Lab 1: Perform Host Discovery
Lab 1: Perform Host Discovery
Module 03: Scanning Networks
Lab 1: Perform Host Discovery
Task 1: Perform Host Discovery using Nmap
NMAP commands
nmap -A 10.10.10.* = scans whole subnet
nmap -O 10.10.10.16 = finds operating system of device
nmap --script smb-os-discovery.nse 10.10.10.16 = OS, computer name, domain, workgroup, and current time over the SMB
nmap -sT -v 10.10.10.16 = tcp full open scan
nmap -sS -v 10.10.10.16 = stealth scan This scanning technique can be used to bypass firewall rules, logging mechanisms, and hide under network traffic.
nmap -sX -v 10.10.10.16 = xmas scan If the target has opened the port, then you will receive no response from the target system. If the target has closed the port, then you will receive a target system reply with an RST.
nmap -sM -v 10.10.10.16 = Maimon scan open/filtered on the target machine, which means a firewall has been configured on the target machine.
nmap -sA -v 10.10.10.16 = The ACK flag probe scan no response implies that the port is filtered (stateful firewall is present), and an RST response means that the port is not filtered.
nmap -sU -v 10.10.10.16 = 20 minutes scan sends UDP packets to the target host; no response means that the port is open. If the port is closed, an ICMP port unreachable message is received.
nmap -sN -T4 -A -v 10.10.10.9 = null scan time template agressive scan
nmap -sI -v 10.10.10.9 = scan to send spoof source address to discover avalable services
nmap -sY -v 10.10.10.9 = sctp scan chunk response implies port open abort means closed
nmap -sZ -v 10.10.10.9 = sctp cookie echo scan
nmap -sV 10.10.10.16 = detects service versions Service version detection helps you to obtain information about the running services and their versions on a target system. Obtaining an accurate service version number allows you to determine which exploits the target system is vulnerable to.
nmap -sn -PR [Target IP Address] = -sn: disables port scan and -PR: performs ARP ping scan.The ARP ping scan probes ARP request to target host; an ARP response means that the host is active.
nmap -sn -PU [Target IP Address], = -PU: performs the UDP ping scan. The UDP ping scan sends UDP packets to the target host; a UDP response means that the host is active. If the target host is offline or unreachable,
nmap -sn -PE [Target IP Address] = -PE: performs the ICMP ECHO ping scan. If the target host is alive, it will return an ICMP ECHO reply. This scan is useful for locating active devices or determining if the ICMP is passing through a firewall.
nmap -sn -PE [Target Range of IP Addresses] = ICMP ECHO ping sweep to discover live hosts from a range of target IP addresses.
nmap -sn -PP [target IP address] = ICMP timestamp ping scan
nmap -sn -PM [target IP address] = ICMP address mask ping scan
nmap -sn -PS [target IP address] = TCP SYN Ping Scan: This technique sends empty TCP SYN packets to the target host, ACK response means that the host is active.
nmap -sn -PA [target IP address] = TCP ACK Ping Scan: This technique sends empty TCP ACK packets to the target host; an RST response means that the host is active.
nmap -sn -PO [target IP address] = IP Protocol Ping Scan: This technique sends different probe packets of different IP protocols to the target host, any response from any probe indicates that a host is active.
open zenmap
run commands above if needed depending on case
Lab Scenario
As a professional ethical hacker or pen tester, you should be able to scan and detect the active network systems/devices in the target network. During the network scanning phase of security assessment, your first task is to scan the network systems/devices connected to the target network within a specified IP range and check for live systems in the target network.
Lab Objectives
- Perform host discovery using Nmap
- Perform host discovery using Angry IP Scanner
Overview of Host Discovery
Host discovery is considered the primary task in the network scanning process. It is used to discover the active/live hosts in a network. It provides an accurate status of the systems in the network, which, in turn, reduces the time spent on scanning every port on every system in a sea of IP addresses in order to identify whether the target host is up.
The following are examples of host discovery techniques:
- ARP ping scan
- UDP ping scan
- ICMP ping scan (ICMP ECHO ping, ICMP timestamp, ping ICMP, and address mask ping)
- TCP ping scan (TCP SYN ping and TCP ACK ping)
- IP protocol scan
Task 1: Perform Host Discovery using Nmap
Nmap is a utility used for network discovery, network administration, and security auditing. It is also used to perform tasks such as network inventory, managing service upgrade schedules, and monitoring host or service uptime.
Here, we will use Nmap to discover a list of live hosts in the target network. We can use Nmap to scan the active hosts in the target network using various host discovery techniques such as ARP ping scan, UDP ping scan, ICMP ECHO ping scan, ICMP ECHO ping sweep, etc.
Here, we will consider EC-Council as a target organization.
By default, Windows 10 machine selected, click Ctrl+Alt+Delete.
Alternatively, you can also click Ctrl+Alt+Delete button under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Ctrl+Alt+Delete button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
By default, Admin user profile is selected, click Pa$$w0rd to paste the password in the Password field and press Enter to login.
Alternatively, you can also click Pa$$w0rd under Windows 10 machine thumbnail in the Resources pane or Click Type Text | Type Password button under Commands (thunder icon) menu.
If Welcome to Windows wizard appears, click Continue and in Sign in with Microsoft wizard, click Cancel.
Networks screen appears, click Yes to allow your PC to be discoverable by other PCs and devices on the network.
Navigate to the Desktop and double-click Nmap - Zenmap GUI shortcut.
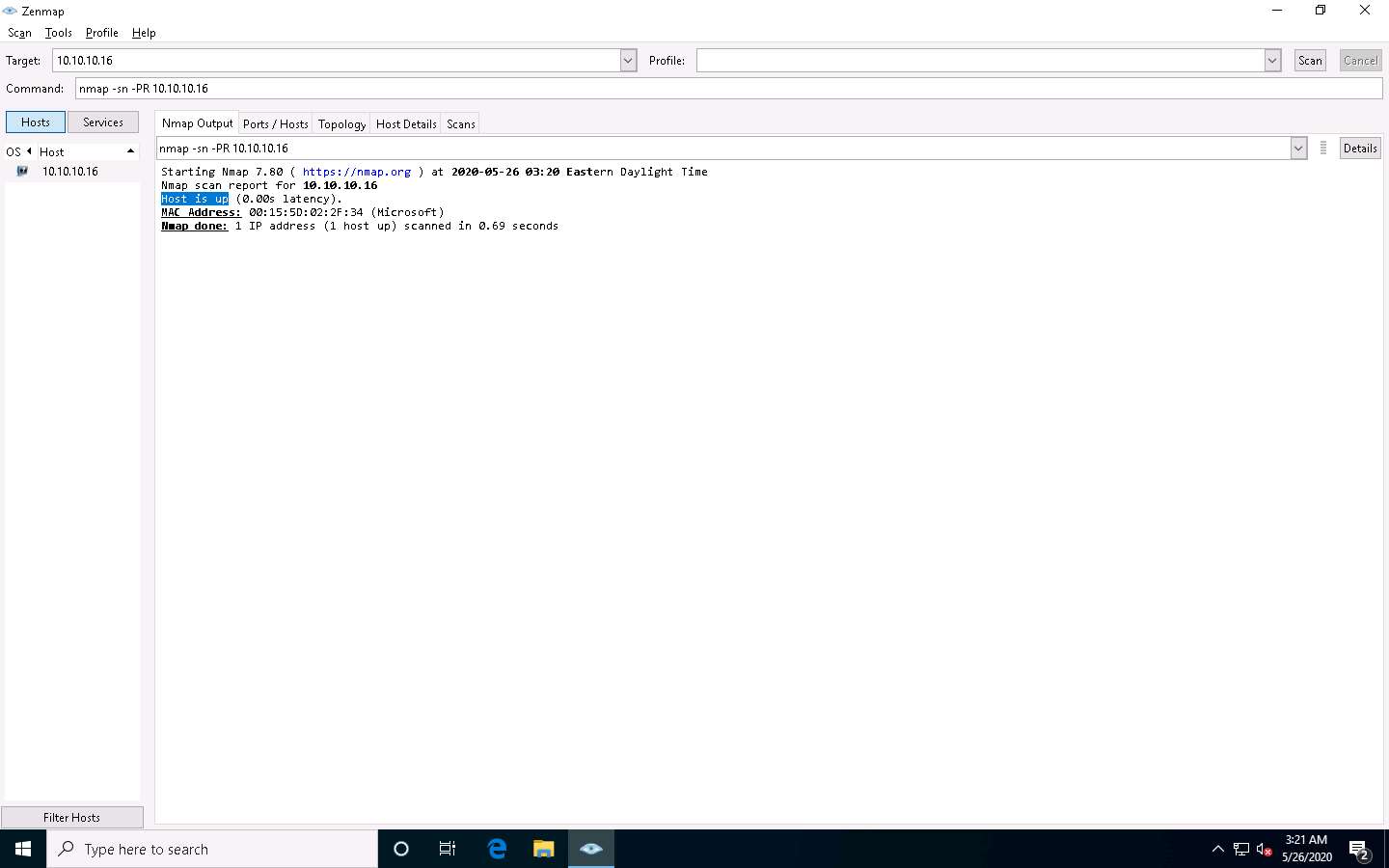
The Nmap - Zenmap GUI appears; in the Command field, type the command nmap -sn -PR [Target IP Address] (here, the target IP address is 10.10.10.16) and click Scan.
-sn: disables port scan and -PR: performs ARP ping scan.
The scan results appear, indicating that the target Host is up, as shown in the screenshot.
In this lab, we are targeting the Windows Server 2016 (10.10.10.16) machine.
The ARP ping scan probes ARP request to target host; an ARP response means that the host is active.
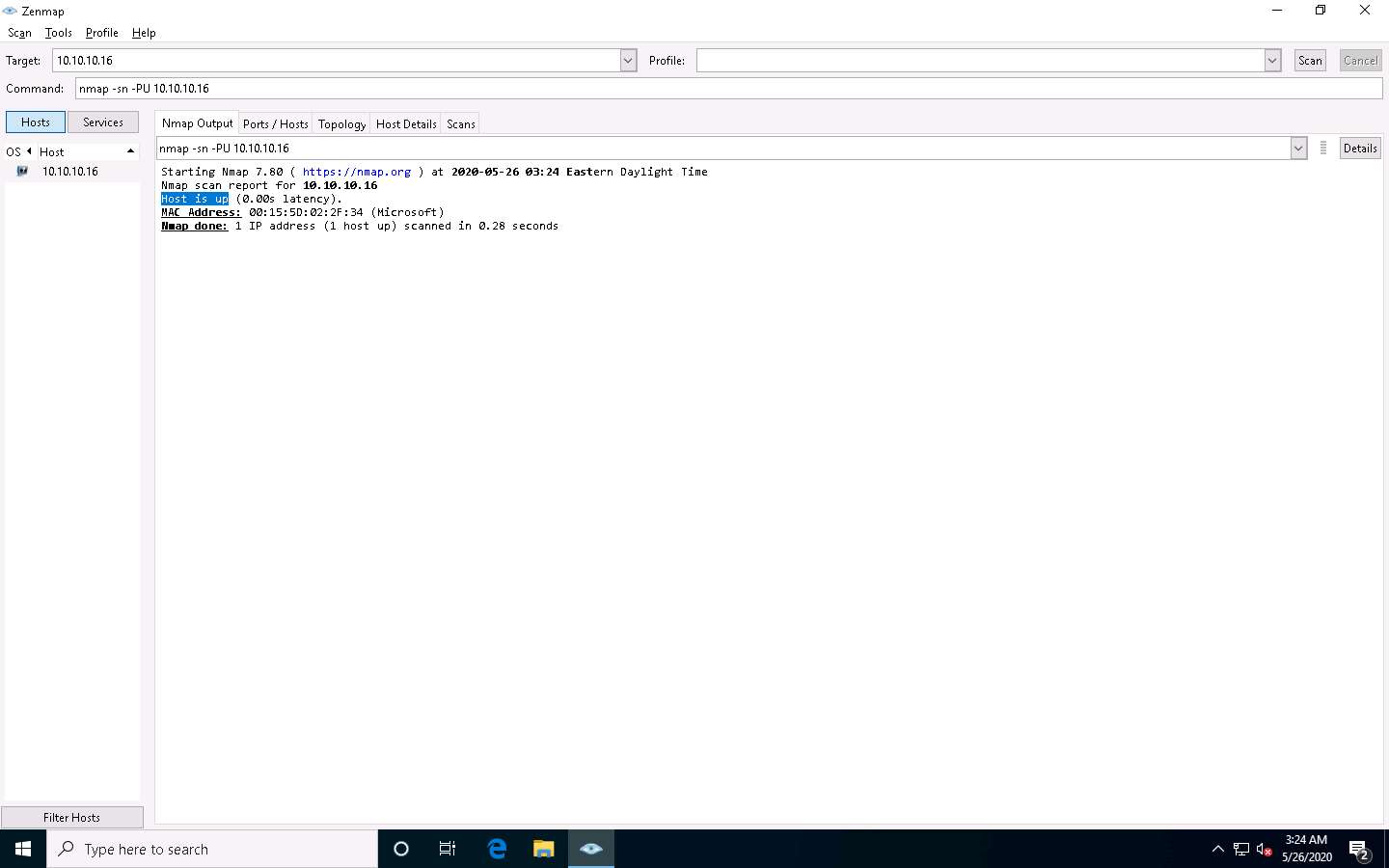
In the Command field, type nmap -sn -PU [Target IP Address], (here, the target IP address is 10.10.10.16) and click Scan. The scan results appear, indicating the target Host is up, as shown in the screenshot.
-PU: performs the UDP ping scan.
The UDP ping scan sends UDP packets to the target host; a UDP response means that the host is active. If the target host is offline or unreachable, various error messages such as “host/network unreachable” or “TTL exceeded” could be returned.
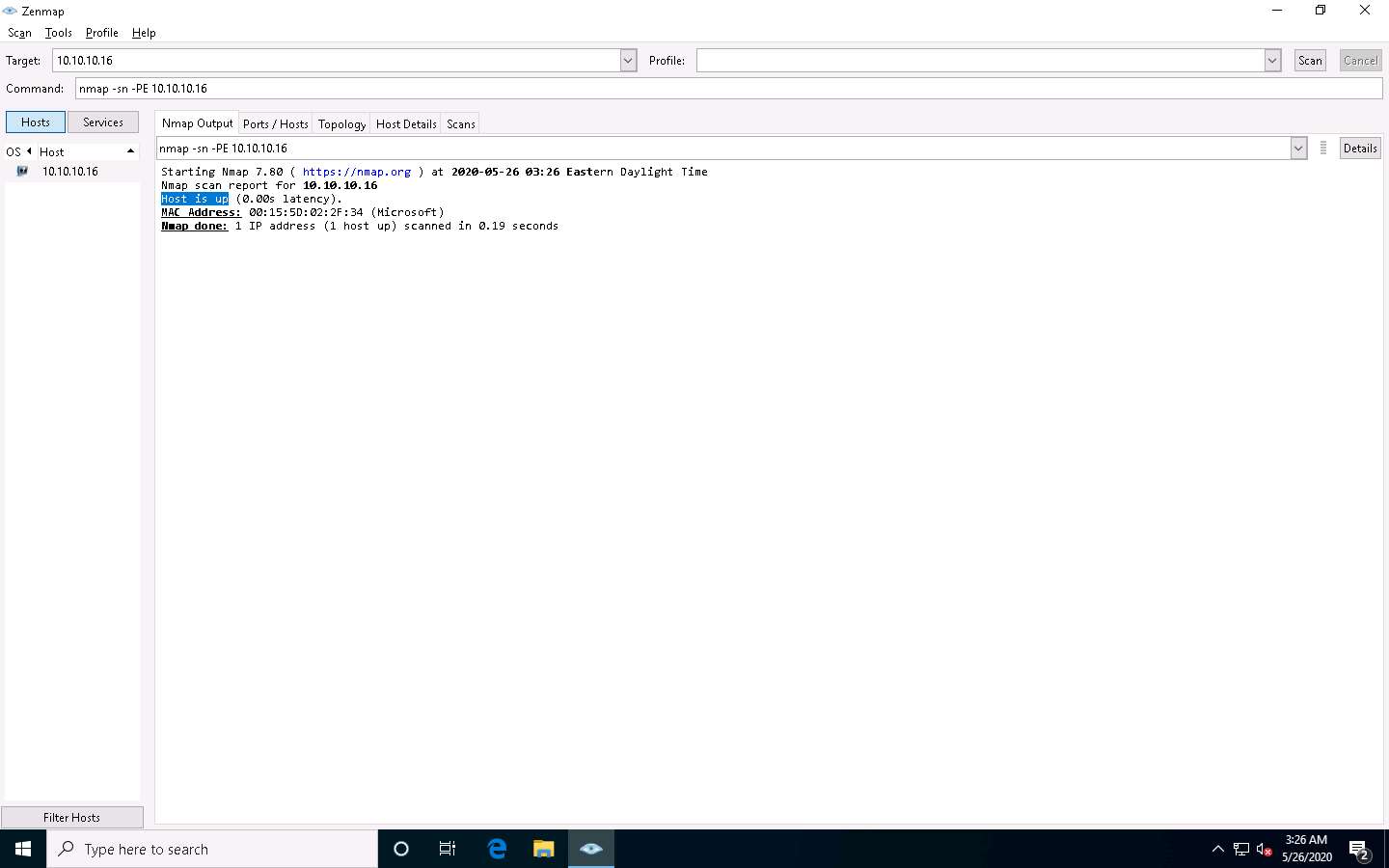
Now, we will perform the ICMP ECHO ping scan. In the Command field, type nmap -sn -PE [Target IP Address], (here, the target IP address is 10.10.10.16) and click Scan. The scan results appear, indicating that the target Host is up, as shown in the screenshot.
-PE: performs the ICMP ECHO ping scan.
The ICMP ECHO ping scan involves sending ICMP ECHO requests to a host. If the target host is alive, it will return an ICMP ECHO reply. This scan is useful for locating active devices or determining if the ICMP is passing through a firewall.
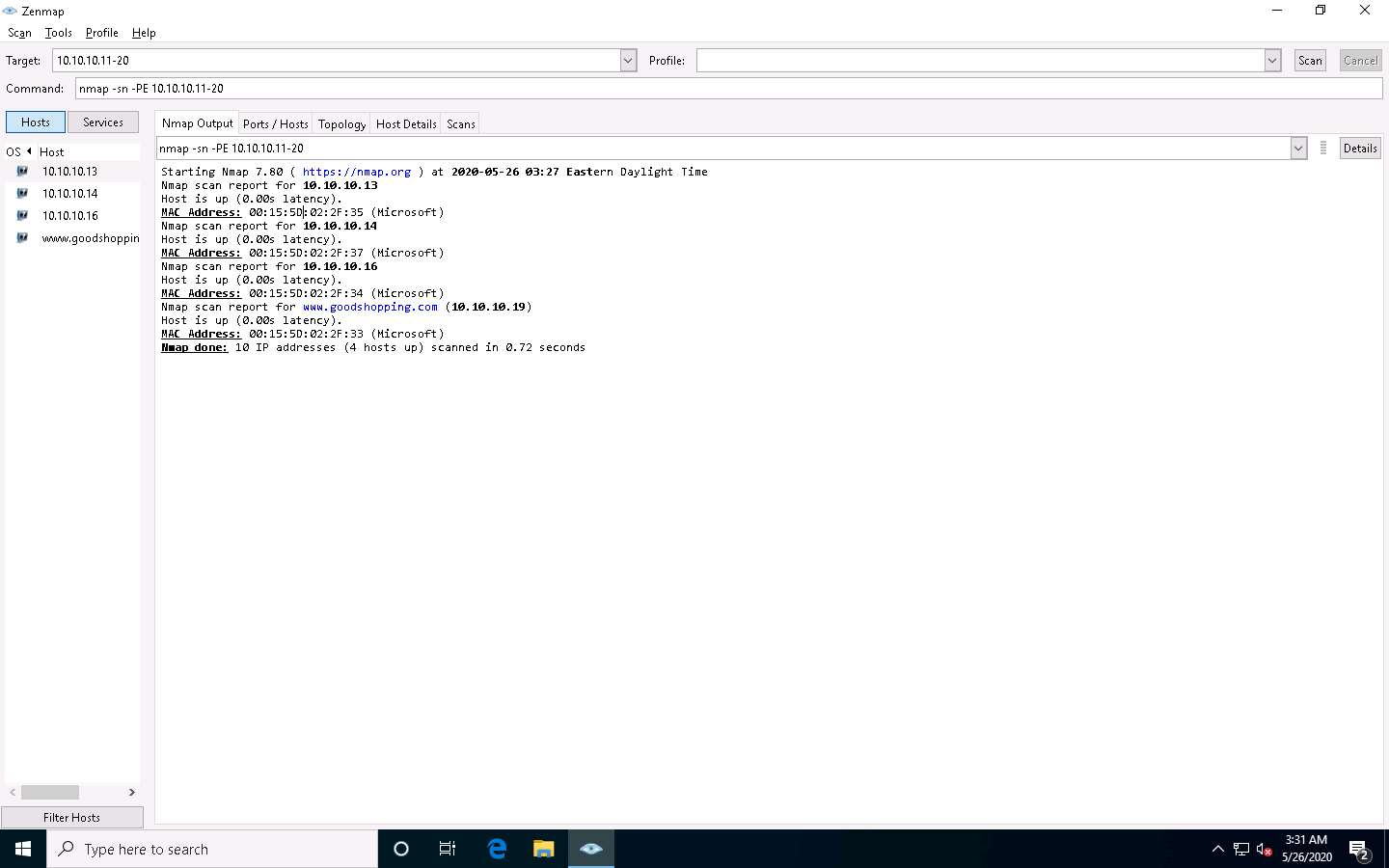
Now, we will perform an ICMP ECHO ping sweep to discover live hosts from a range of target IP addresses. In the Command field, type nmap -sn -PE [Target Range of IP Addresses] (here, the target range of IP addresses is 10.10.10.11-20) and click Scan. The scan results appear, indicating the target Host is up, as shown in the screenshot.
In this lab task, we are scanning Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Parrot Security and Android machines.
The ICMP ECHO ping sweep is used to determine the live hosts from a range of IP addresses by sending ICMP ECHO requests to multiple hosts. If a host is alive, it will return an ICMP ECHO reply.
Apart from the aforementioned network scanning techniques, you can also use the following scanning techniques to perform a host discovery on a target network.
ICMP Timestamp and Address Mask Ping Scan: These techniques are alternatives for the traditional ICMP ECHO ping scan, which are used to determine whether the target host is live specifically when administrators block the ICMP ECHO pings.
Example –
ICMP timestamp ping scan
# nmap -sn -PP [target IP address]
ICMP address mask ping scan
# nmap -sn -PM [target IP address]
TCP SYN Ping Scan: This technique sends empty TCP SYN packets to the target host, ACK response means that the host is active.
# nmap -sn -PS [target IP address]
TCP ACK Ping Scan: This technique sends empty TCP ACK packets to the target host; an RST response means that the host is active.
# nmap -sn -PA [target IP address]
IP Protocol Ping Scan: This technique sends different probe packets of different IP protocols to the target host, any response from any probe indicates that a host is active.
# nmap -sn -PO [target IP address]
This concludes the demonstration of discovering the target host(s) in the target network using various host discovery techniques.
Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Comments
Post a Comment