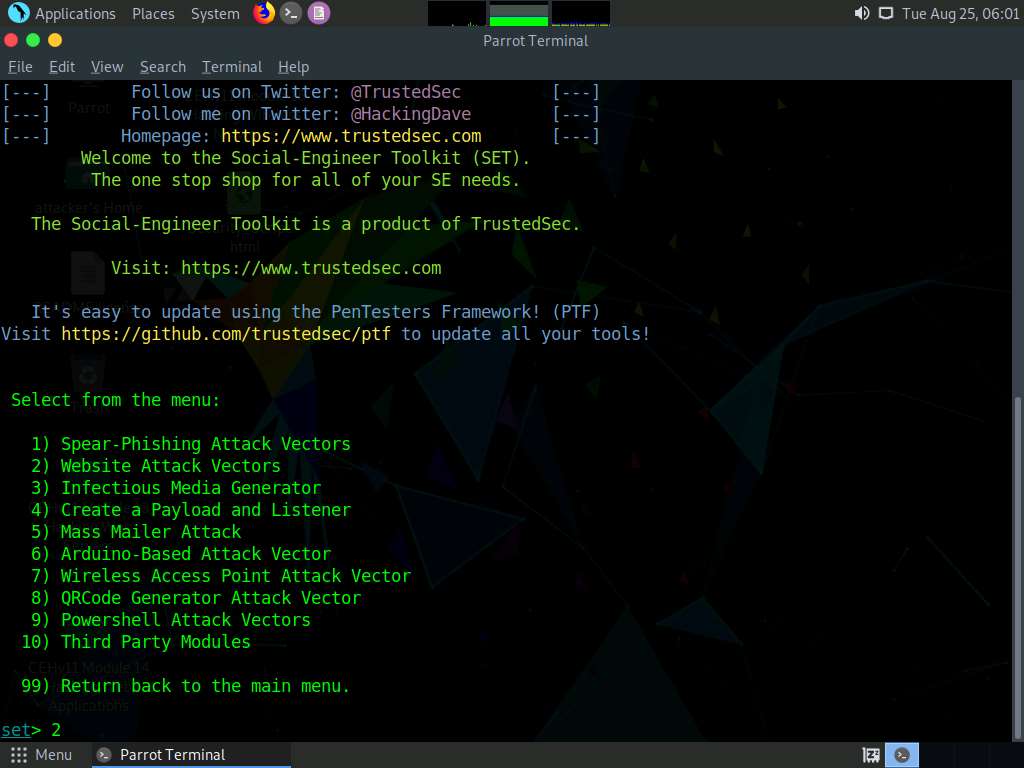
A list of options for Social-Engineering Attacks appears; type 2 and press Enter to choose Website Attack Vectors.
A list of options in Website Attack Vectors appears; type 3 and press Enter to choose Credential Harvester Attack Method.
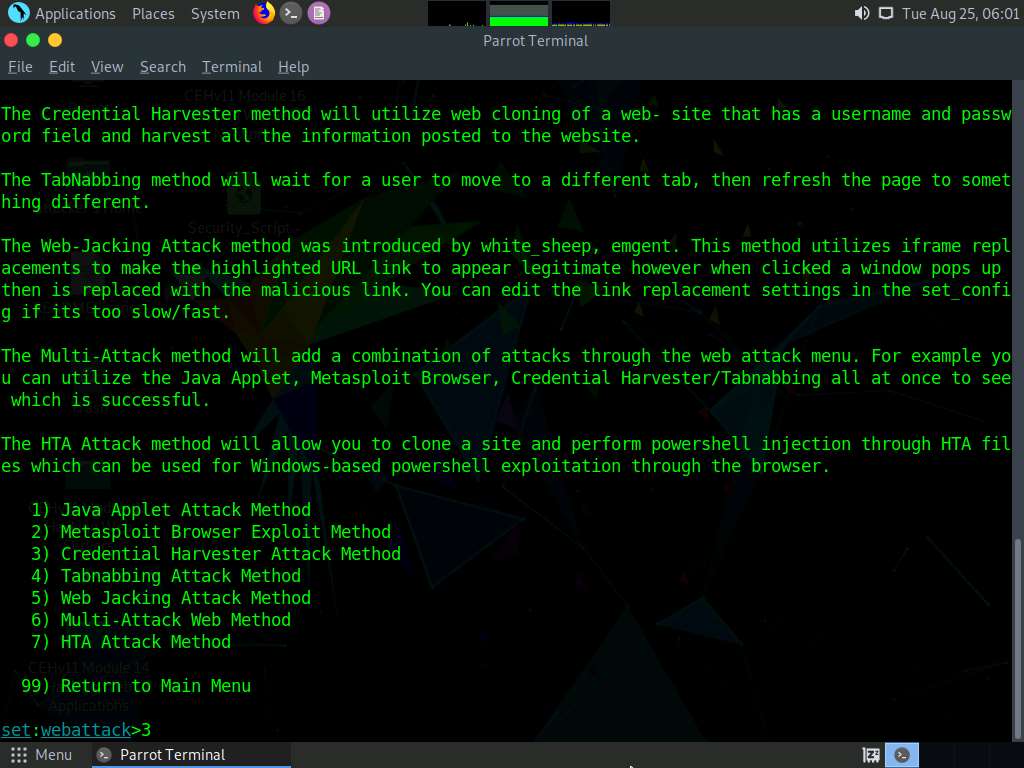
Type 2 and press Enter to choose Site Cloner from the menu.
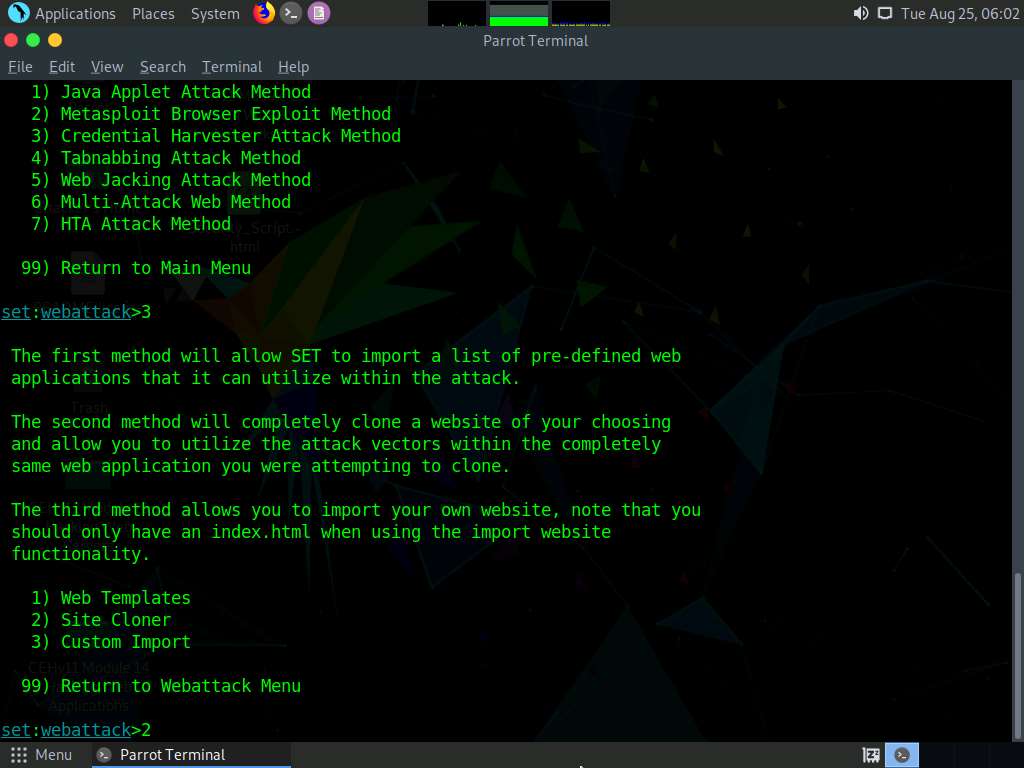
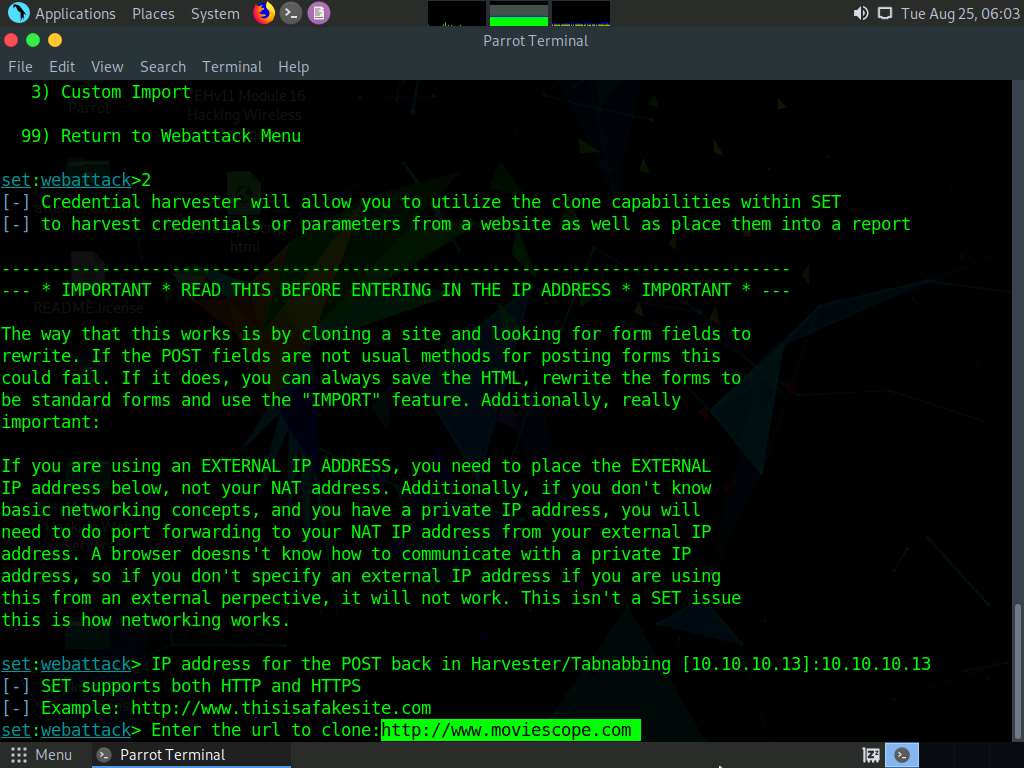
Type the IP address of the local machine (10.10.10.13) in the prompt for “IP address for the POST back in Harvester/Tabnabbing” and press Enter.
In this case, we are targeting the Parrot Security machine (IP address: 10.10.10.13). These details may vary in your lab environment.
Now, you will be prompted for the URL to be cloned; type the desired URL in “Enter the url to clone” and press Enter. In this task, we will clone the URL http://www.moviescope.com.
You can clone any URL of your choice.
If a message appears that reads Press {return} if you understand what we’re saying here, press Enter.
After cloning is completed, a highlighted message appears. The credential harvester initiates, as shown in the screenshot.
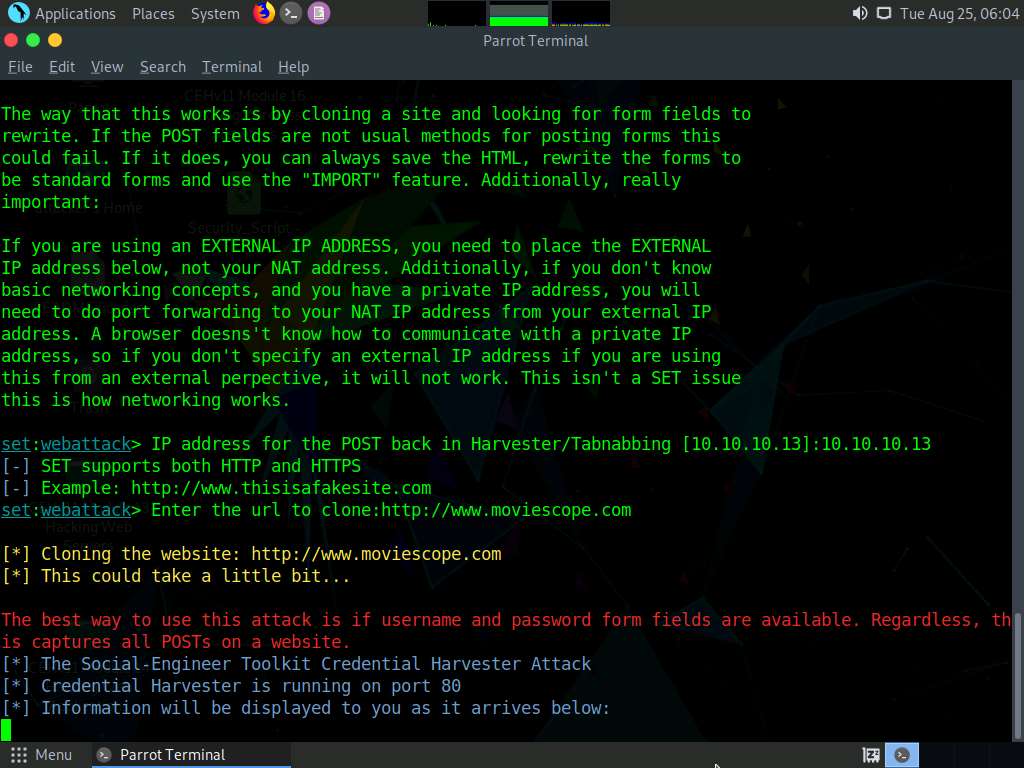
Having successfully cloned a website, you must now send the IP address of your Parrot Security machine to a victim and try to trick him/her into clicking on the link.
Click Firefox icon from the top-section of the Desktop to launch a web browser window and open your email account (in this example, we are using Mozilla Firefox and Gmail, respectively). Log in, and compose an email.
You can log in to any email account of your choice.
After logging into your email account, click the Compose button in the left pane and compose a fake but enticing email to lure a user into opening the email and clicking on a malicious link.
A good way to conceal a malicious link in a message is to insert text that looks like a legitimate MovieScope URL (in this case), but that actually links to your malicious cloned MovieScope page.
Position the cursor where you wish to place the fake URL, then click the Insert link icon.
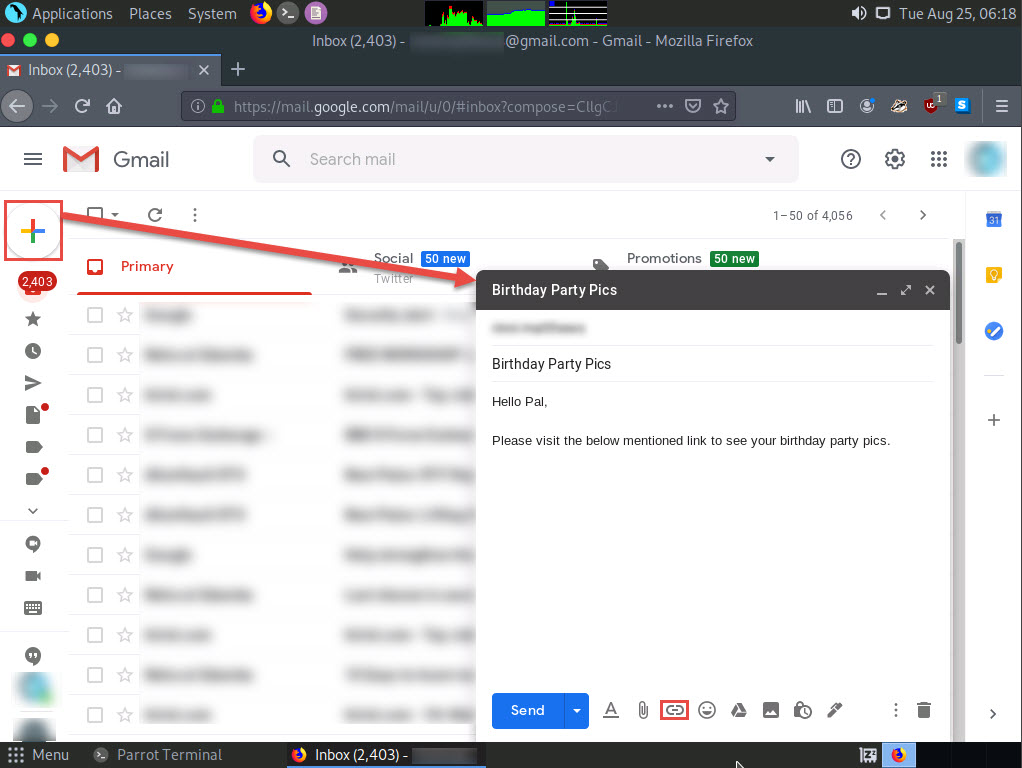
In the Edit Link window, first type the actual address of your cloned site in the Web address field under the Link to section. Then, type the fake URL in the Text to display field. In this case, the actual address of our cloned MovieScope site is http://10.10.10.13, and the text that will be displayed in the message is http://www.moviescope.com/party_pics; click OK.
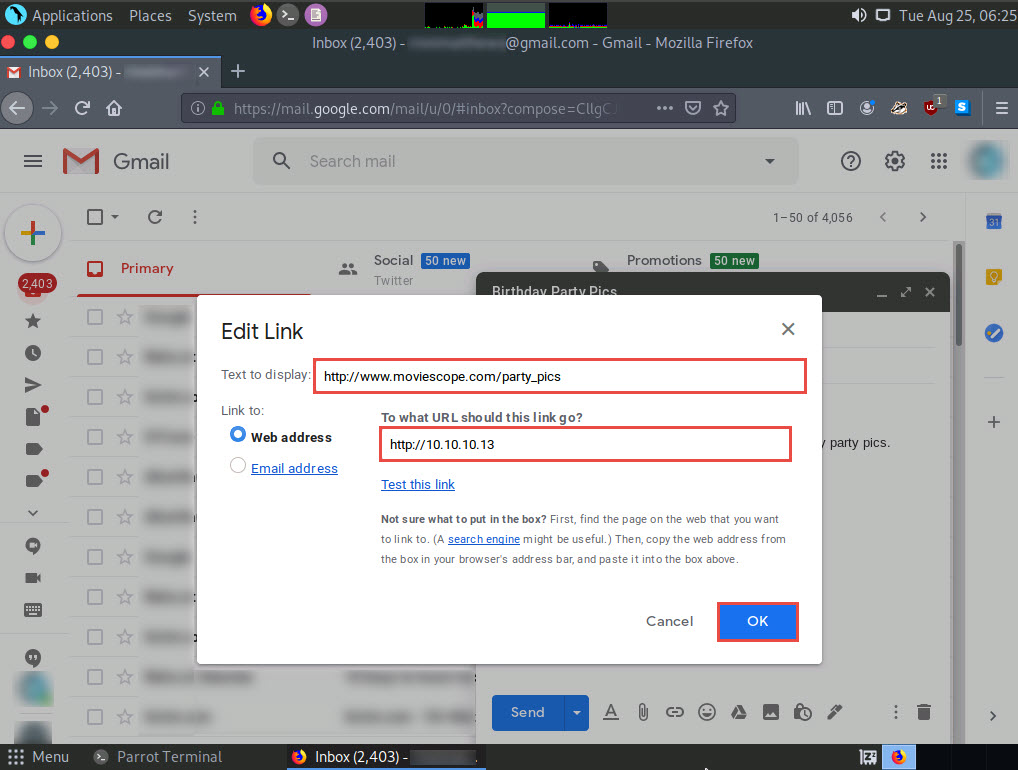
The fake URL should appear in the message body, as shown in the screenshot.
Verify that the fake URL is linked to the correct cloned site: in Gmail, click the link; the actual URL will be displayed in a “Go to link” pop-up. Once verified, send the email to the intended user.
Click Windows 10 to switch to the Windows 10 machine and click Ctrl+Alt+Delete. By default, Admin user profile is selected, click Pa$$w0rd paste the password in the Password field and press Enter to login.
Alternatively, you can also click Pa$$w0rd under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Type Text | Type Password button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
If Welcome to Windows wizard appears, click Continue and in Sign in with Microsoft wizard, click Cancel.
Networks screen appears, click Yes to allow your PC to be discoverable by other PCs and devices on the network.
Open any web browser (in this example, we are using Mozilla Firefox), sign in to the email account to which you sent the phishing mail as an attacker. Open the email you sent previously and click to open the malicious link.
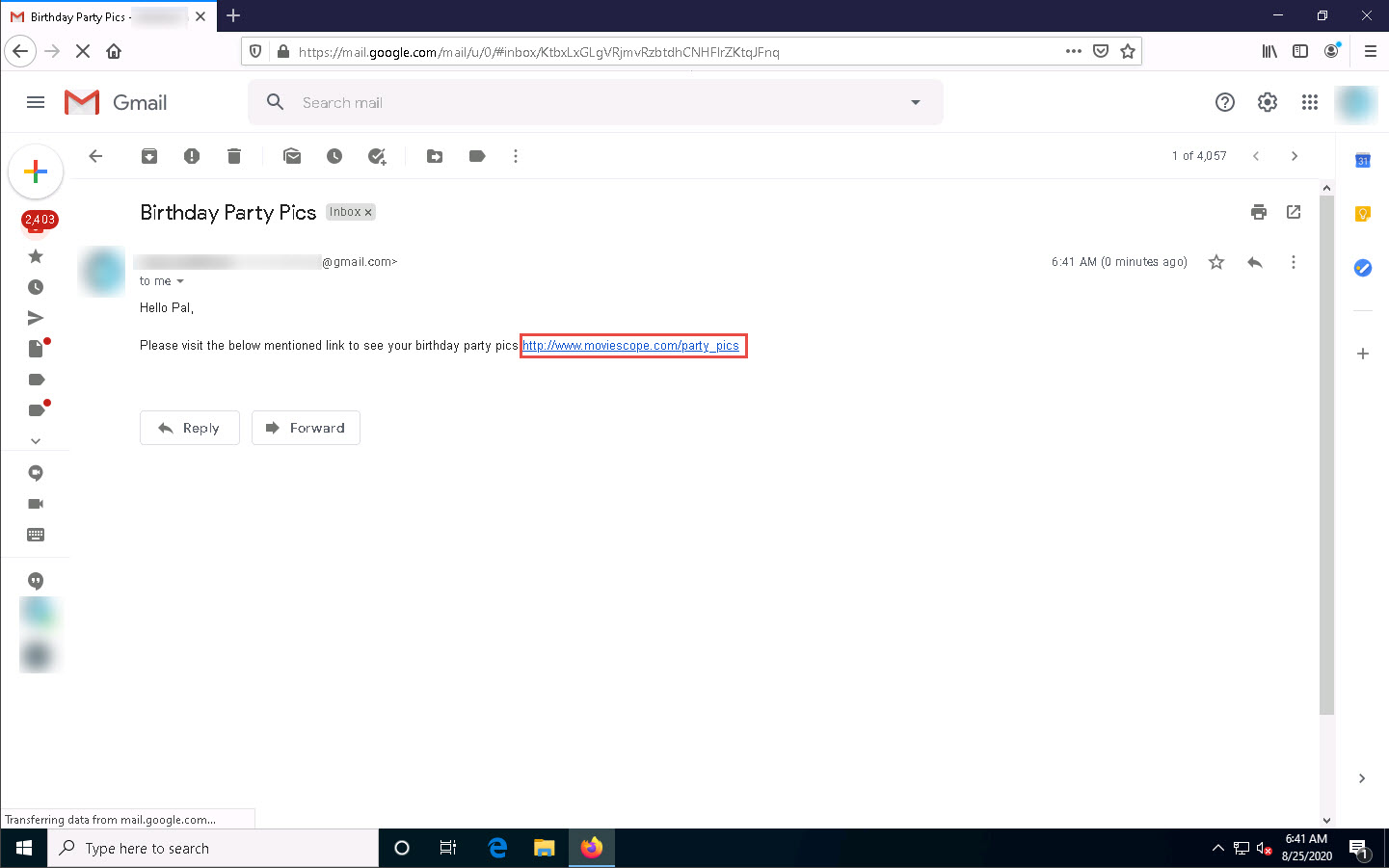
When the victim (you in this case) clicks the URL, a new tab opens up, and he/she will be presented with a replica of www.moviescope.com.
The victim will be prompted to enter his/her username and password into the form fields, which appear as they do on the genuine website. When the victim enters the Username and Password and clicks Login, he/she will be redirected to the legitimate MovieScope login page. Note the different URLs in the browser address bar for the cloned and real sites.
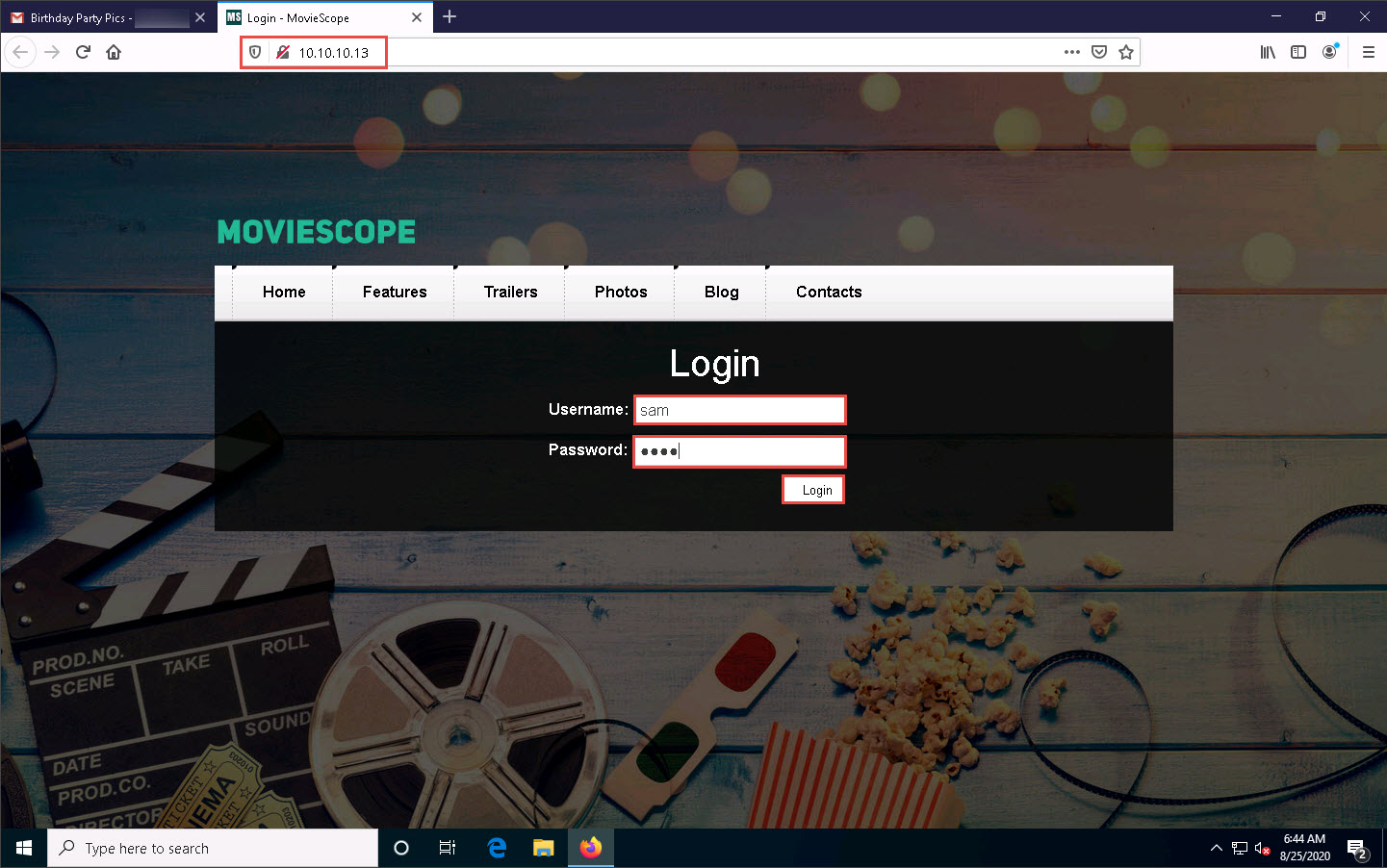
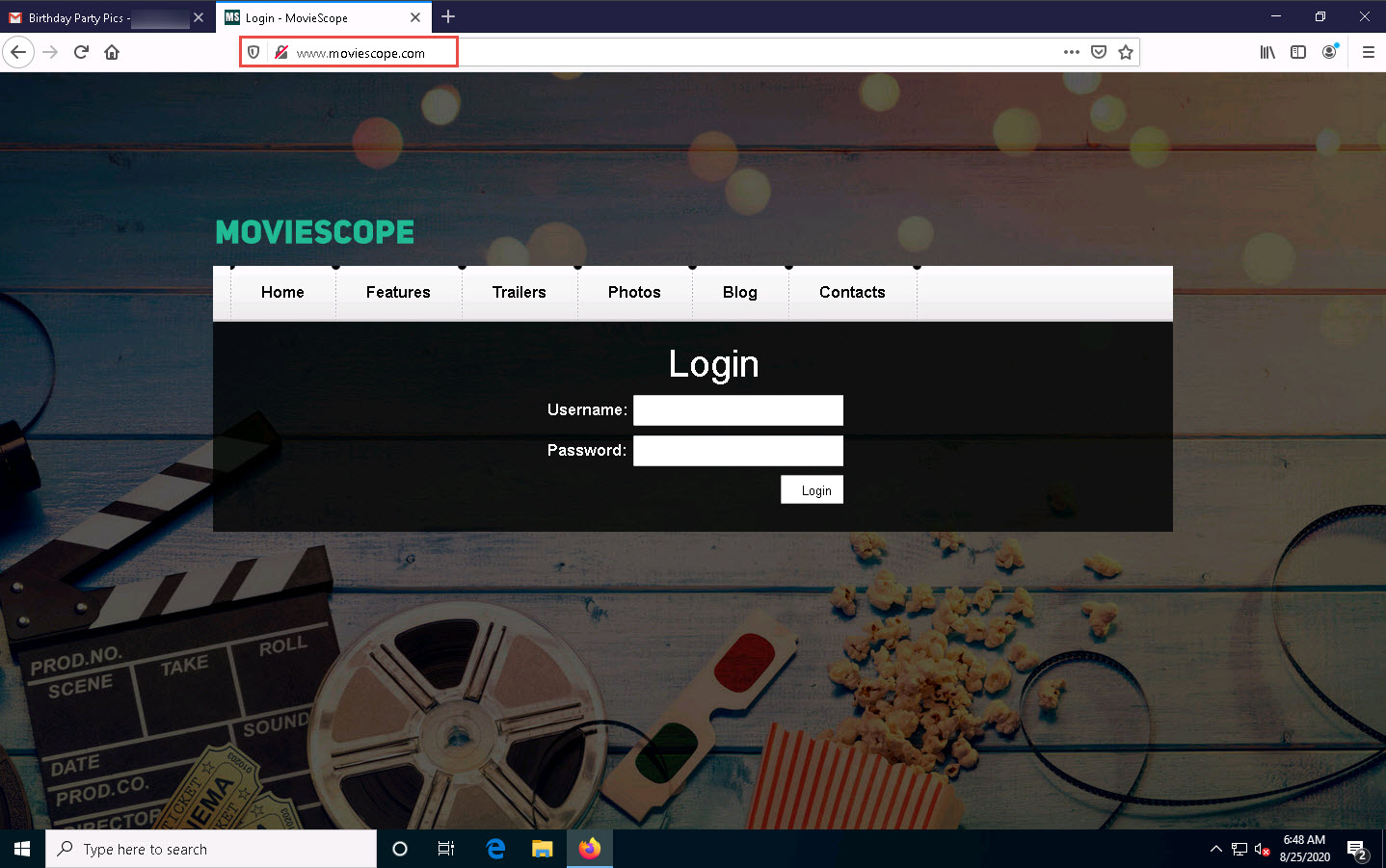
Now, click Parrot Security to switch back to the Parrot Security machine and switch to the terminal window.
As soon as the victim types in his/her Username and Password and clicks Login, SET extracts the typed credentials. These can now be used by the attacker to gain unauthorized access to the victim’s account.
Scroll down to find Username and Password displayed in plain text, as shown in the screenshot.
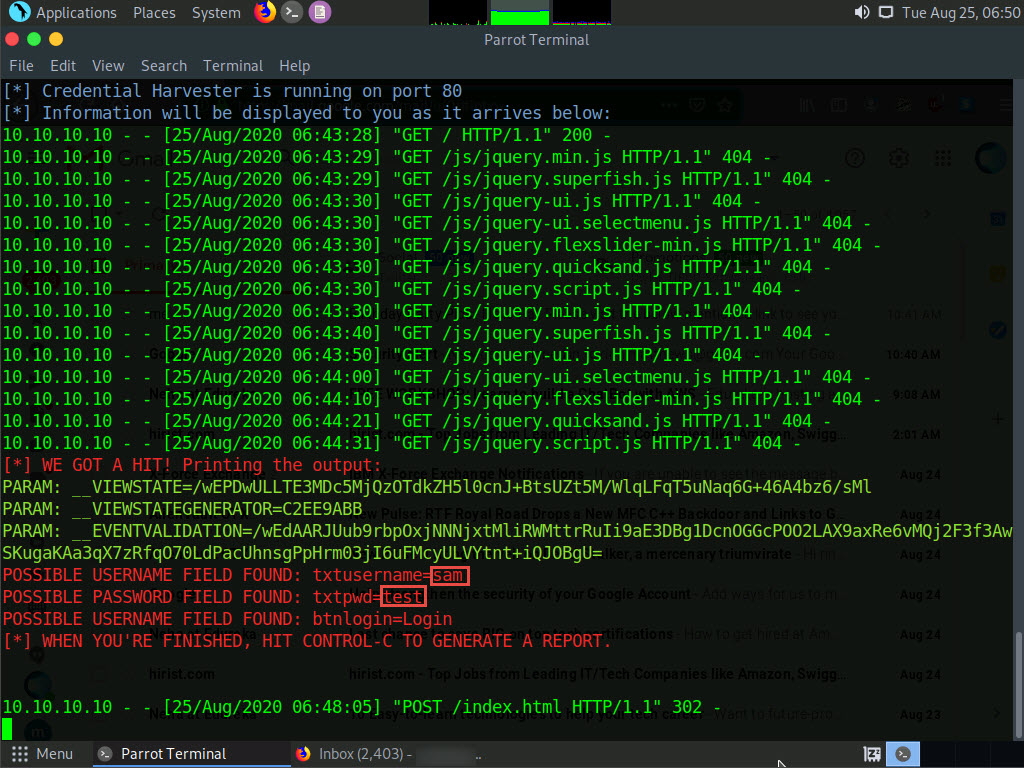
This concludes the demonstration of phishing user credentials using the SET.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Task 2: Perform Phishing using ShellPhish
In a phishing attack, an attacker poses as a legitimate website or company by registering a fake domain name, building a lookalike website, and then mailing a link to the fake website to several users. When users click on the link, they are redirected to the fake webpage, where they are lured into sharing sensitive details such as contact details, account numbers, or credit card information, without realizing that they are on a phishing site.
In phishing attacks, phishers (attackers) can target individuals who avail bank and online payment services. They send messages to bank customers that claim to be from a bank and appear legitimate, because attackers use manipulated URLs and website forgery to deceive victims. Not realizing that they are on a fake website, users provide their personal information and bank details. However, it is not only bank customers who are targeted, hackers are also increasingly engaging in spear-phishing campaigns against bank employees.
Various phishing techniques include:
- Spear Phishing: A targeted attack aimed at specific individuals within an organization
- Whaling: An attack that targets high profile executives like CEOs, CFOs, politicians, and celebrities, who have extensive access to confidential and highly valuable information
- Pharming: An attack in which web traffic is redirected to a fraudulent website by installing a malicious program on a personal computer or server
- Spimming: A variant of spam that exploits Instant Messaging platforms to flood spam across the network
ShellPhish is a phishing tool used to obtain user credentials for various social networking platforms such as Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. It can also provide the victim system’s public IP address, browser information, hostname, and geolocation
Here, we will use ShellPhish to mount a phishing attack with a cloned Instagram login page
Click the MATE Terminal icon at the top of the Desktop window to open a Terminal window.
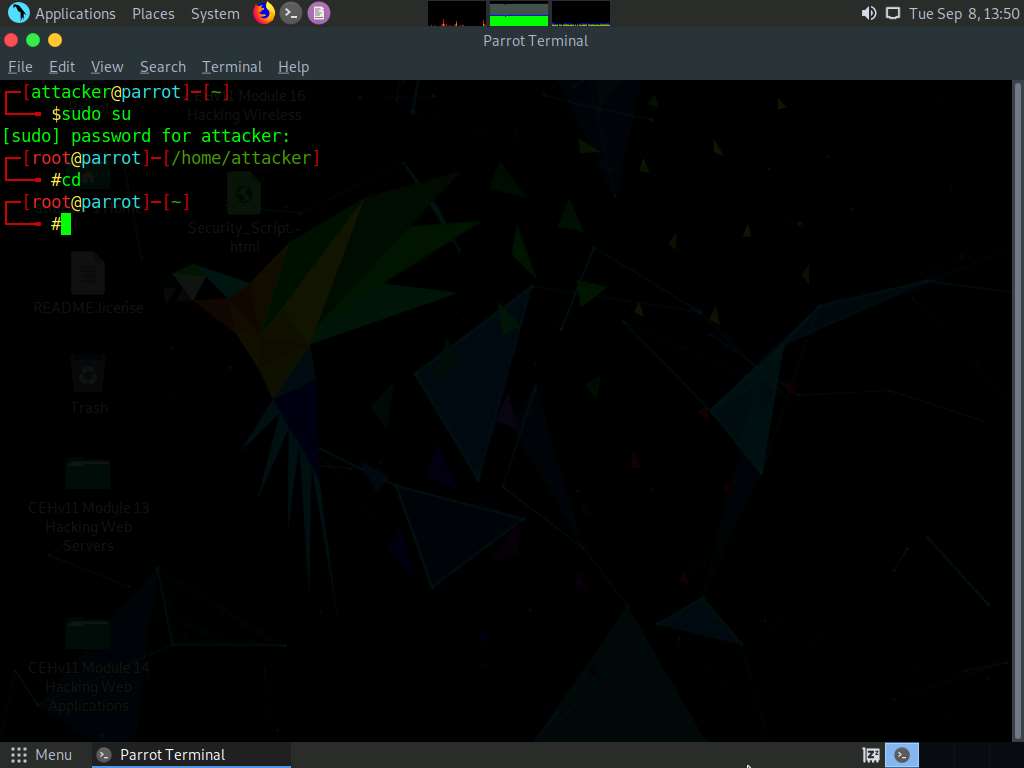
In the Parrot Terminal window. In the terminal window, type sudo su and press Enter to run the programs as a root user.
In the [sudo] password for attacker field, type toor as a password and press Enter.
The password that you type will not be visible.
Now, type cd and press Enter to jump to the root directory.
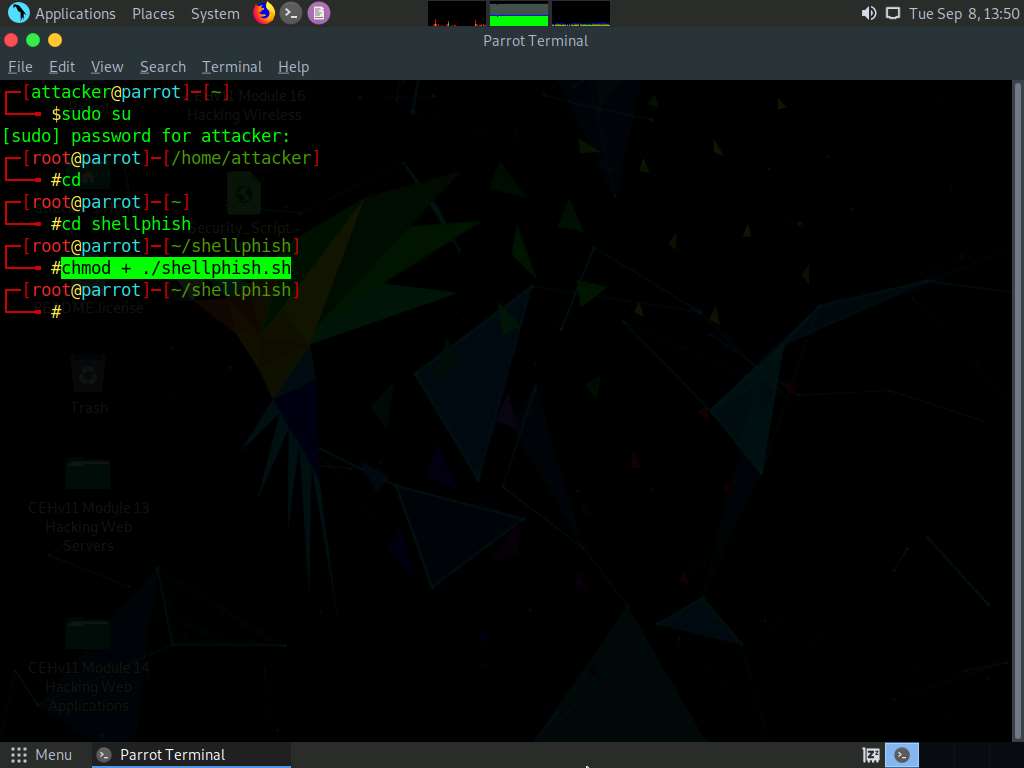
Type cd shellphish and press Enter to navigate to the ShellPhish folder.
Type chmod +x ./shellphish.sh and press Enter to change the file’s access permissions.
In the terminal window, type ./shellphish.sh and press Enter.
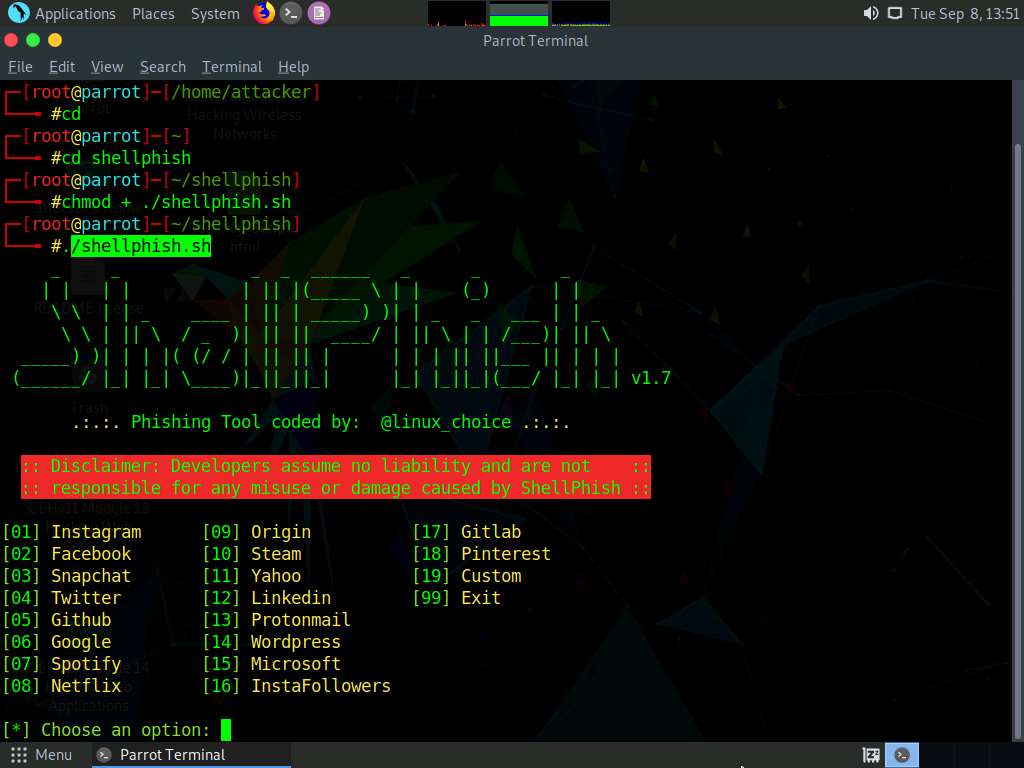
The ShellPhish options appear; type 1 and press Enter to choose the [01] Instagram option
In this example, we will clone the Instagram login page. However, you can clone any website from the given options.
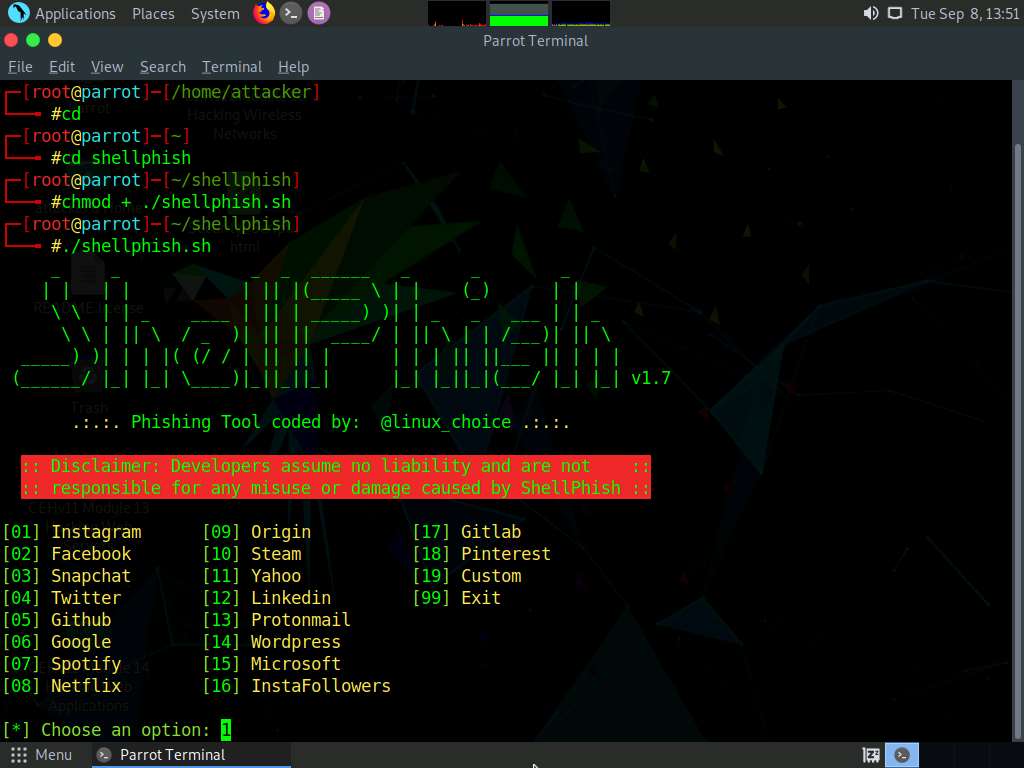
In the Choose a Port Forwarding option, type 2 to select Ngrok and press Enter.
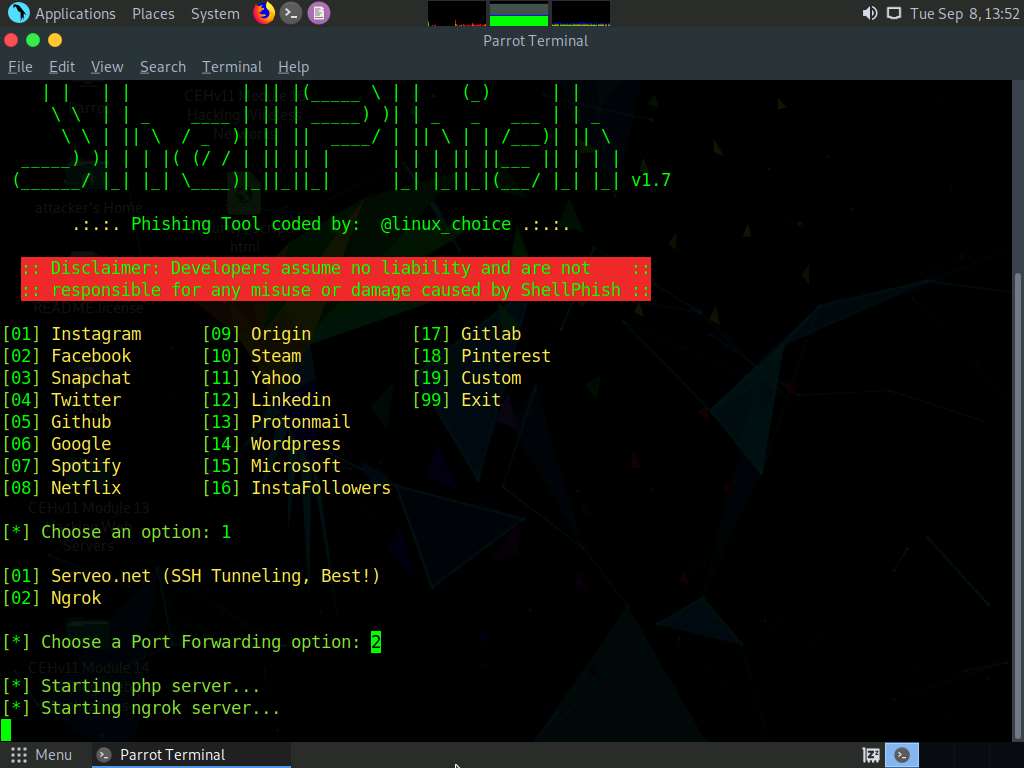
A malicious link to a cloned version of the selected social networking site appears next to the instruction Send this link to the Target. Copy the link.
If the malicious link is not generated, then close the Terminal window and perform steps#1-9 again.
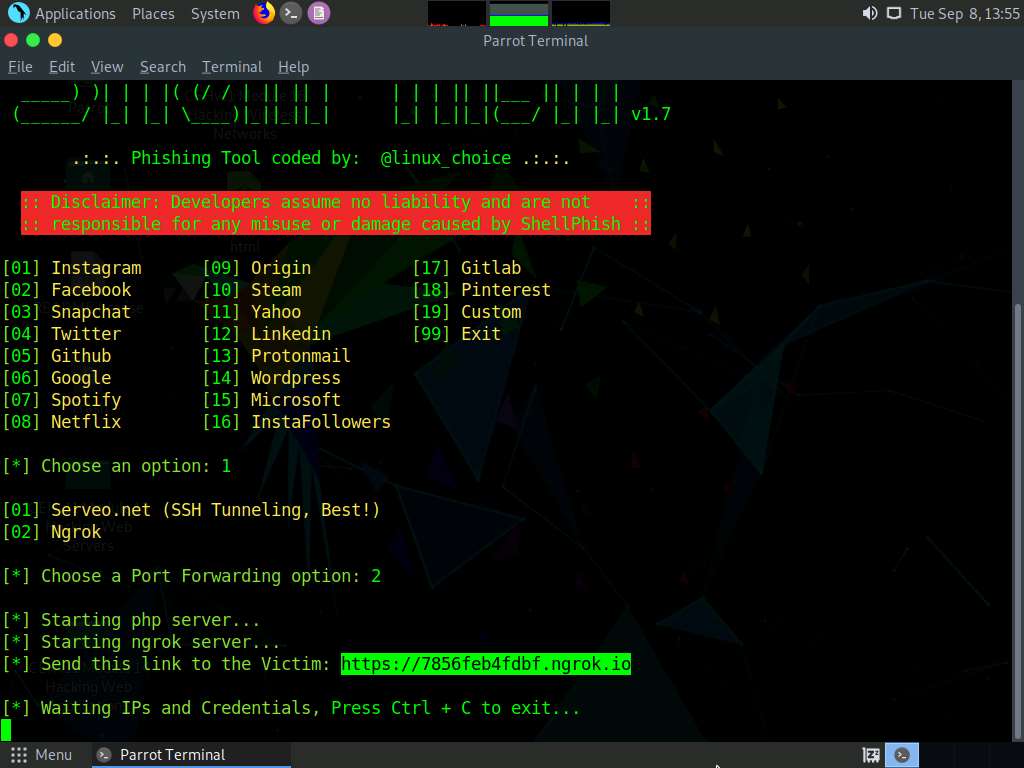
Having successfully created a clone website, we will now send the malicious link to the victim through an email and try to trick him/her into clicking on it.
Launch a web browser and open your email account (in this example, we are using Mozilla Firefox and Gmail, respectively); log in.
You can use any email account of your choice.
After logging into your Gmail account, click the Compose button in the left pane and compose a fake, but enticing, email to lure a user into opening the email and clicking on a malicious link (see Task 1.3. above).
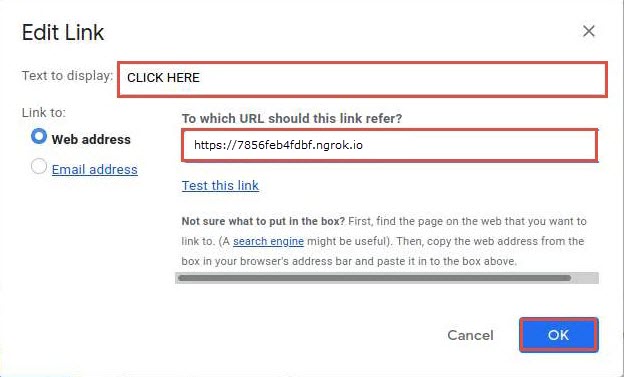
Position the cursor where you wish to place the fake URL in the message. Then, click the Insert link icon at the bottom of the email window
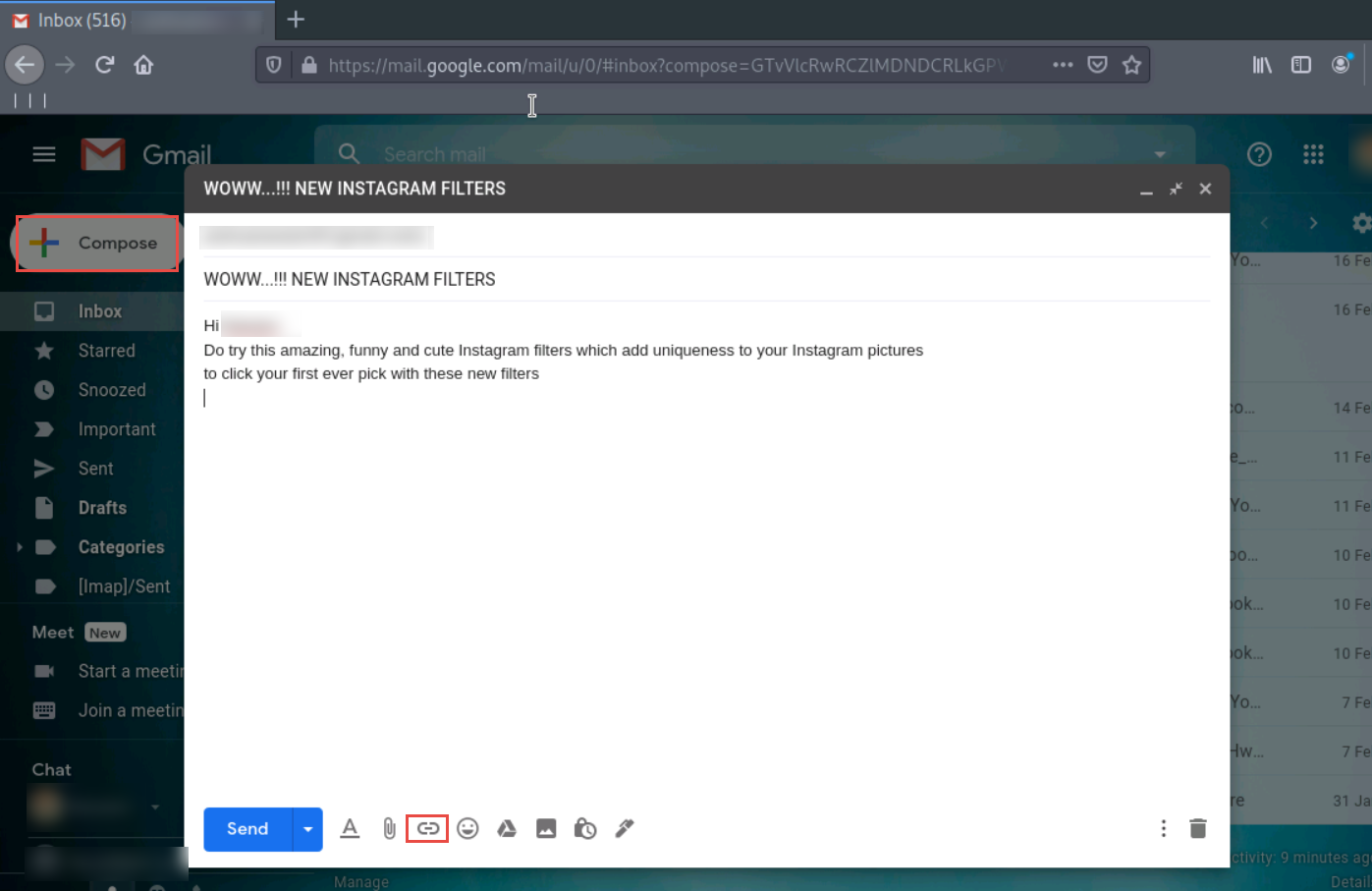
In the Edit Link window, paste the copied malicious link in the Web address field under the Link to section. In the Text to display field, type CLICK HERE and click the OK button.
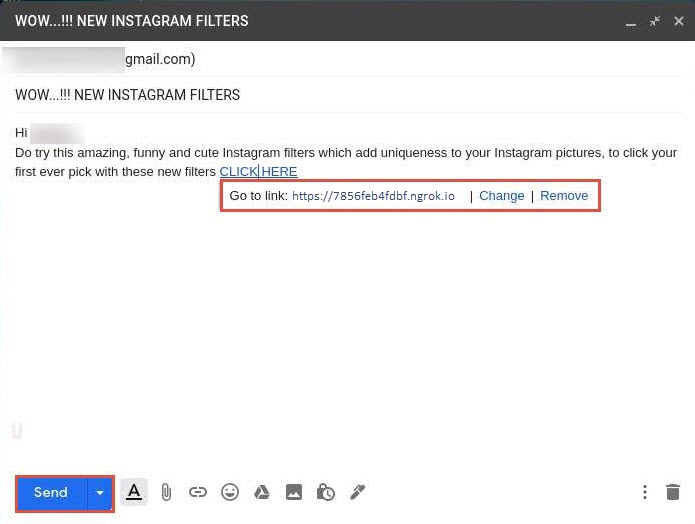
The fake link should appear in the message body, as shown in the screenshot.
Verify that the fake link is linked to the correct cloned site: in Gmail, click the link; the actual URL will be displayed in a “Go to link” pop-up. Once verified, send the email to the intended user.
Click Windows 10 to switch to the Windows 10 machine, click Ctrl+Alt+Delete.
Alternatively, you can also click Ctrl+Alt+Delete button under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Ctrl+Alt+Delete button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
By default, Admin user profile is selected, click Pa$$w0rd to paste the password in the Password field and press Enter to login.
Alternatively, you can also click Pa$$w0rd under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Type Text | Type Password button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
If Welcome to Windows wizard appears, click Continue and in Sign in with Microsoft wizard, click Cancel.
Networks screen appears, click Yes to allow your PC to be discoverable by other PCs and devices on the network.
Open any web browser (here, we are using Mozilla Firefox), sign in to the email account to which you sent the phishing mail as an attacker. Open the email you sent previously and click HERE to open the malicious link.
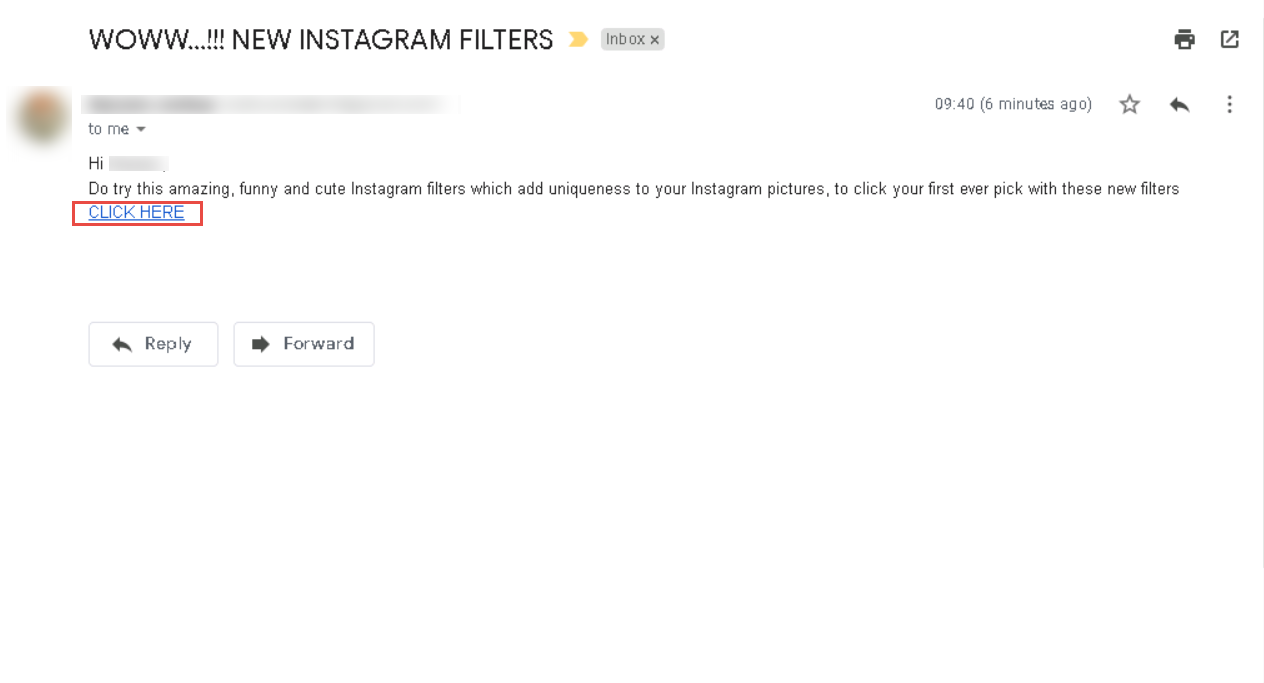
When the victim (you in this case) clicks the CLICK HERE hyperlink, a new tab opens up, and he/she will be presented with a replica of www.instagram.com.
The victim will be prompted to enter his/her username and password into the form fields, which appears to be the genuine Instagram login page. When the victim enters the Phone number, username, or email and Password and clicks Log In, he/she is redirected to the legitimate Instagram login page. Note the different URLs in the browser address bar for the fake and real login pages
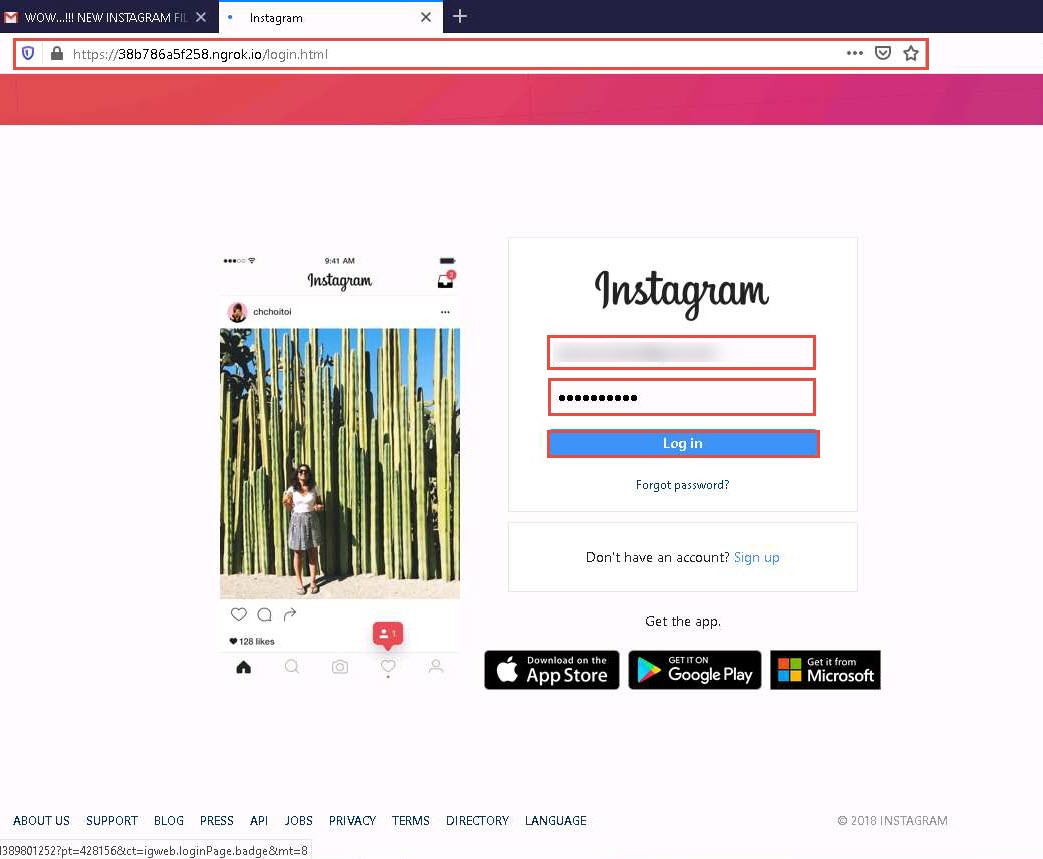
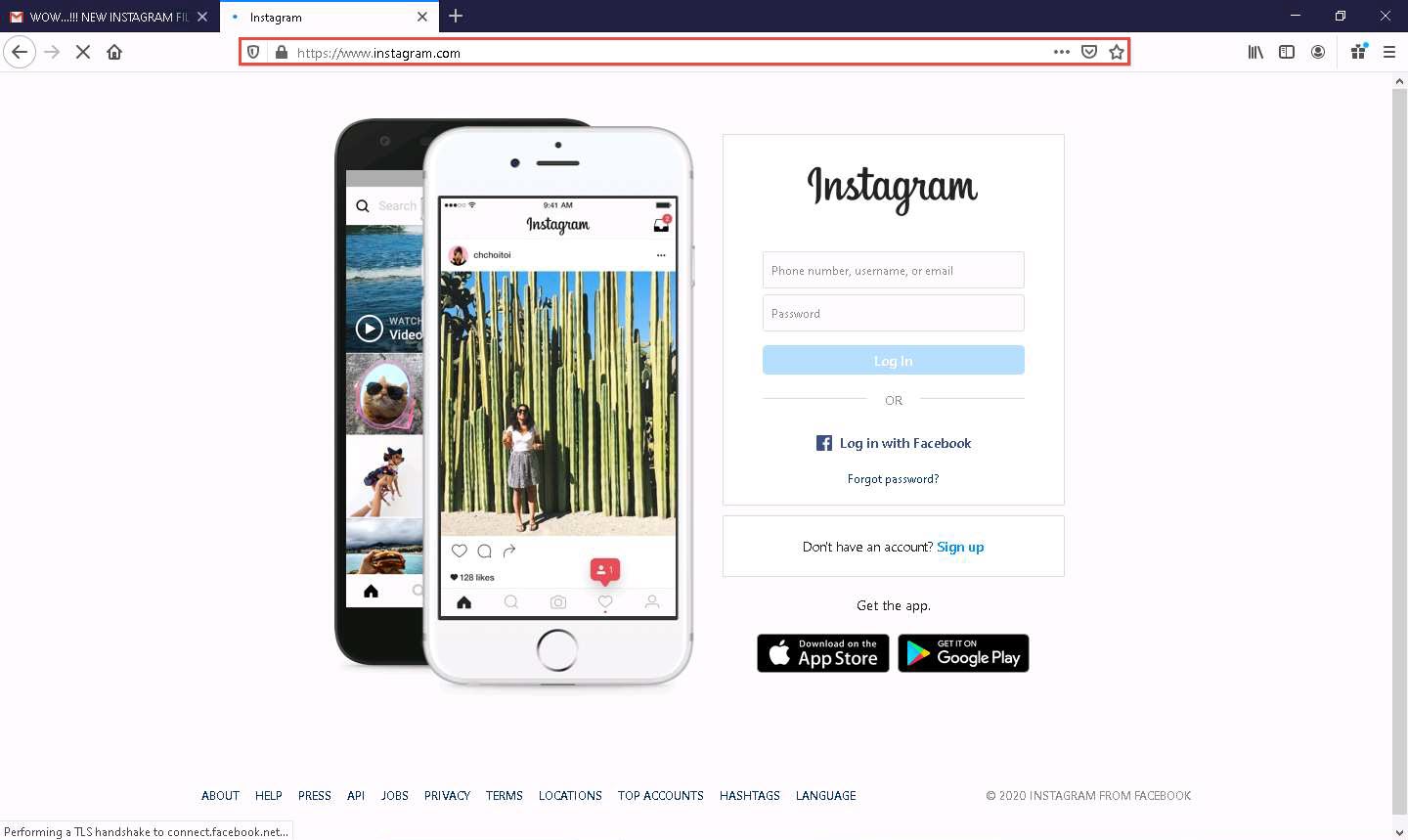
Click on @lab.VirtualMachine(ParrotSecurity).SelectLink to switch back to the Parrot Security machine and observe the terminal window running ShellPhish.
As soon as the victim opens the malicious link, information such as Victim IP, User-Agent, Hostname and IP Continent is displayed, along with the obtained Instagram credentials. This information can be used by the attacker to gain unauthorized access to the victim’s account.
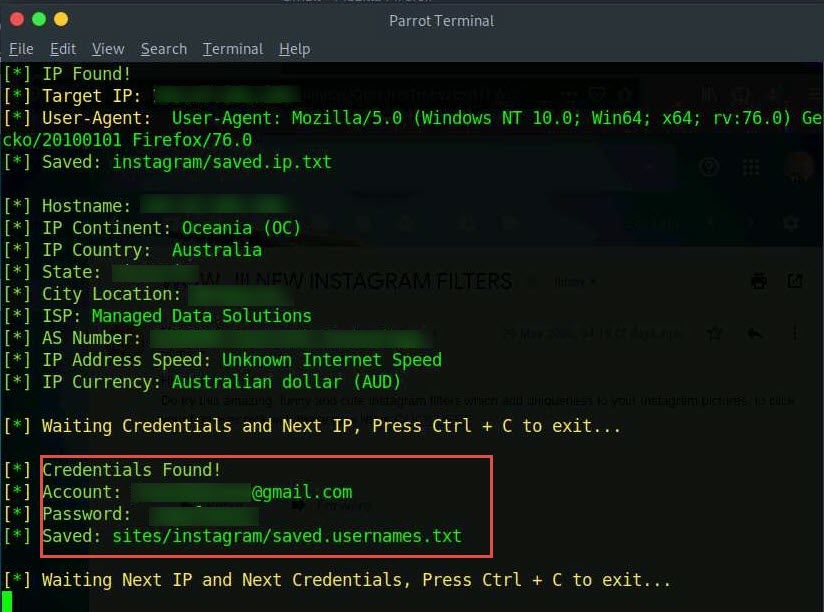
This concludes the demonstration of phishing victim’s credentials using ShellPhish.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Comments
Post a Comment